
Chapter 20. Chapter 20: Introduction to Animal Physiology
Review & Rehearse

Instructions
Review the visual summaries and answer the essay questions below.
Make sure to enter a brief response that completely answers each question and explains your reasoning. When you click "Submit," you will be provided instant feedback, allowing you to check if your response is correct.
(This activity contains 12 total essay questions. Each new question will be revealed once you complete the preceding question.)
1.


1. What is the major benefit to organisms of multicellularity?
2.
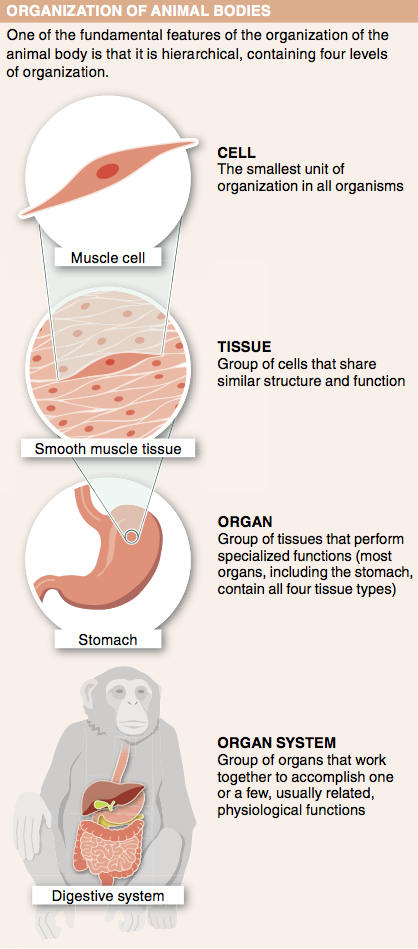
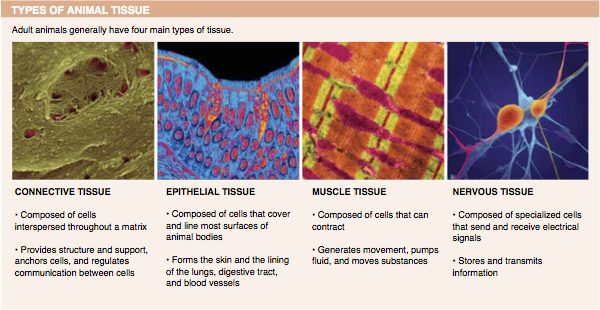
2. Why is connective tissue sometimes referred to as “cellular glue”?
3.
3. Describe one way that epithelium functions in the secretion of molecules.
4.
4. Describe the three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates and their similarities and differences.
5.
5. What is a possible consequence of damage to your glial cells?
6.

6. Which organ system regulates the rate at which the heart pumps blood?
7.


7. What is hyperthermia? How does it reflect a failure of the body to maintain homeostasis?
8.
8. Multicellularity and large body size typically lead to the increased importance of the internal (relative to the external) environment in influencing cell functioning. Why?
9.

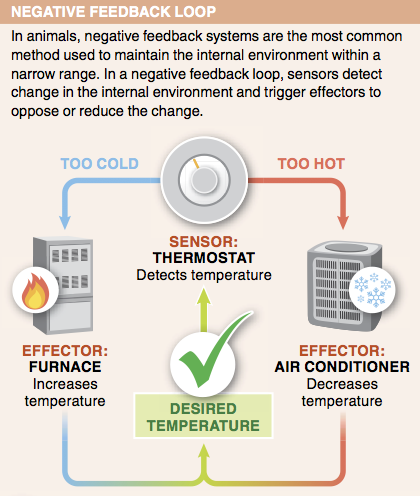
9. In organisms, why are negative feedback systems more common than positive feedback systems?
10.

10. An organism’s temperature is a function of the heat produced by its body in conjunction with the heat transferred from the environment to its body or from its body to the environment. Describe two ways in which heat exchange occurs.
11.

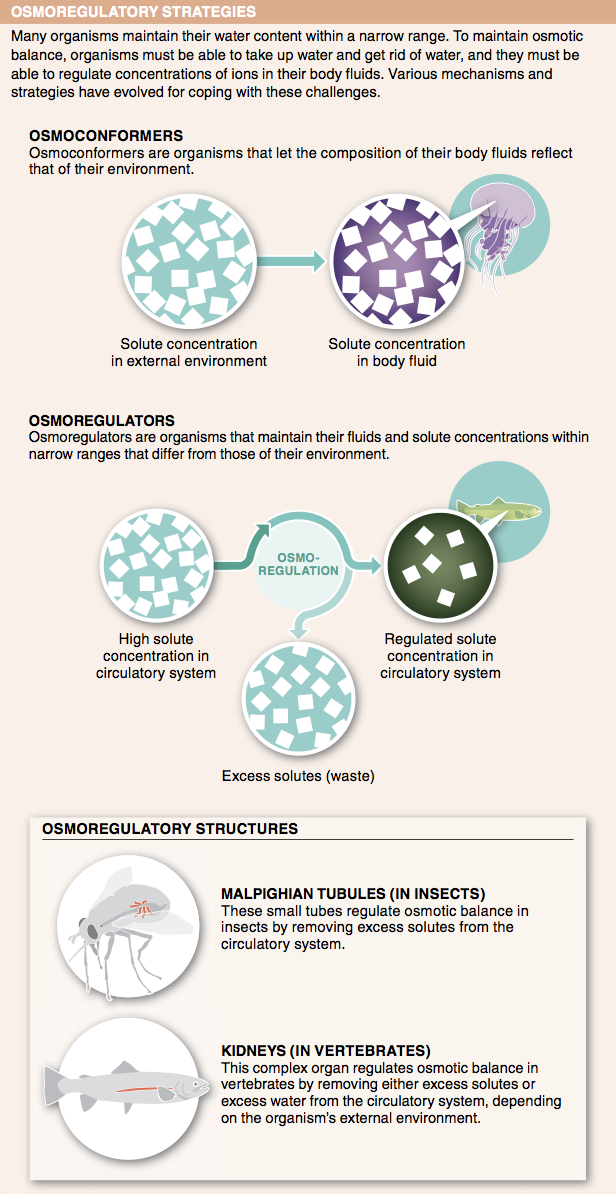
11. Does an invertebrate osmoconformer living in salt water have a set point with respect to the solute concentrations in its body fluids? Why or why not?
12.
12. Describe the factors that influence the amount of urine produced by a human in one day.
Activity results are being submitted...