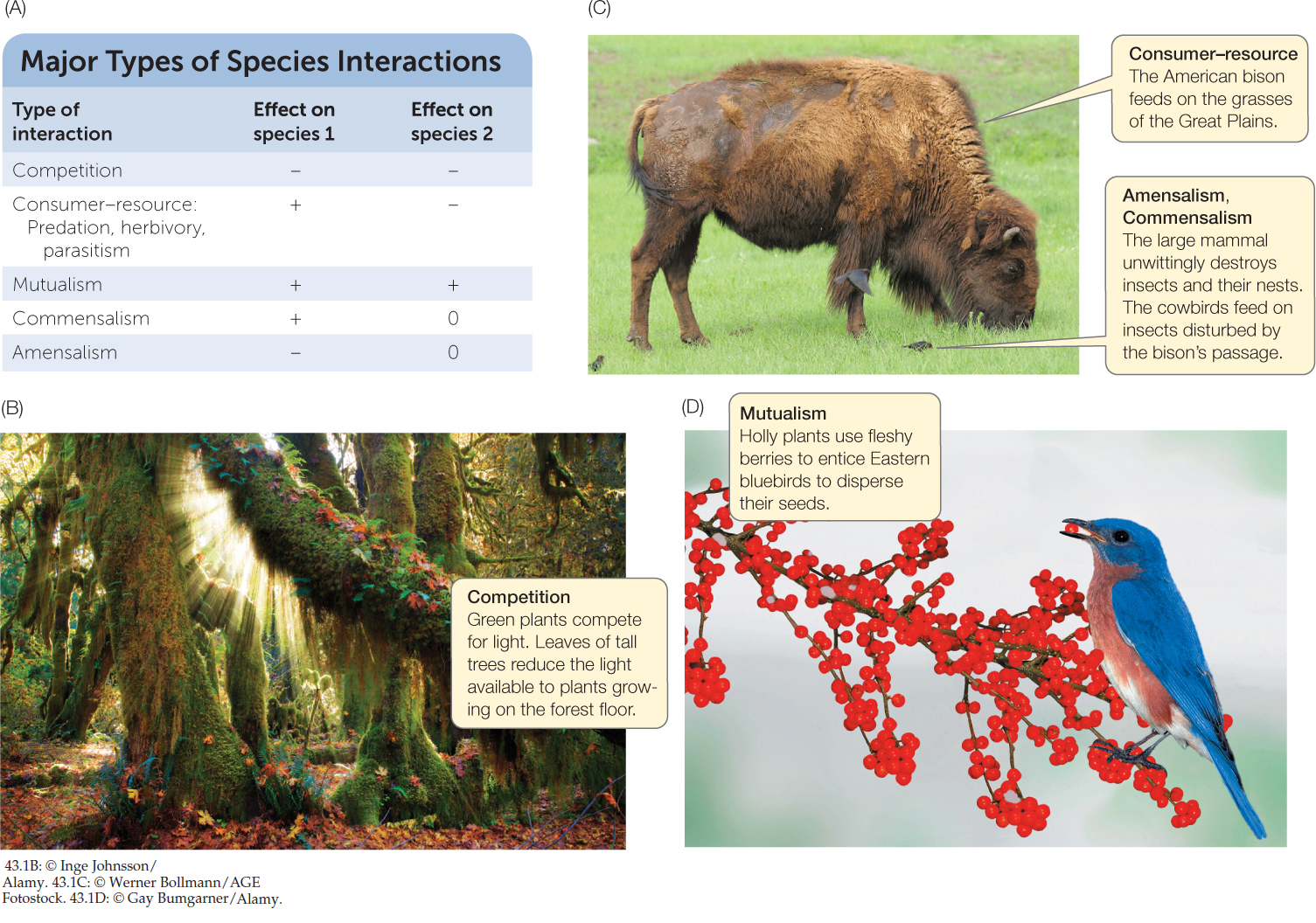
Figure 43.1: Types of Interspecific Interactions (A) Interactions between species can be grouped into categories based on whether their influence on fitness is positive (+), negative (–), or neutral (0). (B) The characteristics of canopy (treetop) and understory (lowgrowing) vegetation in a forest are largely a product of competition for light. (C) Commensalisms between large grazing ungulates (hoofed animals) and insect-eating birds are found in grassland environments around the world. (D) The interaction between berry-producing plants and berry-eating birds is a mutualism. Here an Eastern bluebird (Sialia sialis) gains nutrition by eating holly berries (Ilex opaca). The holly’s seeds pass through the bird’s gut unharmed, and are deposited in nutrient-rich feces away from the parent plant.