
Chapter 18. Chapter 18: Growth and Reproduction in Plants
Review & Rehearse

Instructions
Review the visual summaries and answer the essay questions below.
Make sure to enter a brief response that completely answers each question and explains your reasoning. When you click "Submit," you will be provided instant feedback, allowing you to check if your response is correct.
(This activity contains 16 total essay questions. Each new question will be revealed once you complete the preceding question.)
1.


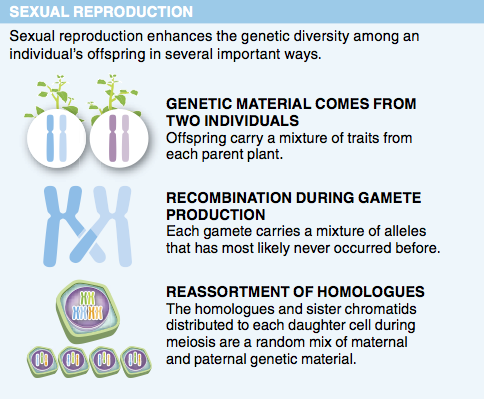
1. How would you describe the genetic makeup of the offspring of aspens growing on the Orkney Islands?
2.
2. Potato plants can reproduce sexually, producing flowers, fruits, and seeds. A potato farmer can collect the seeds and plant them. Alternatively, she can plant some of the potatoes instead. Why might it be preferable to plant potatoes instead of seeds? And which potatoes should be chosen for planting?
3.
3. Why is sexual reproduction in plants especially important in agriculture?
4.
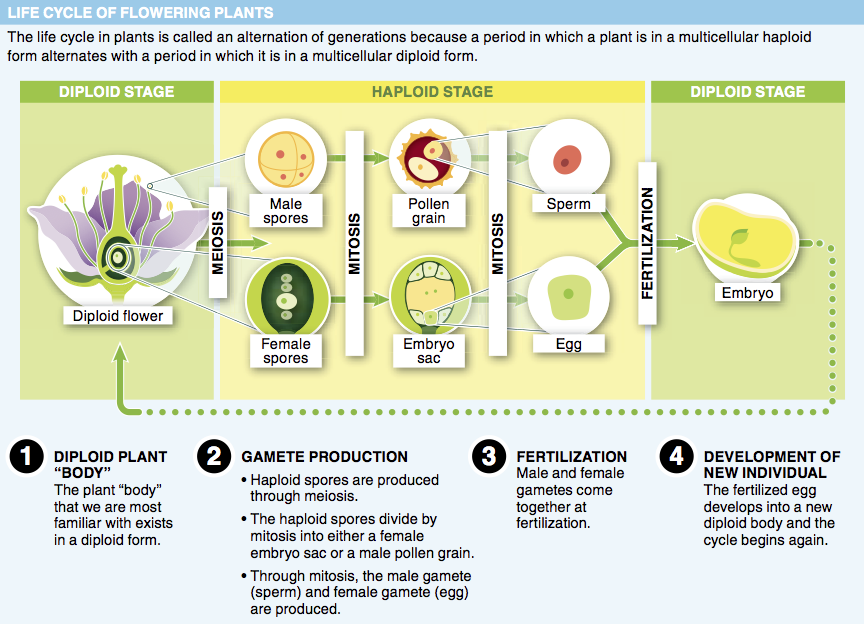

