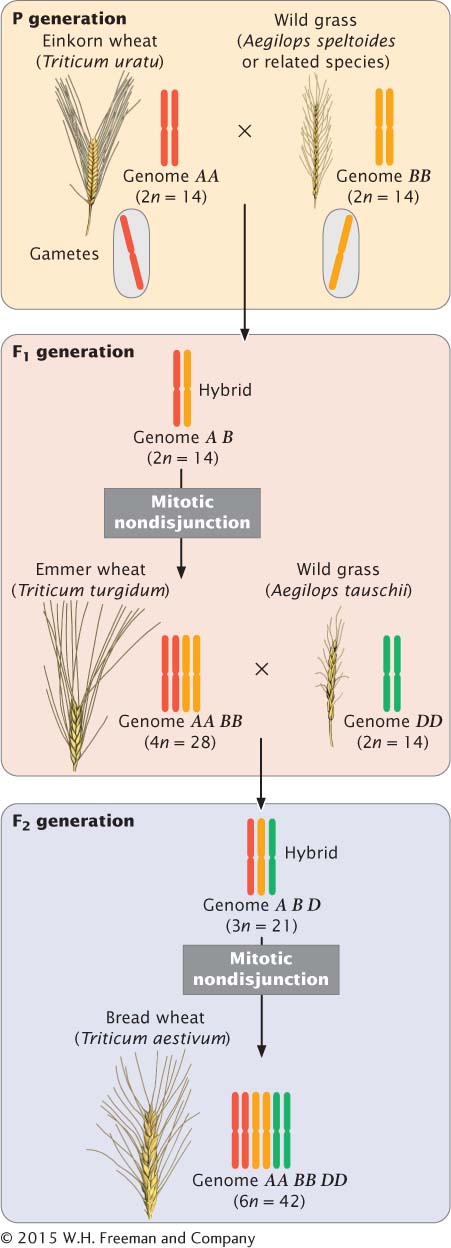
6.26 Modern bread wheat, Triticum aestivum, is a hexaploid with genes derived from three different species. Two diploid species, T. uratu and probably Aegilops speltoides or a related wild grass species, originally crossed to produce a diploid hybrid that underwent chromosome doubling to create T. turgidum. A cross between T. turgidum and A. tauschii produced a triploid hybrid that then underwent chromosome doubling to eventually produce T. aestivum, which is a hexaploid.