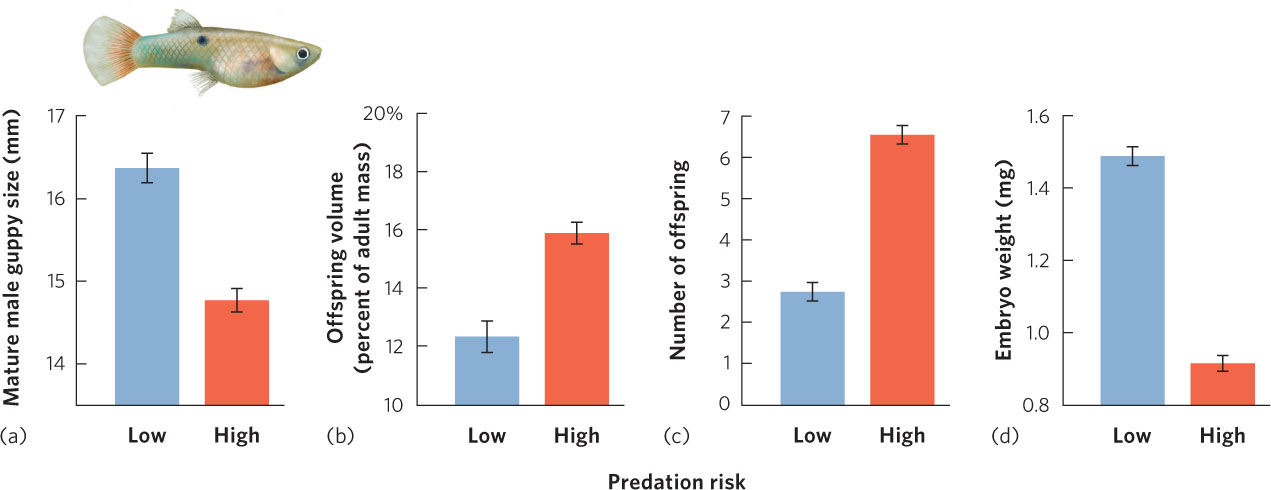
Figure 8.7 Alternate life history strategies of guppies in Trinidad. Guppy populations in streams with a high risk of predation have shorter life spans and those in streams with low predation risk have longer life spans. In response to this difference in longevity, guppies living in predator environments have evolved to (a) mature as smaller males, (b) allocate a greater fraction of energy to offspring, (c) produce more offspring, and (d) produce smaller offspring. Error bars are standard deviations.
Data from D. N. Reznick et al., Life history evolution in guppies (Poecilia reticulata: Poeciliidae). 4. Convergence in life history phenotypes, American Naturalist 147 (1996): 319–338.