CHAPTER 32 Test Your Knowledge
DRIVING QUESTION 1
How is a plant body structured, and how do plants obtain water and grow?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 32.1 and 32.2, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 Draw and label a diagram of two adjacent plant cells. Include key intracellular structures.
Draw and label a diagram of two adjacent plant cells. Include key intracellular structures.
 Which of the following statements represents a true distinction between xylem and phloem?
Which of the following statements represents a true distinction between xylem and phloem?
a. Xylem provides support only; phloem provides transport.
b. Xylem provides water and nutrient transport; phloem provides sugar transport.
c. Xylem transports materials from shoots to roots; phloem transports materials in either direction.
d. Xylem transports sugars in either direction; phloem transports water from roots to shoots
e. all of the above
 What is the function of the cuticle?
What is the function of the cuticle?
a. It enables neighboring cells to stick together.
b. It provides rigidity to the cell wall.
c. It is toxic to many herbivorous insects.
d. It prevents water loss.
e. It is sticky and helps pollen stick to a plant during pollination.
USE IT
 Paper is made from wood that is broken down to pulp. Why are lignin-digesting enzymes included in the pulping process? Would these enzymes have to be included in the pulping process if paper were made from green leaves? Explain your answer.
Paper is made from wood that is broken down to pulp. Why are lignin-digesting enzymes included in the pulping process? Would these enzymes have to be included in the pulping process if paper were made from green leaves? Explain your answer.
DRIVING QUESTION 2
How do plants obtain nutrients?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 32.3, 32.4, and 32.5, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 Plants are autotrophs and can make sugar from CO2. How do they obtain CO2?
Plants are autotrophs and can make sugar from CO2. How do they obtain CO2?
a. through stomata
b. by absorption through the root system
c. by digesting insects
d. by breaking down carbon-rich carbohydrates stored in roots
e. a and b
 When stomata are open, what is happening?
When stomata are open, what is happening?
a. O2 is entering the plant for photosynthesis.
b. CO2 is entering the plant for photosynthesis.
c. H2O is entering the plant for photosynthesis.
d. H2O is leaving the plant.
e. a, b, and c
f. b and d
 What is found in root nodules?
What is found in root nodules?
a. PEP carboxylase
b. CO2
c. bacteria
d. phosphorus
e. stored glucose
USE IT
 Describe the “conflict” that plants face with respect to opening and closing their stomata.
Describe the “conflict” that plants face with respect to opening and closing their stomata.
 Are trumpet pitchers strict autotrophs? Explain your answer.
Are trumpet pitchers strict autotrophs? Explain your answer.
 If you applied to the soil around your plants a chemical that kills bacteria (but not plants), why might your plants die?
If you applied to the soil around your plants a chemical that kills bacteria (but not plants), why might your plants die?
 Why may the bright coloration of a trumpet pitcher have a different function than do the bright colors of yellow or orange squash blossoms? (Hint: Squash are pollinated by bees.)
Why may the bright coloration of a trumpet pitcher have a different function than do the bright colors of yellow or orange squash blossoms? (Hint: Squash are pollinated by bees.)
 If a plant could not make chlorophyll, would you expect it to survive? Why or why not?
If a plant could not make chlorophyll, would you expect it to survive? Why or why not?
736
INTERPRETING DATA
 Scientists carried out an experiment to examine the effect of CO2 concentrations on plant growth in a semi-arid (that is, a dry) grassland environment in Colorado. They set up several plots in the field, consisting of chambers that allowed the concentration of CO2 to be controlled. One set of plots (A) was kept at ambient CO2 concentration, and one set (B) was kept at elevated CO2 concentration (two times ambient). In mid-July the total plant mass in each plot set was recorded. The data for three consecutive years are shown in the table. (In order to establish a baseline, the CO2 levels in 1996 were not manipulated.)
Scientists carried out an experiment to examine the effect of CO2 concentrations on plant growth in a semi-arid (that is, a dry) grassland environment in Colorado. They set up several plots in the field, consisting of chambers that allowed the concentration of CO2 to be controlled. One set of plots (A) was kept at ambient CO2 concentration, and one set (B) was kept at elevated CO2 concentration (two times ambient). In mid-July the total plant mass in each plot set was recorded. The data for three consecutive years are shown in the table. (In order to establish a baseline, the CO2 levels in 1996 were not manipulated.)
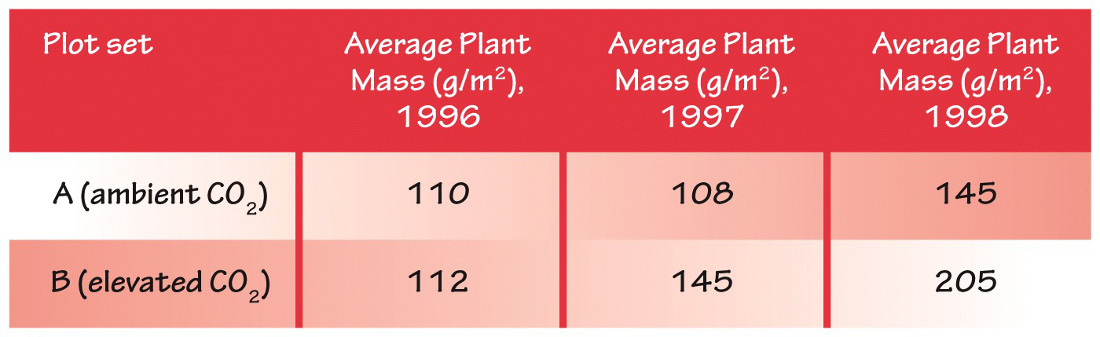
a. Graph these data.
b. Are there any differences between different plot sets in any given year? If so, describe the differences observed.
c. Are there any differences in the same plot set between years? If so, describe the differences and propose an explanation.
d. What are the implications of this study for grassland productivity (at least in Colorado) with rising CO2 levels?
