Chapter 5
¼ wild-
type eyes, wild- type wings; ¼ red eyes, wild- type wings; ¼ wild- type eyes, white- banded wings; ¼ red eyes, white- banded wings. The recombinant progeny are the 19 with red eyes, wild-
type wings and the 16 with wild- type eyes, white- banded wings. recombination frequency = recombinants/total progeny × 100% = (19 + 16)/879 × 100% = 4.0%
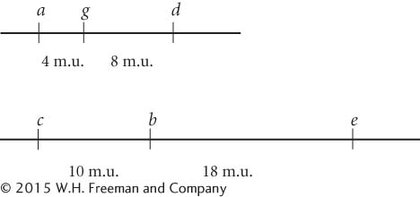
The distance between the genes is 4 map units.
The genes are linked and have not assorted independently.
Because the genes for leaf shape and fruit spines are 32.6 m.u. apart, we expect that 32.6% of the progeny of the cross will be recombinants. There will be two types of recombinants (those with heart-
shaped leaves and few spines and those with normal- shaped leaves and numerous spines), so each recombinant phenotype will constitute 16.3% of the progeny. The nonrecombinant progeny (those with heart- shaped leaves and numerous spines and those with normal- shaped leaves and few spines) will make up the remainder of the progeny (100% – 32.6% = 67.4%), which will be equally divided between the two nonrecombinant phenotypes (67.4%/2% = 33.7% each). Heart- shaped, numerous spines 33.7% Normal- shaped, few spines 33.7% Heart- shaped, few spines 16.3% Normal- shaped, numerous spines 16.3%
Genotype Body color Eyes Bristles Proportion (a) e+ ro+ f+ normal normal normal 20% e+ ro+ f normal normal forked 20% e ro f+ ebony rough normal 20% e ro f ebony rough forked 20% e+ ro f+ normal rough normal 5% e+ ro f normal rough forked 5% e ro+ f+ ebony normal normal 5% e ro+ f ebony normal forked 5% (b) e+ ro+ f+ normal normal normal 5% e+ ro+ f normal normal forked 5% e ro f+ ebony rough normal 5% e ro f ebony rough forked 5% e+ ro f+ normal rough normal 20% e+ ro f normal rough forked 20% e ro+ f+ ebony normal normal 20% e ro+ f ebony normal forked 20%
Gene f is unlinked to either of these groups; it is on a third linkage group.
V is the middle gene.
The Wx–V distance = 7 m.u. and the Sh–V distance = 30 m.u. The Wx–Sh distance is the sum of these two distances, or 37 m.u.
Coefficient of coincidence = 0.80; interference = 0.20.
All the progeny receive p sh-1 Hb2 from the male parent, shown as the lower chromosome in each progeny type. The upper chromosomes are the products of meiosis in the heterozygous parent, and are identified in the table. The nonrecombinants have p sh-1 Hb2 or P Sh-1 Hb1; the double crossovers have p Sh-1 Hb2 or P sh-1 Hb1. The two classes differ in the Sh-1 locus; therefore, Sh-1 is the middle locus.
P and Sh-1: Recombinants have P sh-1 or p Sh-1. Recombination frequency = (57 + 45 + 1)/708 = 0.145 = 14.5 m.u.
Sh-1 and Hb: Recombinants have Sh-1 Hb2 or sh-1 Hb1. Recombination frequency = (6 + 5 + 1)/708 = 0.017 = 1.7 m.u.
Expected double crossovers = RF1 × RF2 × total progeny = 0.145(0.017)(708) = 1.7
Coefficient of coincidence = number of observed double crossovers/number of expected double crossovers = 1/1.7 = 0.59
Interference = 1 − coefficient of coincidence = 0.41
Genotype Body Eyes Wings Proportion B+ pr+ vg+ normal normal normal 40.7% b pr vg black purple vestigial 40.7% b+ pr+ vg normal normal vestigial 6.3% b pr vg+ black purple normal 6.3% b+ pr vg normal purple vestigial 2.8% b pr+ vg+ black normal normal 2.8% b+ pr vg+ normal purple normal 0.2% b pr+ vg black normal vestigial 0.2%