ULTRATRACE MINERALS
ULTRATRACE MINERALS minerals that are found in the body, but not considered “essential” at this time
In addition to trace minerals, individuals may also need to ensure that they are getting enough of the ultratrace minerals, which have potential intake requirements of less than 1 microgram per day. The ultratrace minerals include arsenic (As), boron (B), nickel (N), silicon (Si), and vanadium (V). Although scientists have not yet identified specific biological or physiological functions for ultratrace minerals, and these minerals are not currently classified as essential nutrients, animal data suggest that they may be important for human nutrition. Daily recommendations for the intake of ultratrace minerals are considered ND, or “not determinable,” because so little data exists; as a result, food is considered the only safe source of these nutrients to avoid possible overconsumption.
■ ■ ■
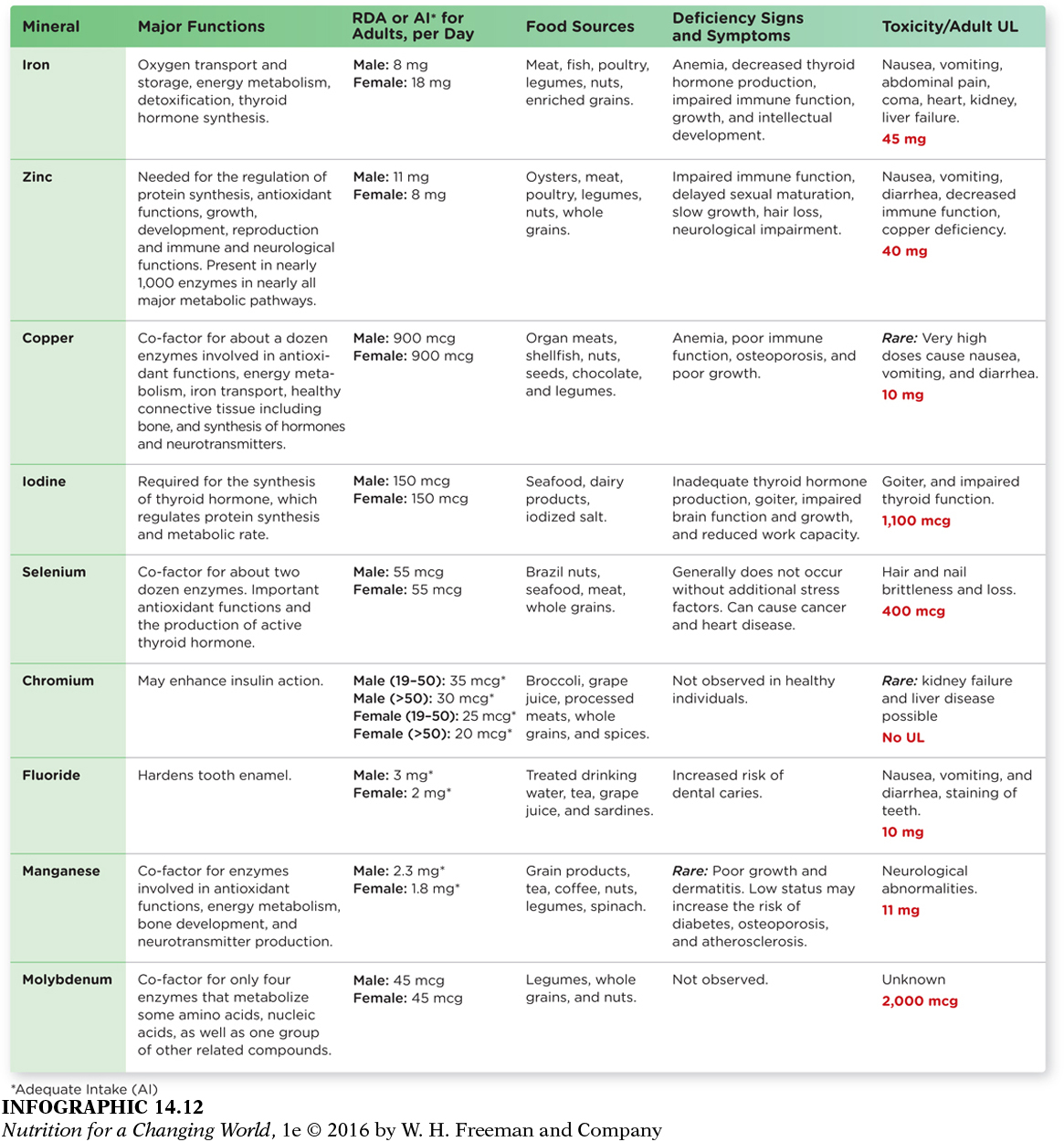
All of the trace minerals found in your body could fit in the palm of your hand. Yet their contributions are crucial to your health. Their functions are as important as the functions of the major minerals calcium and phosphorus, which each account for more than a pound of your body weight. The key is to consume a range of foods to meet our need for trace minerals—
329
330