SOURCE: Morgan, J. A., et al. (2001) Elevated CO2 enhances water relations and productivity and affects gas exchange in C3 and C4 grasses of the Colorado shortgrass steppe. Global Change Biology 7:451–466.
DRIVING QUESTION 3
How do plants reproduce, respond to stimuli, and protect themselves?
By answering the questions below and studying Infographics 32.6, 32.7, 32.8, 32.8, 32.10, and 32.11, you should be able to generate an answer for the broader Driving Question above.
KNOW IT
 What characterizes a dormant seed?
What characterizes a dormant seed?
a. the presence of sperm
b. the presence of eggs
c. the presence of an embryonic plant
d. the absence of ABA
e. the presence of several pollen grains
 Describe how fertilization follows pollination in an angiosperm. What has to happen, and what plant structures are involved?
Describe how fertilization follows pollination in an angiosperm. What has to happen, and what plant structures are involved?
 Which of the following pigments are present in green leaves late in the summer?
Which of the following pigments are present in green leaves late in the summer?
a. chlorophyll
b. carotene
c. xanthophyll
d. all of the above
e. a and b
 Which of the following hormones helps fruit to ripen?
Which of the following hormones helps fruit to ripen?
a. auxin
b. ethylene
c. gibberellins
d. estrogen
e. anthocyanin
 If you wanted a plant to grow really tall, which hormone should you apply?
If you wanted a plant to grow really tall, which hormone should you apply?
a. auxin
b. ethylene
c. gibberellins
d. anthocyanin
e. ABA
USE IT
 Why do seedless grapes need hormone treatment to develop big clusters of big grapes, while seeded varieties can develop large fruits without exogenous (that is, externally applied) hormones?
Why do seedless grapes need hormone treatment to develop big clusters of big grapes, while seeded varieties can develop large fruits without exogenous (that is, externally applied) hormones?
 Nopales are cactus pads (the large, thick “leaves” of the prickly pear cactus) and make a delicious salad. What antiherbivory mechanism fails when we succeed in making ensalada de nopales—prickly pear salad?
Nopales are cactus pads (the large, thick “leaves” of the prickly pear cactus) and make a delicious salad. What antiherbivory mechanism fails when we succeed in making ensalada de nopales—prickly pear salad?
737
MINI CASE
 The Natural Products Branch of the National Cancer Institute looks for defensive compounds produced by plants, microbes, and marine organisms that may have anticancer activity. Once compounds have been isolated, they can be chemically modified to enhance their activity. Several drugs have come out of this program, including eribulin mesylate, a chemically modified compound originally purified from a sea sponge. This drug has been approved for women with metastatic breast cancer whose disease thus far has not been responsive to treatment. In a clinical trial, patients taking eribulin mesylate had a significantly longer survival time (13.1 months) than patients taking chemotherapy regimens prescribed by their oncologists (10.6 months). (Data are from http://www.cancer.gov/ncicancerbulletin/041911/page5.)
The Natural Products Branch of the National Cancer Institute looks for defensive compounds produced by plants, microbes, and marine organisms that may have anticancer activity. Once compounds have been isolated, they can be chemically modified to enhance their activity. Several drugs have come out of this program, including eribulin mesylate, a chemically modified compound originally purified from a sea sponge. This drug has been approved for women with metastatic breast cancer whose disease thus far has not been responsive to treatment. In a clinical trial, patients taking eribulin mesylate had a significantly longer survival time (13.1 months) than patients taking chemotherapy regimens prescribed by their oncologists (10.6 months). (Data are from http://www.cancer.gov/ncicancerbulletin/041911/page5.)
The first step in developing drugs such as these is to prepare extracts by grinding up the natural product. Design a procedure to test such extracts for anticancer activity. Consider what tests you will use to determine if an extract has an anticancer activity, and what variables you will measure and manipulate in order to find promising candidates to advance along the drug discovery pipeline.
BRING IT HOME
 Many everyday products contain compounds derived from plants. A few of these are: Caffeinated sodas or energy drinks
Many everyday products contain compounds derived from plants. A few of these are: Caffeinated sodas or energy drinks
Camphor and menthol-containing vapor rubs and steams (for congestion and muscle aches) Nicotine
Tea tree oil for minor skin irritations and infections
Quinine-containing tonic water
You, members of your family, or your friends may have used some or all of these. For each item listed, do some internet research to identify the plant (find both the scientific and common name) and something else about it that interests you (e.g., where is the plant found, whether it has historically been used for medicinal purposes, are there other sources of the compound).