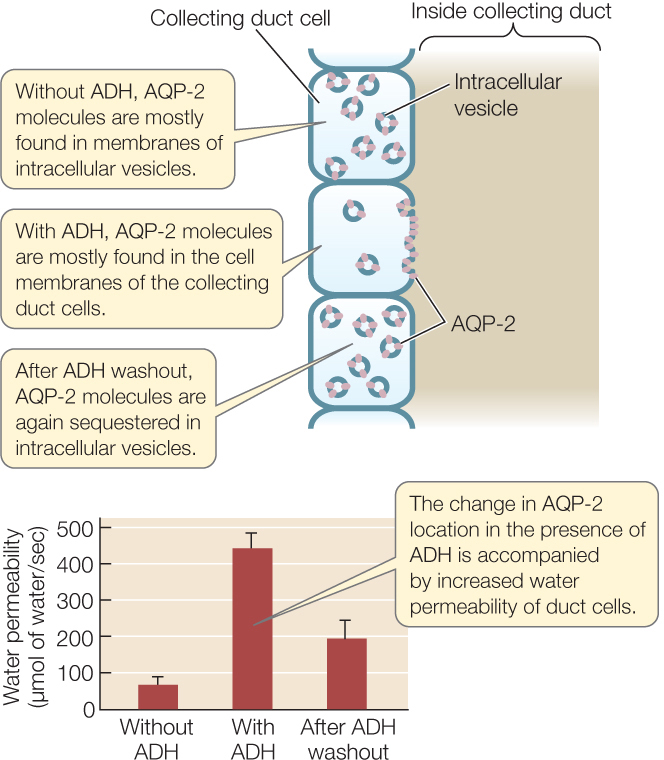
Figure 36.10: ADH Activates Insertion of Aquaporins into Cell Membranes Aquaporin proteins make some regions of renal tubules permeable to water. One type of aquaporin, AQP-2, is responsible for the permeability of the collecting duct cells in a mammal. How does antidiuretic hormone (ADH) act on molecules of AQP-2 to control the level of water permeability in renal cells?a