Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms
A significant contribution of molecular genetics has been to provide numerous genetic markers that can be used in gene mapping. One group of such markers comprises restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs), which are variations (polymorphisms) in the patterns of fragments produced when DNA molecules are cut with the same restriction enzyme (Figure 14.11). These differences are inherited and can be used in mapping, just as allelic differences are used to map conventional genes.
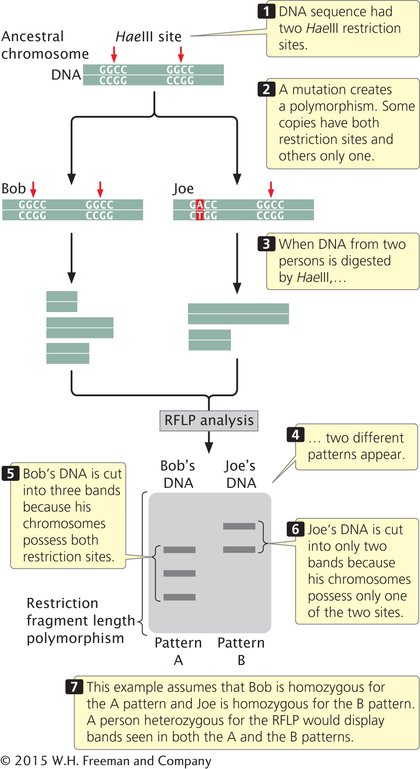
Figure 14.11: Restriction fragment length polymorphisms are genetic markers that can be used in mapping.
To illustrate mapping with RFLPs, consider Huntington disease, an autosomal dominant disorder. In the family shown in Figure 14.12, the father is heterozygous both for Huntington disease (Hh) and for RFLP alleles (AC). From the father, each child inherits either a Huntington-disease allele (H) or a normal allele (h); any child inheriting the H allele develops the disease because it is an autosomal dominant disorder. The child also inherits one of the two RFLP alleles from the father, either A or C, which produces the corresponding RFLP pattern. In Figure 14.12, every child who inherits the C pattern from the father also inherits Huntington disease (and therefore the H allele), which shows that the RFLP is closely linked to the disease-causing gene. If we had observed no correspondence between the inheritance of the RFLP pattern and the inheritance of the disease, the lack of correspondence would indicate that the loci encoding the RFLP and Huntington disease are assorting independently and are not linked. However, in recent years the availability of inexpensive DNA sequencing technology (described below) has decreased the use of RFLPs in gene mapping and genetic diagnosis. Today, the diagnosis of Huntington disease is routinely carried out by amplifying a portion of the Huntington disease gene with PCR.
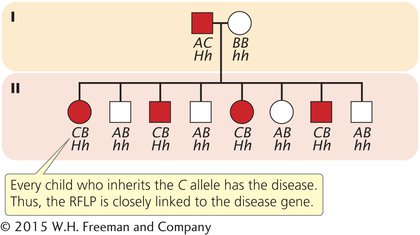
Figure 14.12: Restriction fragment length polymorphisms can be used to detect linkage. The letter H refers to the Huntington disease allele; h refers to the normal allele. A, B, and C refer to RFLP alleles. Every child who inherits the C RFLP allele has Huntington disease, indicating that the genes that encode the RFLP and Huntington disease are closely linked.
CONCEPTS
Restriction fragment length polymorphisms are variations in the pattern of fragments produced by restriction enzymes, which reveal variations in DNA sequences.

