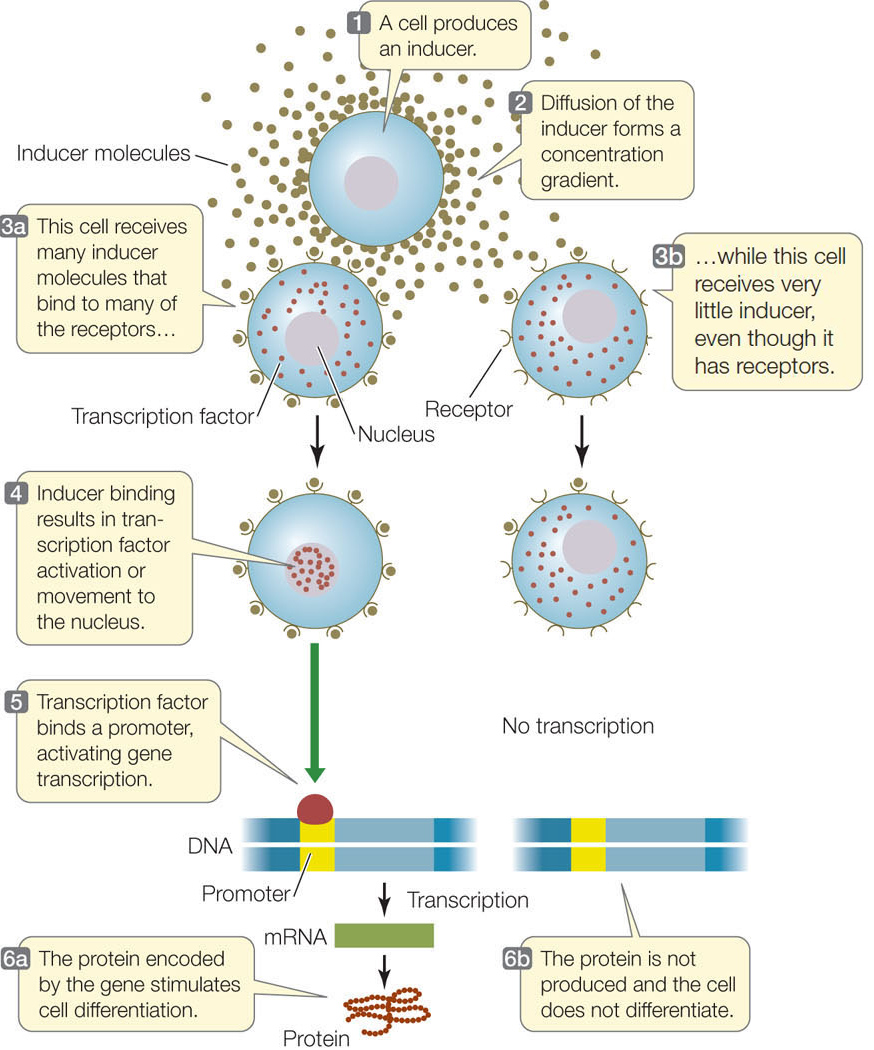
Figure 14.9: The Concept of Embryonic Induction The concentration of an inducer directly affects the degree to which a transcription factor is activated. The inducer acts by binding to a receptor on the target cell. This binding is followed by signal transduction involving transcription factor activation or movement from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. In the nucleus, the transcription factor acts to stimulate the expression of genes involved in cell differentiation.