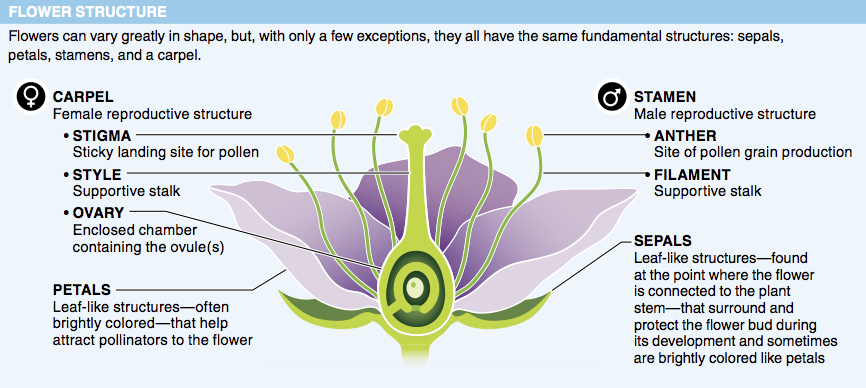
4. After an egg is fertilized, which part of the flower develops into a seed?
5.
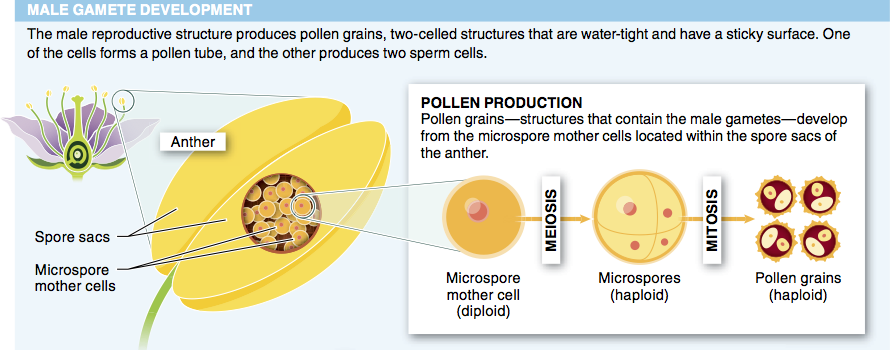
5. Which feature of pollen contributes to its “success” as an allergen?
6.
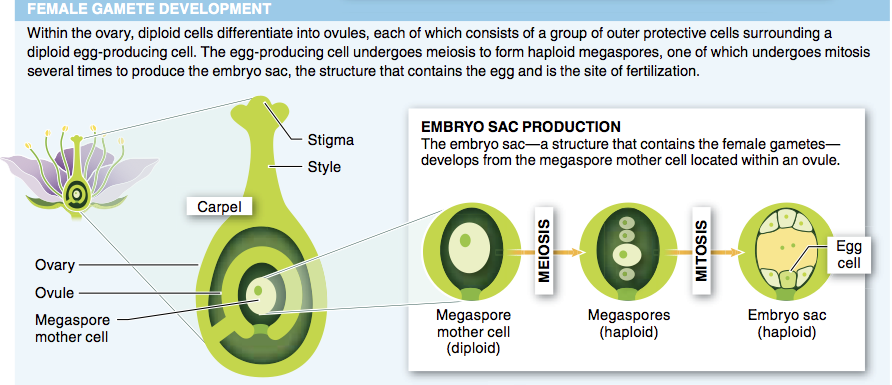
6. In which part of the flower does fertilization occur?
7.


