8.9 Analyzing The Science
One important value of forest ecosystems is their capacity to store carbon, thereby keeping it out of Earth’s atmosphere and mitigating climate change. Intact ecological communities are better at performing this ecosystem service than degraded ones. All ecosystems can both take up carbon and emit it; it is the net difference between accumulation versus emission that tells us whether the ecosystem is a net sink or source of carbon to the atmosphere. Globally, terrestrial ecosystems are a major net sink for atmospheric carbon dioxide, storing about 1 metric gigaton of carbon per year. Wetlands store even more carbon than most forests, making wetlands extremely important carbon sinks.
CARBON ACCUMULATION IN DIFFERENT WETLAND SEDIMENTS
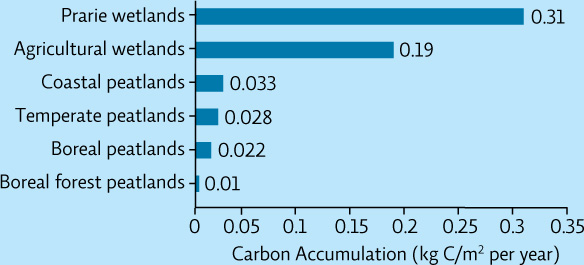
INTERPRETATION
Question 8.13
Xfd3dY1B4ki3CflLjQ97jE4uA197pHEbmkZSpJxdvUkNDr/49kA5xBuNeYk8+dR9UyzhfNzrAlWujzJ8XQhpxkF7ZW9muXfcQuestion 8.14
/pMSTYeawsFtTffGBUUgX7ZyDwGrISxnZlpSB3kvlsW1u5YheFayNjFalFs8w01kCuO6Qr7AAgRw7CjFem55dl0QRGiGo7y/KYnZ1y5umVRllLGWh43jm+JHiOgWuut+LY7hTJiFekIBfDUVoeuoQPlQas9Mst8v6+JvgwLNHQZAR0tmvuPuJU4sr/aDiBC4dUATG6NnVaPMYMaTSJIAiBsIycIXwUmPstxqH3nVapaITntLWwZcaEzJIjA=ADVANCE YOUR THINKING
Question 8.15
Fy8NHS54tYbIMYAgG/dIqOP9wdqI3hu3H2ST34+LeD47S3jzQfK3OhOjkFhLCDvC5yUH4rdyFGCJh9pCtxEgvnTx61s=Question 8.16
0luuSRpBCJINZoT2XyE8oCIUTp9H63sxNkJ+VuNuYCkTkQXuhvT5cUjNcXSVTe37uXvmcNSRGbDvpf9hlKkDRQg8F11RDHPS42fsiXhy30CzPxj562n8TPSHRTW4WnaiL9kJGgczv9falOeIf67KqLRcEzE/TOQG+Uo6AA==Question 8.17
3wGbSp1fduB4K8r/ygIR7Dg/TXuI51vXWgneSdyqKGLrWIsL8/SFY4efEF00gEU/viVodIlry/Z3P9RiY9xGdF4NGFmSmw66rKbiNSGYI41WhK54X/LadeaSHSWhoZCmRDvPVgQ4bQhatVlgrXgmIyzSEsF3ZUfk+ipdftRl30b4+VeLyieh/q51JlOWaHRD+8k+w8xBQkllXAaeMDGZ3iZd/kyCjhGAsCR2BRkAqR57w6L8MiDLC6sm5wv2oBy1oq3jlg==147