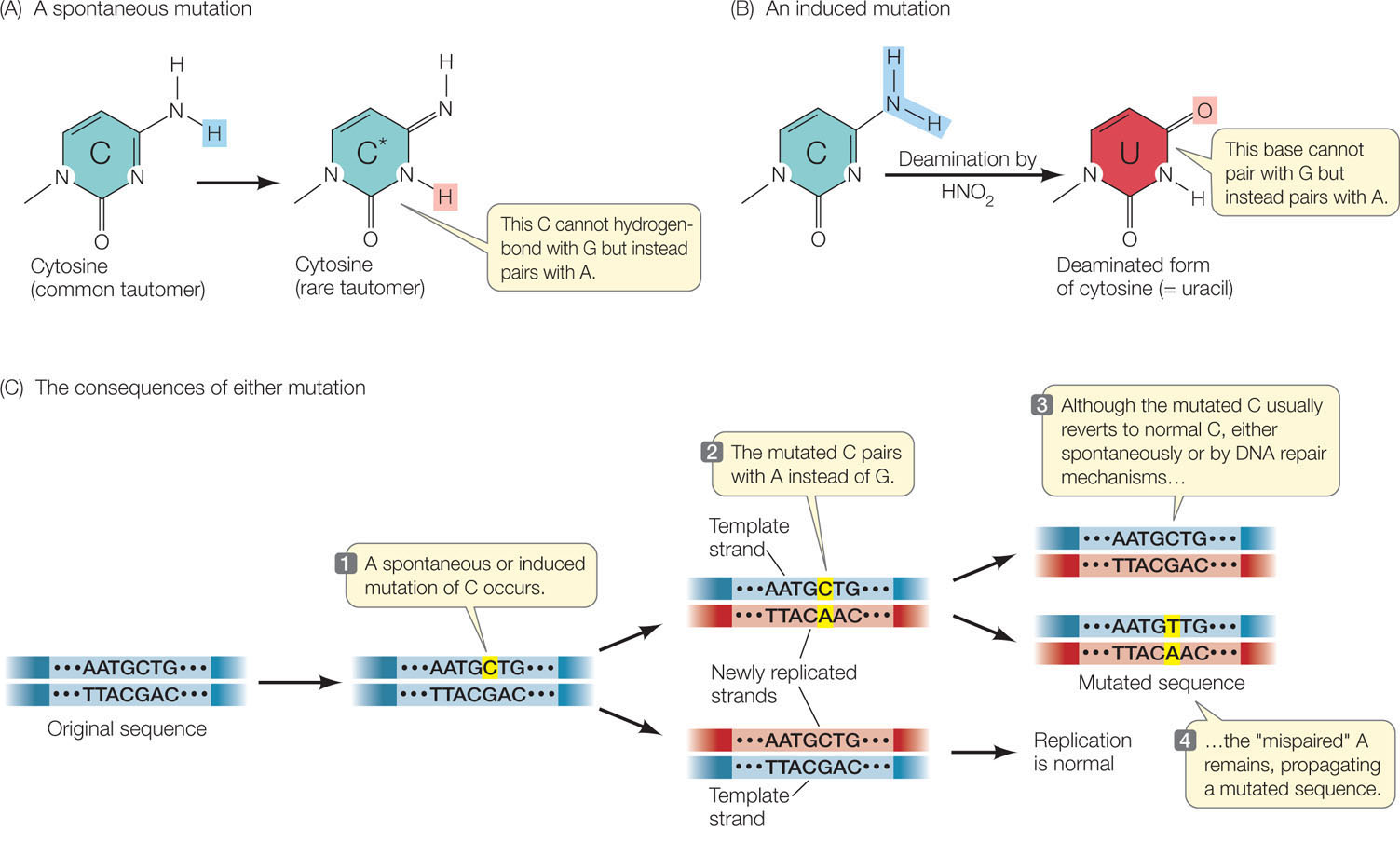
Figure 9.18: Spontaneous and Induced Mutations (A) Each of the nitrogenous bases exists in both a common (prevalent) form and a rare form. When a base spontaneously switches to its rare tautomer, it can pair with a different base. (B) Mutagens such as nitrous acid can induce changes in the bases. (C) The results of both spontaneous and induced mutations are permanent changes in the DNA sequence following replication.