23.17–23.19 The brain is organized into distinct structures dedicated to specific functions.
There are several distinct regions in the brain, each of which is the control center for various activities in the body.
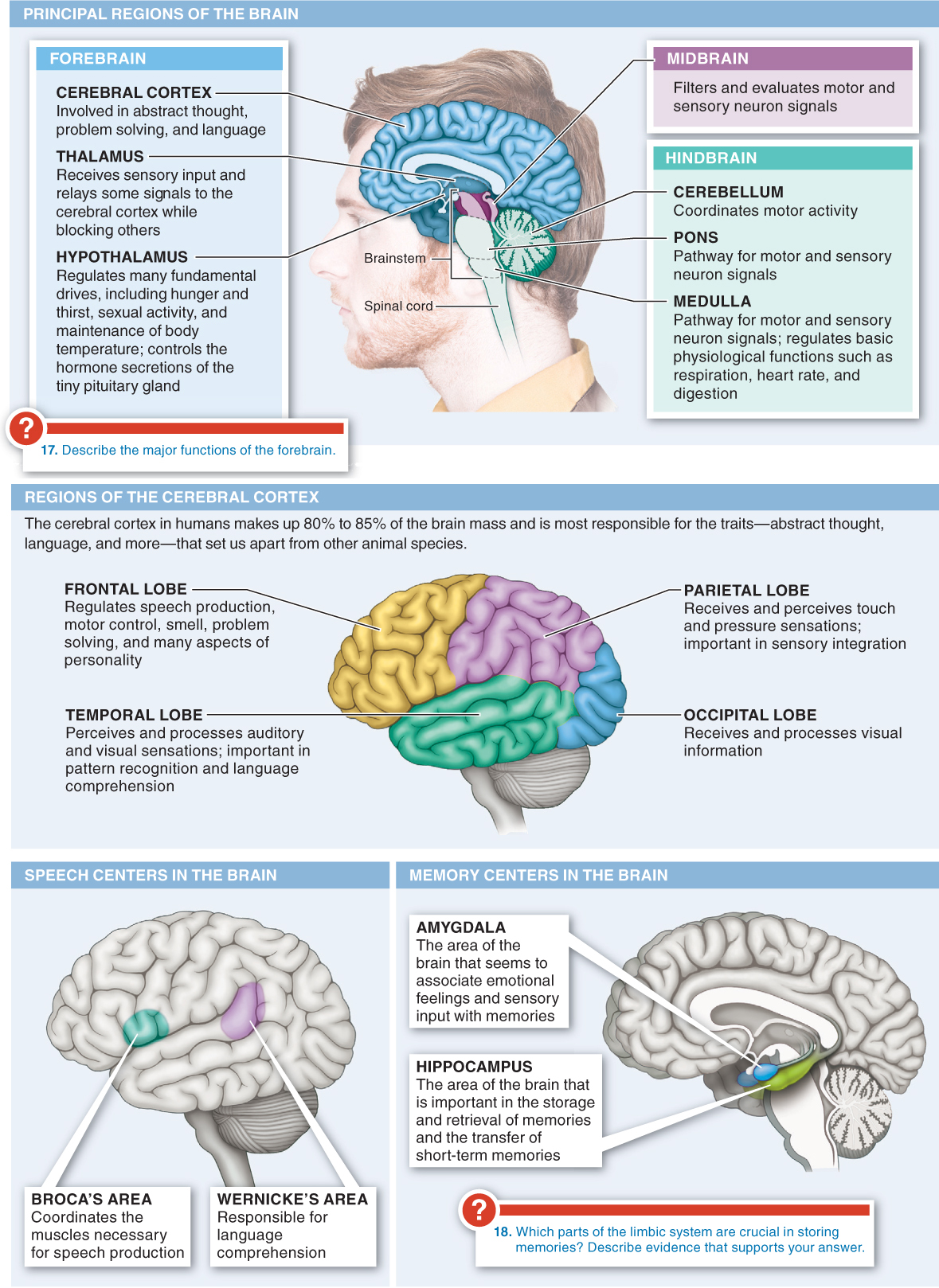
967
Question 23.31
Because cone cells are less sensitive to light than are rod cells:
- a) cones are better suited for daylight vision.
- b) cones are better suited for night vision.
- c) cones are better suited for peripheral vision.
- d) Both a) and c) are correct.
- e) Both b) and c) are correct.

Question 23.32
The connective tissue that connects a muscle to a bone is known as:
- a) collagen.
- b) a ligament.
- c) cartilage.
- d) a tendon.
- e) None of the above are correct.

Question 23.33
Which of the following is not one of the many functions of an endoskeleton?
- a) storage of vital minerals
- b) production of blood and immune cells
- c) protection of the body’s internal structures
- d) supporting the animal against gravity
- e) All of the above are important functions of an exoskeleton.

Question 23.34
The blood-
- a) is formed from muscle tissue.
- b) is a semi-
permeable barricade that allows essential nutrients and gases to pass through. - c) prevents harmful molecules such as metabolic wastes from entering the brain.
- d) restricts the passage of molecules to neurons but not to glial cells.
- e) Both b) and c) are correct.

Question 23.35
A boy is born with a brain defect in which the two hemispheres of his cerebrum are unable to “talk” to each other (they are not connected). This boy is born without a:
- a) hippocampus.
- b) brainstem.
- c) medulla oblongata.
- d) corpus callosum.
- e) hypothalamus.
