3.12: Cells are connected and communicate with each other.
In multicellular organisms, most cells are connected to other cells by specialized structures that hold them in place and enable them to communicate with each other.
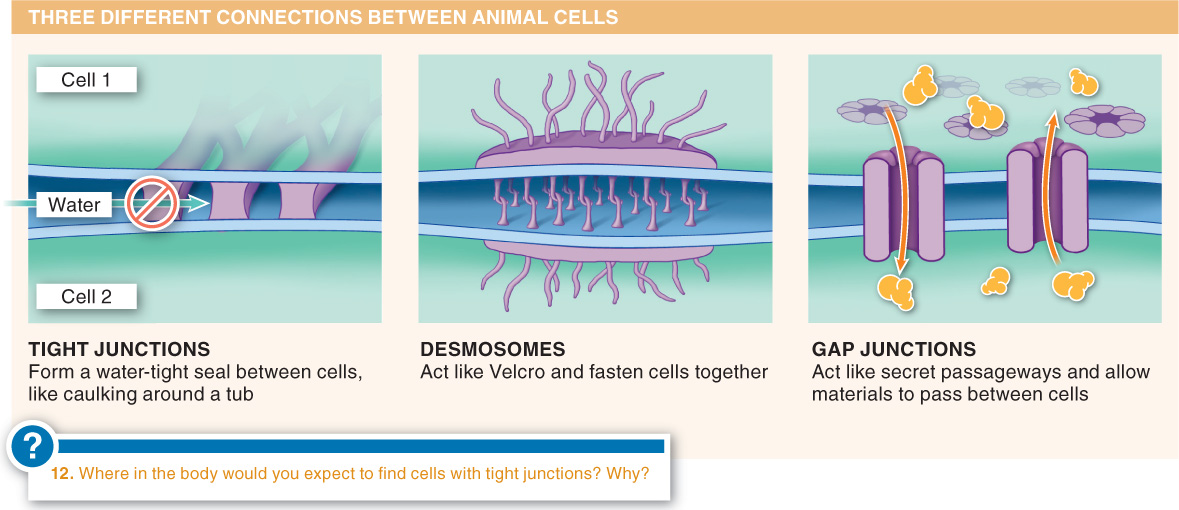
Question 3.24
In an experiment, you measure the concentration of a polar molecule inside and outside a cell. You find that the concentration is high and gradually increasing inside the cell. What is your best hypothesis for the process you are observing?
- a) facilitated diffusion
- b) passive transport
- c) simple diffusion
- d) active transport
- e) endocytosis

Question 3.25
Which of the following structures allow the passage of small molecules between animal cells?
- a) nucleoli
- b) tight junctions
- c) desmosomes
- d) gap junctions
- e) black holes

Question 3.26
The largest structure in a eukaryotic cell is the _____ and it is surrounded by ______ membrane(s).
- a) nucleus; one
- b) nucleus; two
- c) Golgi apparatus; one
- d) mitochondrion; two
- e) mitochondrion; one

Question 3.27
The cytoskeleton:
- a) is a viscous fluid found in all cells.
- b) fills a cell’s nucleus but not the other organelles.
- c) gives an animal cell shape and support, but cannot control movement.
- d) helps to coordinate intracellular movement of organelles and molecules.
- e) All of the above are correct.

Question 3.28
Which of the following statements about mitochondria is correct?
- a) Mitochondria are found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
- b) There tend to be more mitochondria in fat cells than in liver cells.
- c) Most plant cells contain mitochondria.
- d) Mitochondria may have originated evolutionarily as photosynthetic bacteria.
- e) All of the above are correct.
