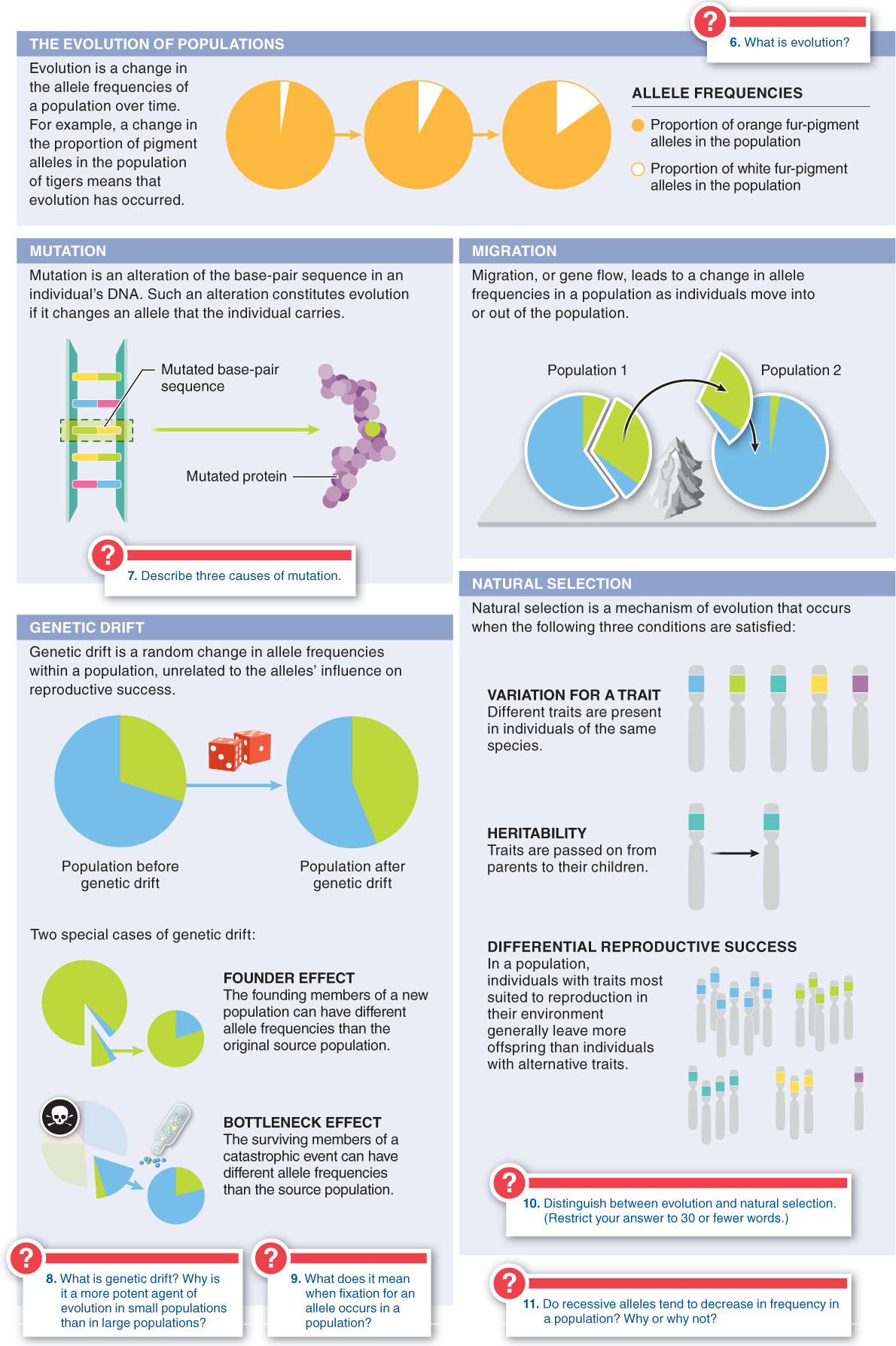
8.5–8.10: Four mechanisms can give rise to evolution.
Evolution—
362
Question 8.15
“Survival of the fittest” may be a misleading phrase to describe the process of evolution by natural selection, because:
- a) it is impossible to determine the fittest individuals in nature.
- b) survival matters less to natural selection than does reproductive success.
- c) natural variation in a population is generally too great to be influenced by differential survival.
- d) during population bottlenecks, it is the least fit individuals that have the greatest survival.
- e) reproductive success, on its own, does not necessarily guarantee evolution.

Question 8.16
Evolutionary adaptation:
- a) refers both to the process by which populations become better matched to their environment and to the features of an organism that make it more fit than other individuals.
- b) cannot occur in environments influenced by humans.
- c) is possible only when there is no mutation.
- d) is responsible for the fact that porcupines are at an unusually high risk of predation.
- e) occurs for physical traits but not behaviors.

Question 8.17
Adaptations shaped by natural selection:
- a) are magnified and enhanced through genetic drift.
- b) are unlikely to be present in humans living in industrial societies.
- c) may be out of date, having been shaped in the past under conditions that differed from those in the present.
- d) represent perfect solutions to the problems posed by nature.
- e) are continuously modified so that they are always matched to the environment in which a population lives.

Question 8.18
In a population in which a trait is exposed to stabilizing selection:
- a) neither the average value nor the variation for the trait changes.
- b) both the average value and the variation for the trait increase.
- c) the average value increases or decreases, and the variation for the trait decreases.
- d) the average value for the trait stays approximately the same, and the variation for the trait decreases.
- e) the average value for the trait stays approximately the same, and the variation for the trait increases.
