26.5–26.10: Specific immunity develops after exposure to pathogens.
The memory of the specific division of the immune system can confer immunity, a state of long-
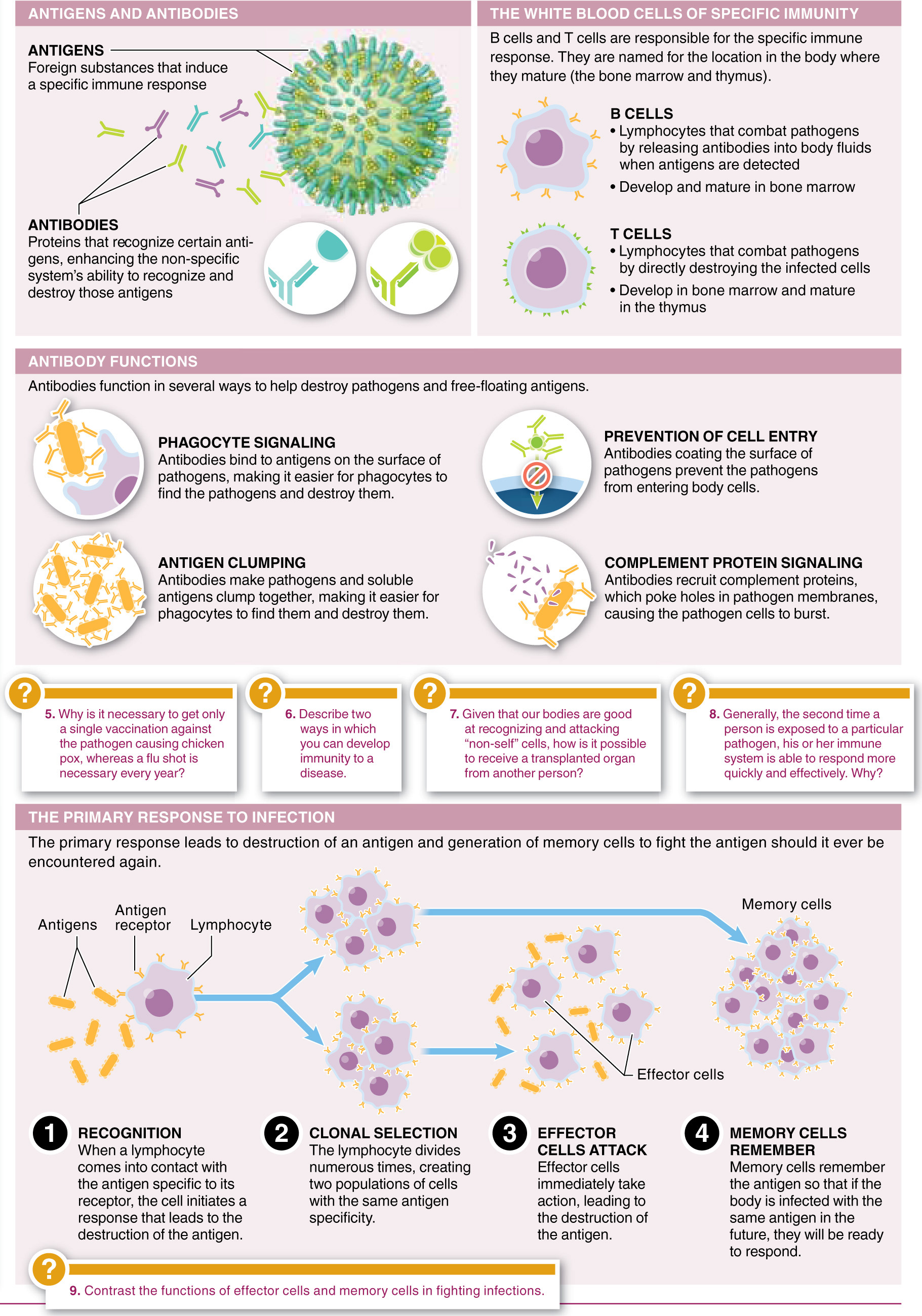
Question 26.16
Why don’t people develop immunity to the common cold?
- a) Actually, many people do develop immunity to the common cold and get sick only from bacterial infections.
- b) There are at least 200 different viruses that can cause the common cold, and they change over time.
- c) Only non-
specific immunity helps individuals fight the common cold; specific immunity is not an effective defense against viruses. - d) The rhinovirus that causes the common cold has no surface antigens and so can move through the body without being detected.
- e) The pathogen that causes the common cold attacks and kills memory cells, continually “erasing” the immune system’s memory of it.

Question 26.17
Antibodies:
- a) are produced by helper B cells.
- b) are produced by helper T cells.
- c) are produced by B cells bound by a specific antigen.
- d) are produced by plasma cells.
- e) are made in the bone marrow.

Question 26.18
The polypeptides that make up the structure of an antibody consist of:
- a) two heavy chains and two light chains, shaped like a “Y,” with a lower constant region and an upper variable region.
- b) two heavy chains and two light chains, shaped like a “Y,” with an upper constant region and a lower variable region.
- c) one heavy chain and one light chain, shaped like a “Y,” with a lower constant region and an upper variable region.
- d) one heavy chain and one light chain, shaped like a “Y,” with an upper constant region and a lower variable region.
- e) Both b) and d) can be correct, depending on the type of antibody

Question 26.19
Which of the following is not a function of helper T cells?
- a) They stimulate B cells to proliferate and produce antibodies.
- b) They activate cytotoxic T cells.
- c) They stimulate B cells to secrete cytokines.
- d) They recognize antigens presented on macrophage surfaces.
- e) All of the above are functions of helper T cells.