7. Describe the coevolution between plants and their animal pollinators.
8.
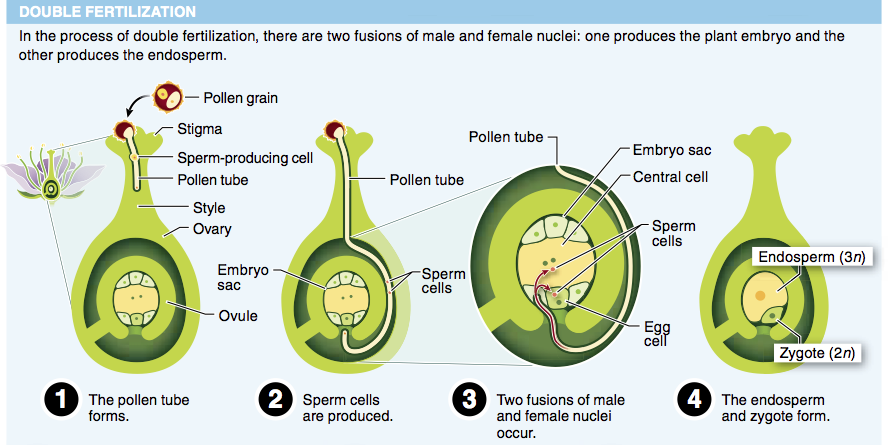
8. If you were stranded on an island and looking for some calorie-rich food, which part of the plant would be best to eat?
9.
9. Why is the process of double fertilization so efficient?
10.
10. Describe some of the evolutionary pros and cons of self-fertilization.
11.
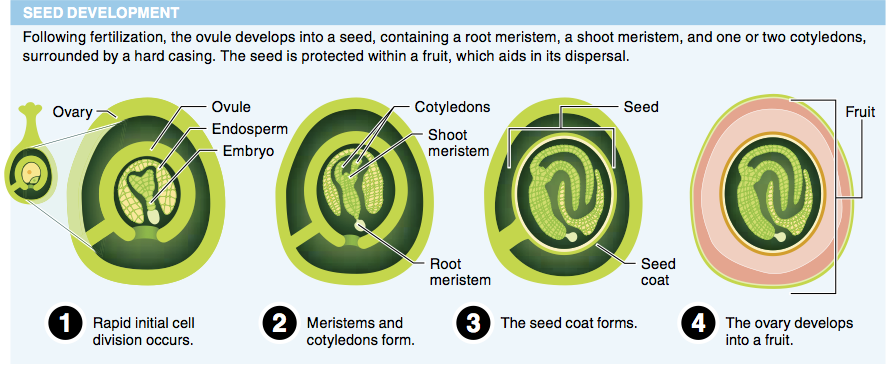
11. Why does metabolism and oxygen consumption stop in seeds once the fruit has formed?
12.
12. Why is it that fruits do not taste good until the seeds inside are fully developed?
13.

13. How is it possible for a seed to grow underground, in the dark, when we know that plants make their food by photosynthesis, which requires light?
14.

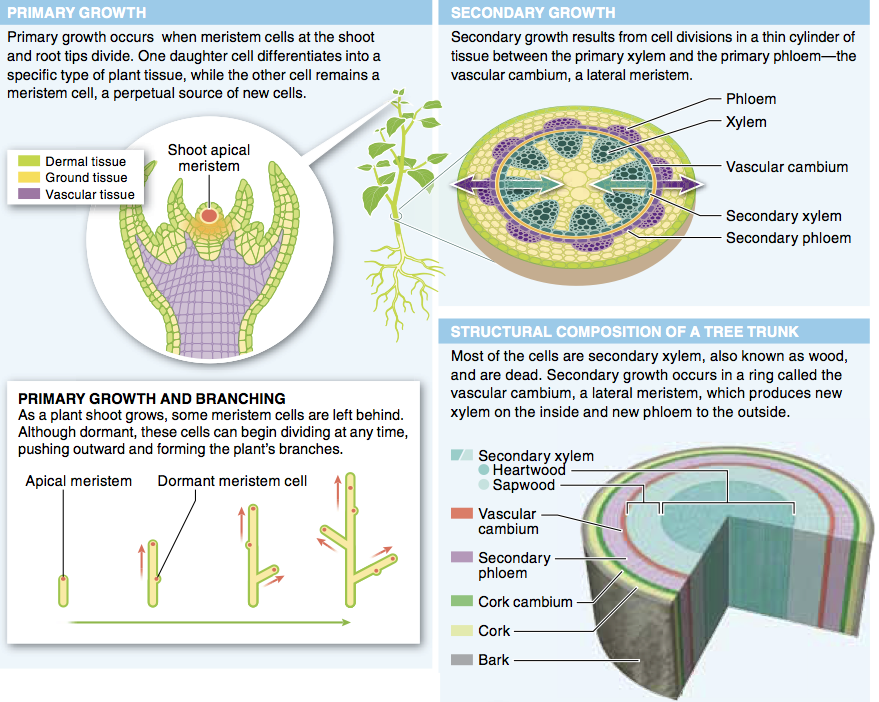
14. If you wanted to induce a plant to grow taller, which part(s) of the plant would you cut off?
15.
15. Describe how branches are formed.
16.
16. Describe two purposes that wood serves in trees.
Activity results are being submitted...