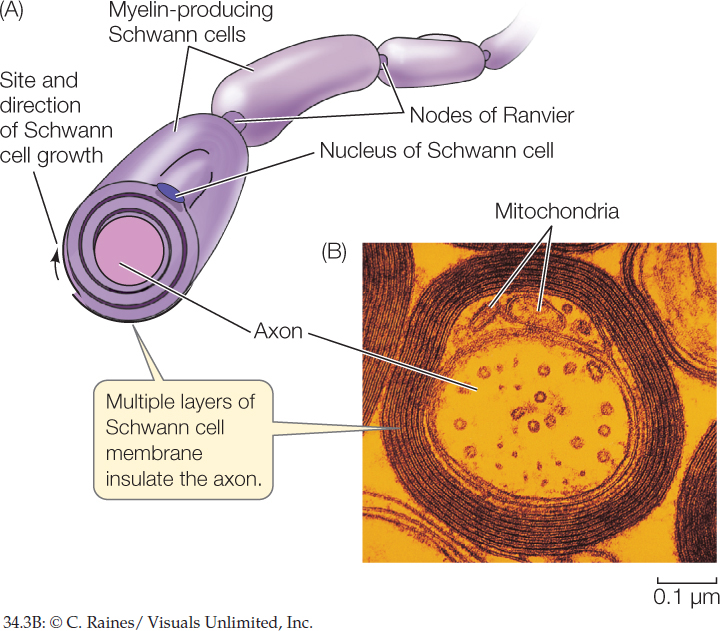
Figure 34.3: Electrically Insulating an Axon (A) Schwann cells wrap around the axon, enclosing the axon in many layers of lipid-rich Schwann cell membrane, called myelin, without intervening cytoplasm. Myelin provides electrical insulation to the axon. At the intervals between Schwann cells—the nodes of Ranvier—the axon is exposed. (B) A myelinated axon, seen in cross section at high magnification by use of an electron microscope.