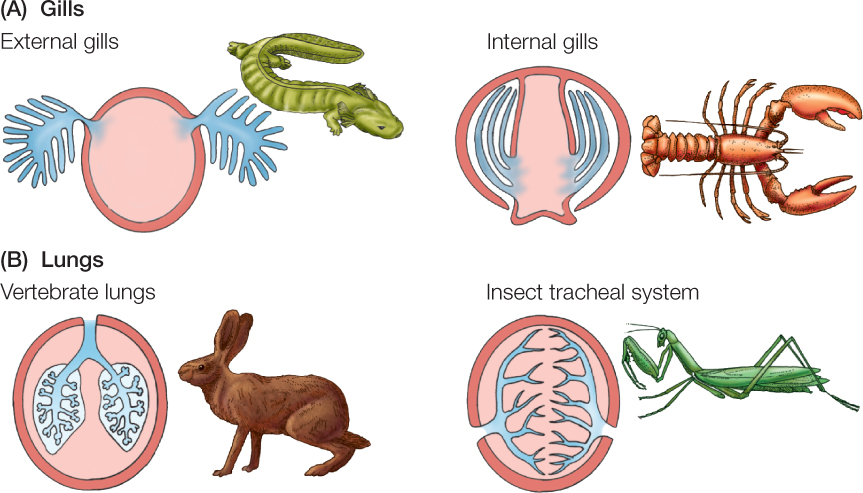
Figure 31.4: Gills and Lungs Physiologists classify all specialized breathing organs (blue in these diagrams) as either gills or lungs, depending on whether they are (A) evaginated structures (folded outward from the body) that are surrounded by the environmental medium or (B) invaginated structures (folded inward into the body) that contain the environmental medium. The use of the word “lungs” does not always match everyday usage. For example, the tracheal breathing system of an insect (discussed later in this chapter) is a lung because it is invaginated and contains air, but it is rarely called a lung in everyday language. Gills are subdivided into external gills (which project directly into the animal’s environment) and internal gills (which project into a protective gill chamber that is ventilated with water).