1079
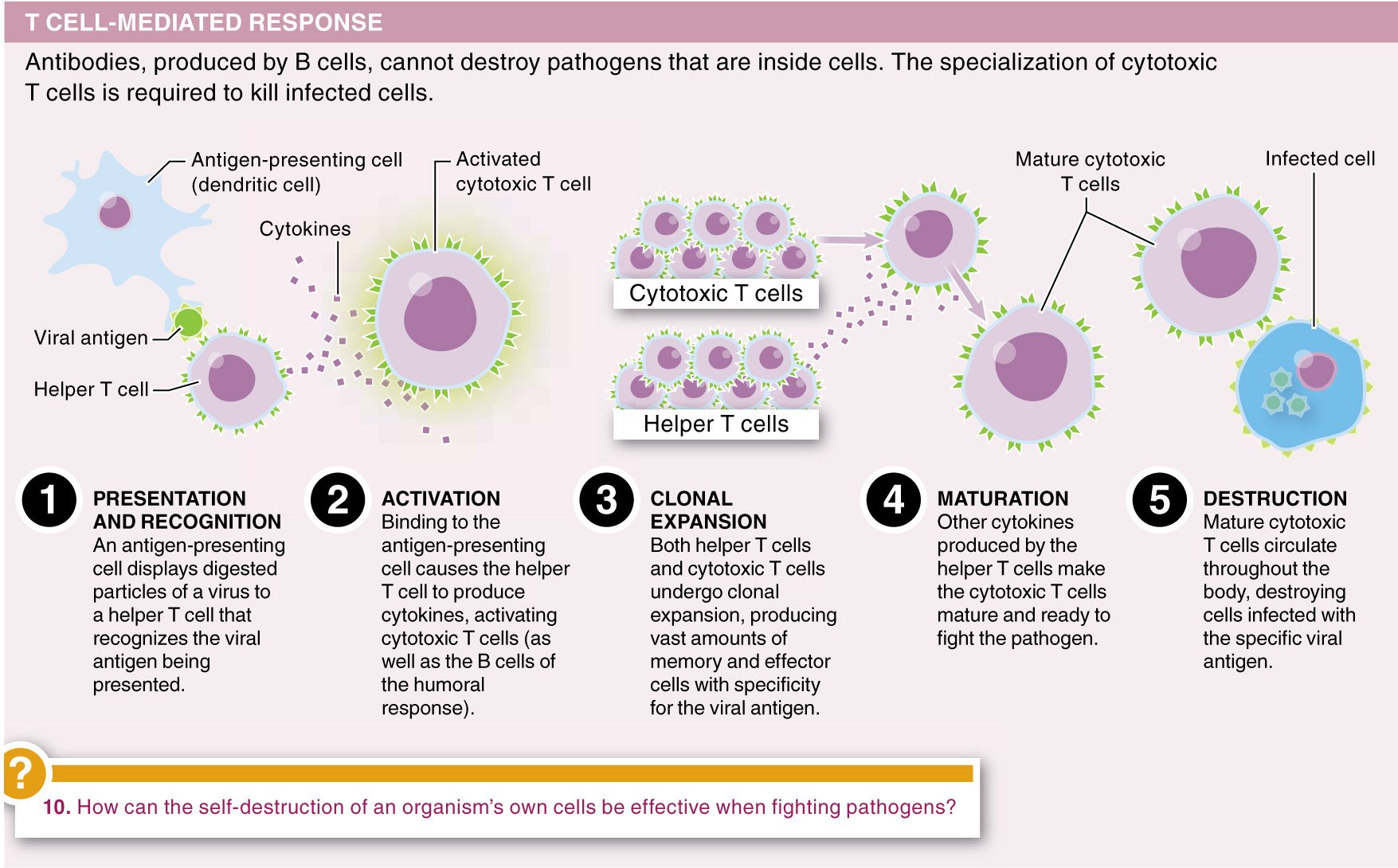
Question 26.20
Autoimmunity is:
- a) one of three lines of defense in the vertebrate immune system.
- b) responsible for muscular dystrophy, which occurs when immune cells destroy the myelin sheath, reducing motor control and balance.
- c) the culprit in rheumatoid arthritis, which occurs when immune attack on the linings of joints causes inflammation.
- d) a consequence of a body’s inability to produce antigens, leading it to attack its own cells as if they were pathogens.
- e) All of the above statements about autoimmunity are correct.

Question 26.21
As the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) begins to kill the host’s, the host’s immune system begins to fail.
- a) thymus cells
- b) spleen cells
- c) red blood cells
- d) white blood cells
- e) liver cells

Question 26.22
Hay fever affects millions of individuals every year and is caused by an allergic reaction to pollen. Which of the following is not a step of the process in which a pollen grain causes an allergic reaction in an individual?
- a) Mast cells burst when they encounter the pollen during the initial exposure, releasing histamine and other chemicals.
- b) During the first exposure, B cells are activated by the pollen and differentiate into antibody-
secreting plasma cells. - c) During the second exposure, the pollen grains are recognized by previously created antibodies on mast cells.
- d) A type of antibody, specific to the pollen grain, is produced during the initial attack, and these antibodies adhere to mast cells, where they remain.
- e) Histamine and other allergen chemicals cause itchy eyes and a runny nose.
