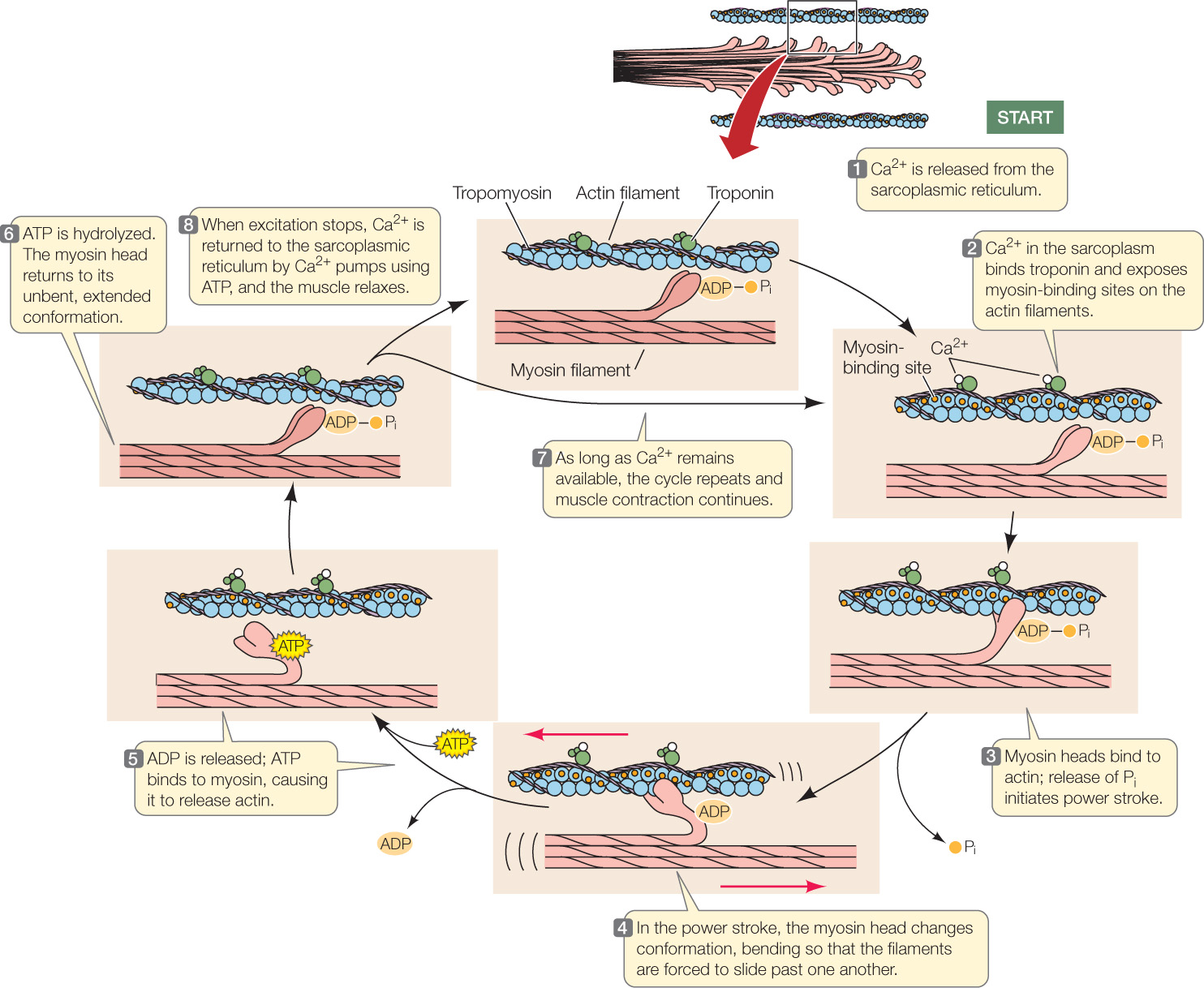
Figure 33.7: Ca2+ Causes Muscle Contraction When Ca2+ binds to troponin, it causes molecular conformation changes that expose the myosin-binding sites on actin. As long as the binding sites are exposed and ATP is available, actin and myosin go through cyclic interactions that use ATP bond energy to pull the actin and myosin filaments past each other, developing mechanical forces. Pi = inorganic phosphate.