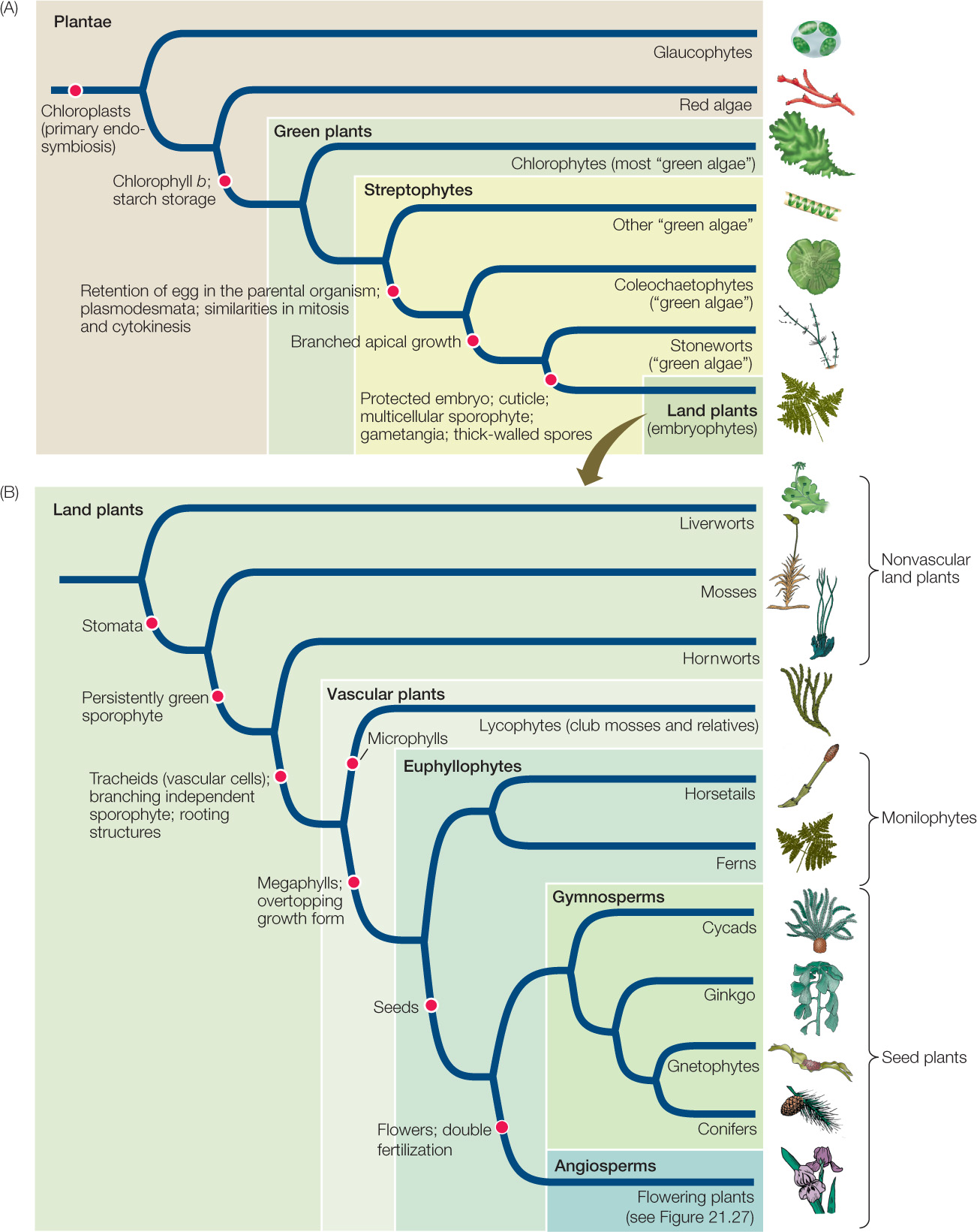
Figure 21.1: The Evolution of Plants (A) In its broadest definition, the term “plant” includes the glaucophytes, red algae, and green plants—all the groups descended from a common ancestor with chloroplasts. (B) Some biologists restrict the term “plant” to the green plants (those with chlorophyll b) or, even more narrowly, to the land plants. Three key characteristics that emerged during the evolution of land plants—protected embryos, vascular tissues, and seeds—led to their success in the terrestrial environment. (See Analyze the Data 21.1 at LaunchPad.)