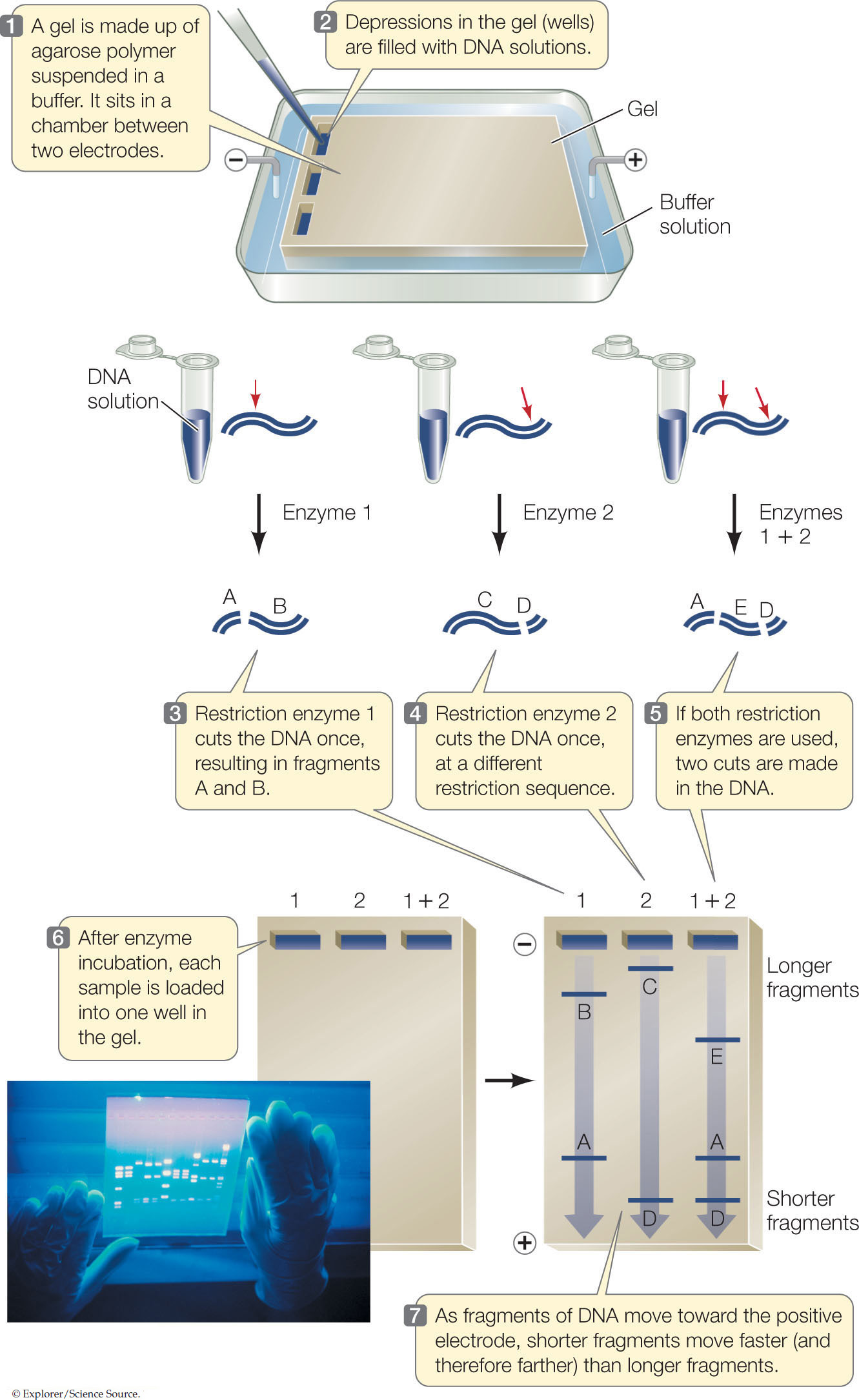
Figure 13.2: Separating Fragments of DNA by Gel Electrophoresis A mixture of DNA fragments is placed in a gel, and an electric field is applied across the gel. The negatively charged DNA moves toward the positive end of the field, with smaller molecules moving faster (and farther) than larger ones. After minutes to hours for separation, the electric power is shut off and the separated fragments can be analyzed.