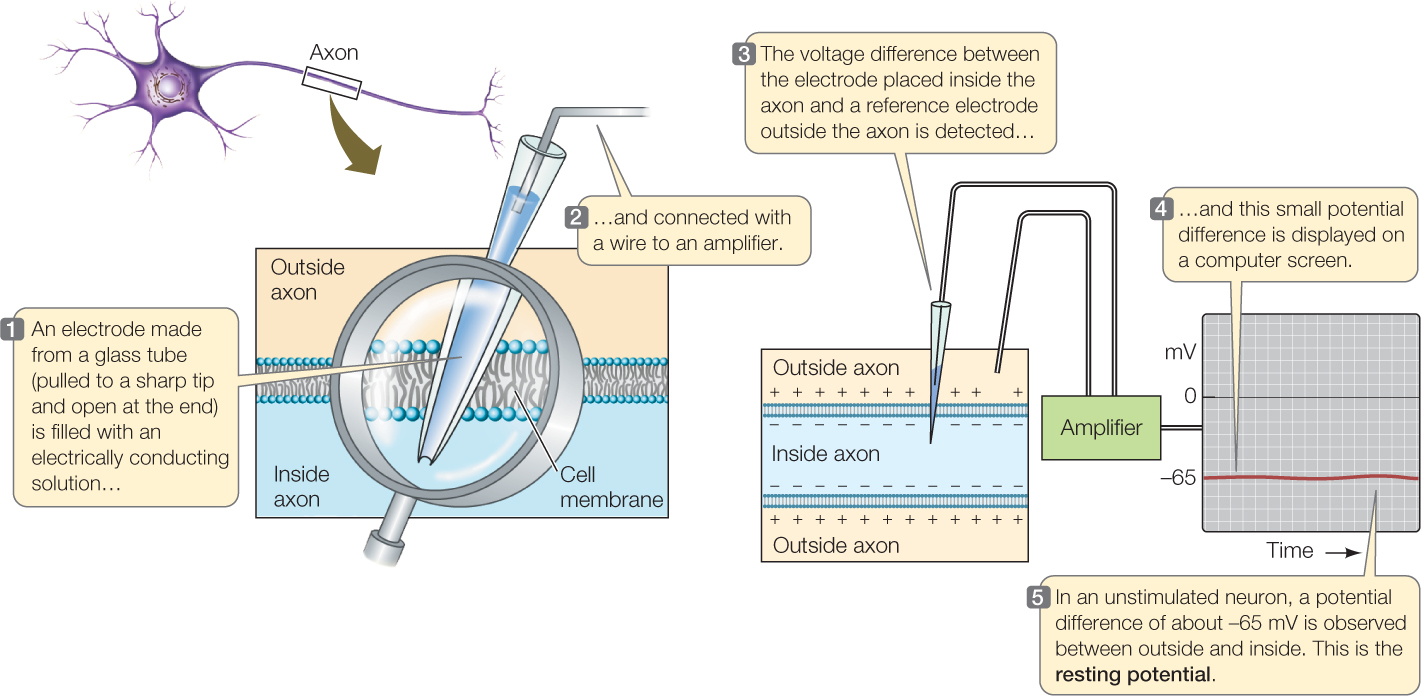
Figure 34.4: Measuring the Membrane Potential An electrode can be made from a fine glass tube with a sharp tip filled with a solution that conducts electric charges. When such an electrode is inserted into an axon and another electrode is placed in the extracellular fluid just outside the axon, the difference in voltage across the axon cell membrane—called the membrane potential—can be measured.