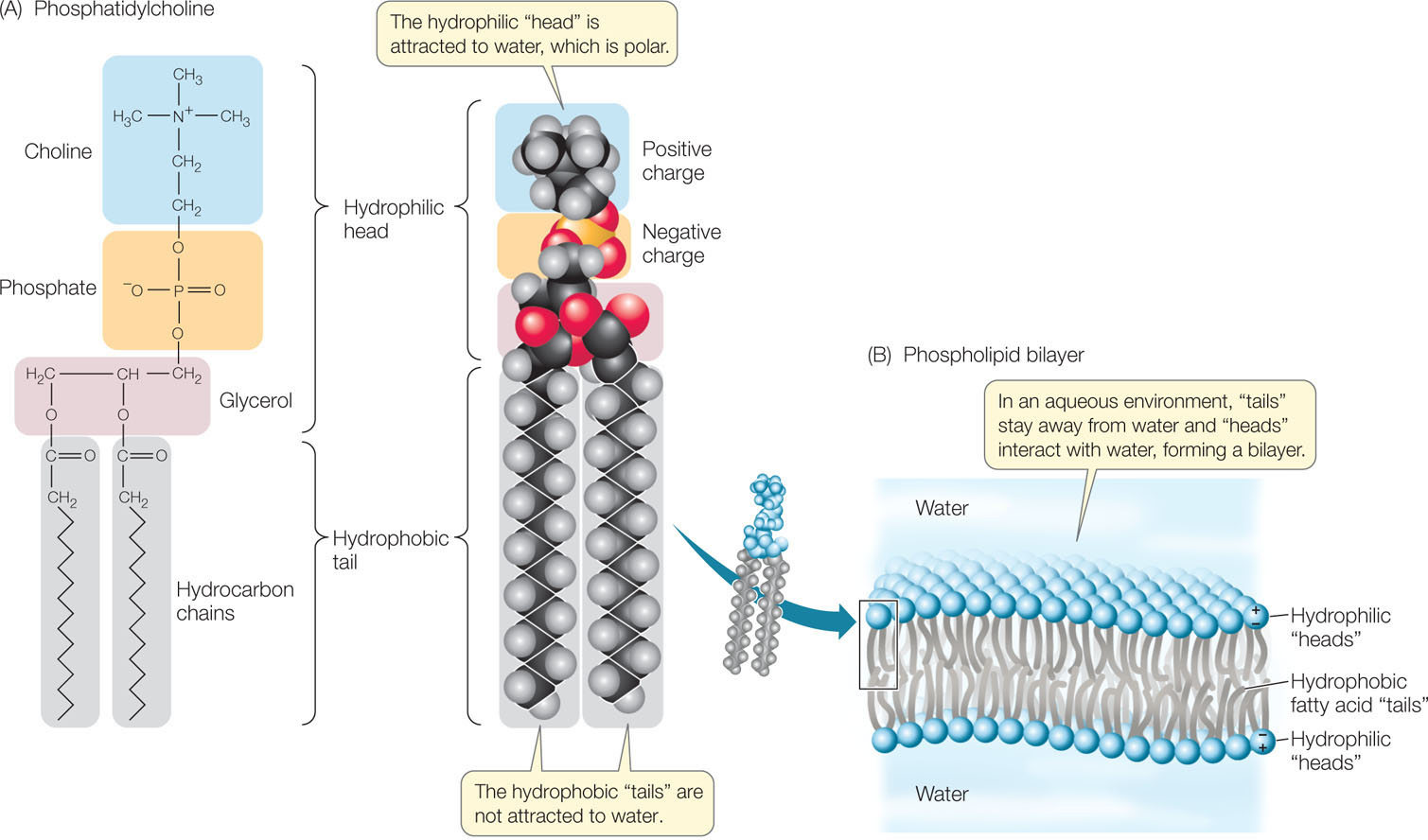
Figure 2.13: Phospholipids (A) Phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) is an example of a phospholipid molecule. In other phospholipids, the amino acid serine, the sugar alcohol inositol, or another compound replaces choline. (B) In an aqueous environment, hydrophobic interactions bring the “tails” of phospholipids together in the interior of a bilayer. The hydrophilic “heads” face outward on both sides of the bilayer, where they interact with the surrounding water molecules.