Application Questions and Problems
Introduction
Question 21.20
The introduction to this chapter describes the long-term effects of diet on the residents of Överkalix, Sweden.
- a. What evidence suggests that these effects are due to epigenetic effects?
- b. What additional evidence would help to demonstrate that these changes are due to epigenetic changes?
Section 21.1
Question 21.21
How do epigenetic traits differ from traditional genetic traits, such as the differences in color and shape of peas that Mendel studied?
Question 21.22
Epigenetics has been described as “inheritance, but not as we know it.” Do you think this is a good definition? Why or why not?
Section 21.2
Question 21.23
What would be required to prove that a phenotype is caused by an epigenetic change?
Question 21.24
Which honeybee in Figure 21.4 (the worker or the queen) will have more copies of 5-methylcytosine in its DNA? Explain your answer.
Question 21.25
What would be the effect of deleting the Dnmt3 gene in honeybees?
Question 21.26
Much of DNA methylation in eukaryotes occurs at CpG dinucleotides, but some individual cytosine nucleotides are also methylated to form 5-methylcytosine. Considering what you know about the process by which DNA methylation at CpG dinucleotides is maintained across cell division, do you think that methylation at individual C nucleotides would also be maintained by the same process? Explain your reasoning.
Section 21.3
Question 21.27
A cross between the F1 individual in Figure 21.5 and a plant with genotype B-I B-I will produce progeny with what phenotype?
631
Question 21.28
A scientist does an experiment in which she removes the offspring of rats from their mother at birth and has her genetics students feed and rear the offspring. Assuming that the students do not lick and groom the baby rats as the mother rats normally do, what long-term behavioral and epigenetic effects would you expect to see in the rats when they grow up?
Question 21.29
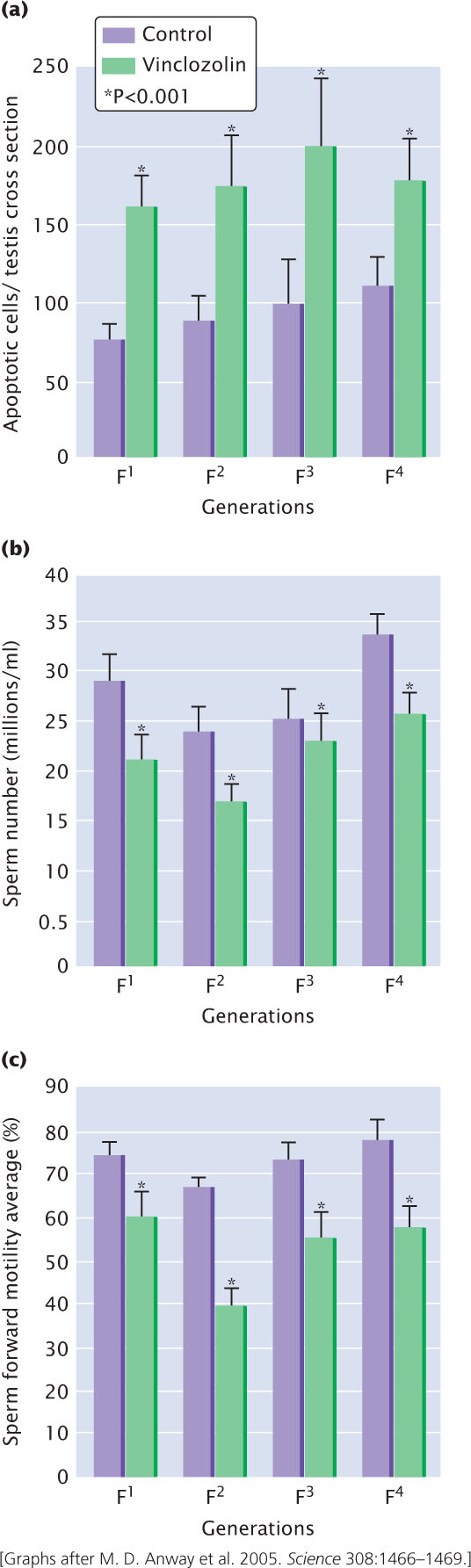
 Pregnant female rats were exposed to a daily dose of 100 or 200 mg/kg of vinclozolin, a fungicide commonly used in the wine industry (M. D. Anway et al. 2005. Science 308:1466–1469). The F1 offspring of the exposed female rates were interbred, producing F2, F3, and F4 rats. None of the F2, F3, or F4 rats were exposed to vinclozolin. Testes from the F1−F4 male rats were examined and compared with those of control rats from females that were not exposed to vinclozolin (see adjoining graphs). These effects were seen in more than 90% of the F1−F4 male offspring. Furthermore, 8% of the F1−F4 males from vinclozolin-exposed females developed complete infertility, compared with 0% of the F1−F4 males of control females. Molecular analysis of the testes demonstrated that DNA methylation patterns differed between offspring of vinclozolin-exposed females and offspring of control females. Provide an explanation for the transgenerational effects of vinclozolin on male fertility.
Pregnant female rats were exposed to a daily dose of 100 or 200 mg/kg of vinclozolin, a fungicide commonly used in the wine industry (M. D. Anway et al. 2005. Science 308:1466–1469). The F1 offspring of the exposed female rates were interbred, producing F2, F3, and F4 rats. None of the F2, F3, or F4 rats were exposed to vinclozolin. Testes from the F1−F4 male rats were examined and compared with those of control rats from females that were not exposed to vinclozolin (see adjoining graphs). These effects were seen in more than 90% of the F1−F4 male offspring. Furthermore, 8% of the F1−F4 males from vinclozolin-exposed females developed complete infertility, compared with 0% of the F1−F4 males of control females. Molecular analysis of the testes demonstrated that DNA methylation patterns differed between offspring of vinclozolin-exposed females and offspring of control females. Provide an explanation for the transgenerational effects of vinclozolin on male fertility.
Question 21.30
Based on the information from studies of the long-term effects of diet on metabolism in mice, what might the epigenetic effects be on the children and grandchildren of people from Överkalix who were exposed to famine as children? Include in your answer the types of epigenetic changes to chromatin you might expect to see and the phenotypic effects on lipid and cholesterol metabolism.
Question 21.31
What would be the effect on X inactivation of adding siRNAs that eliminated the products of each of the following genes?
- a. Xist
- b. Jpx
Section 21.4
Question 21.32
A DNA fragment with the following base sequence has some cytosine bases that are methylated (indicated by C*) and others that are unmethylated. To determine the location of methylated and unmethylated cytosines, researchers sequenced this fragment both with and without treatment with sodium bisulfite. Give the sequence of bases that will be read with and without bisulfite treatment.
—ATCGC*GTTAC *ATTGC *ATCA—
Question 21.33
A geneticist is interested in determining the locations of methylated cytosines within a fragment of DNA. She treats some copies of the fragment with sodium bisulfite and leaves some copies untreated. She then sequences the treated and untreated copies of the fragment and obtains the following results. Give the original sequence of the DNA fragment and indicate the presence of methylated cytosines.
632
| Sequence without treatment: | —AATTGCCCGATCGATTAAGCCA— |
| Sequence with treatment: | —AATTGTTTGATCGATTAAGCTA— |