Facts about the Measles
512
Facts about the Measles
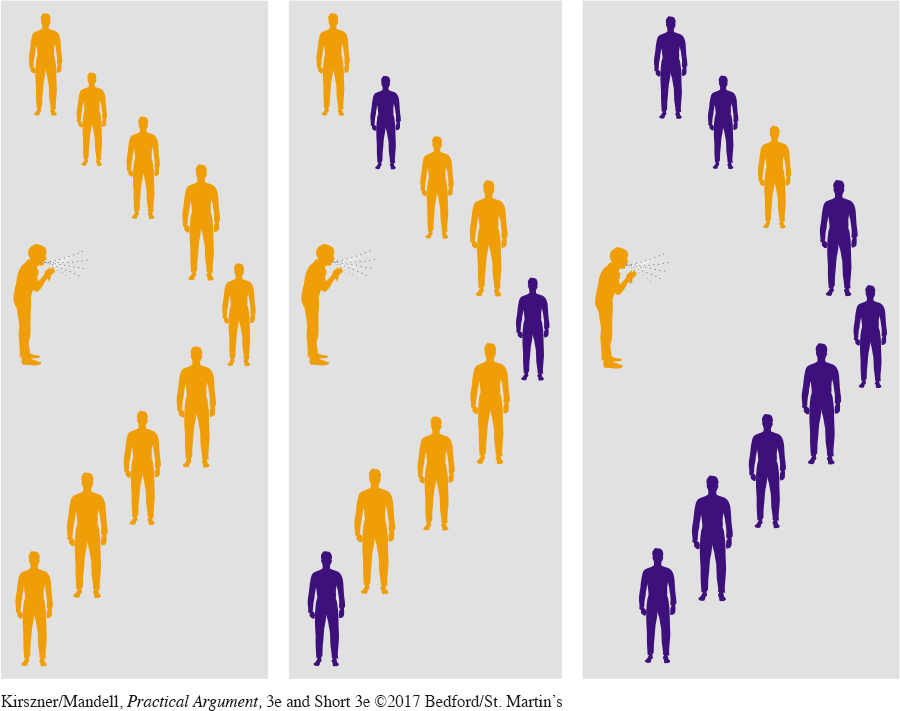
AN OUTBREAK If no one has any immunity to a virus, one person who was infected could spread the virus to twelve to eighteen other people. A single infection could quickly become an epidemic.
HERD EFFECT People who have been vaccinated remove themselves as a potential source for the virus—
HERD IMMUNITY Herd immunity is the threshold needed to end an outbreak quickly. It has been discovered that this occurs when one person with a virus infects (on average) fewer than one other person. In a society where the majority of people are inoculated, the virus has nowhere to travel. Few people become infected, and so even those without the virus are often protected because they come into contact with so few potential carriers.