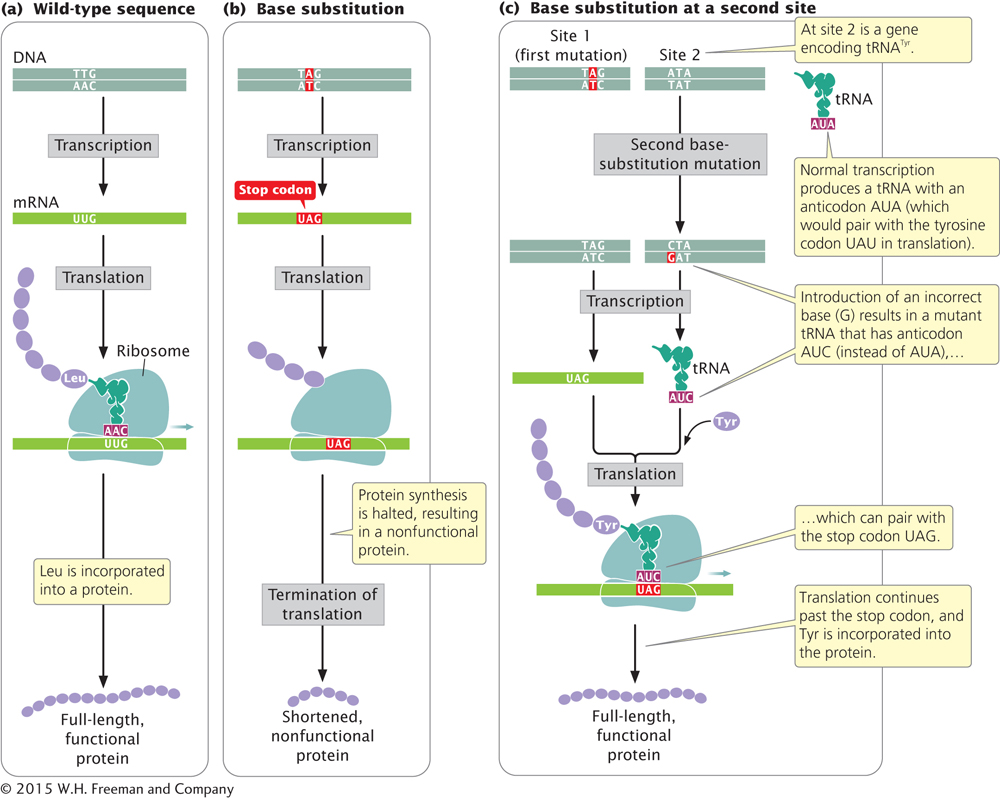
13.9 An intergenic suppressor mutation occurs in a gene other than the one bearing the original mutation. (a) The wild-type sequence produces a full-length, functional protein. (b) A base substitution at a site in the same gene produces a premature stop codon, resulting in a truncated, nonfunctional protein. (c) A base substitution at a site in another gene, which in this case encodes tRNA, alters the anticodon of tRNATyr so that tRNATyr can pair with the stop codon produced by the original mutation, allowing tyrosine to be incorporated into the protein and translation to continue.