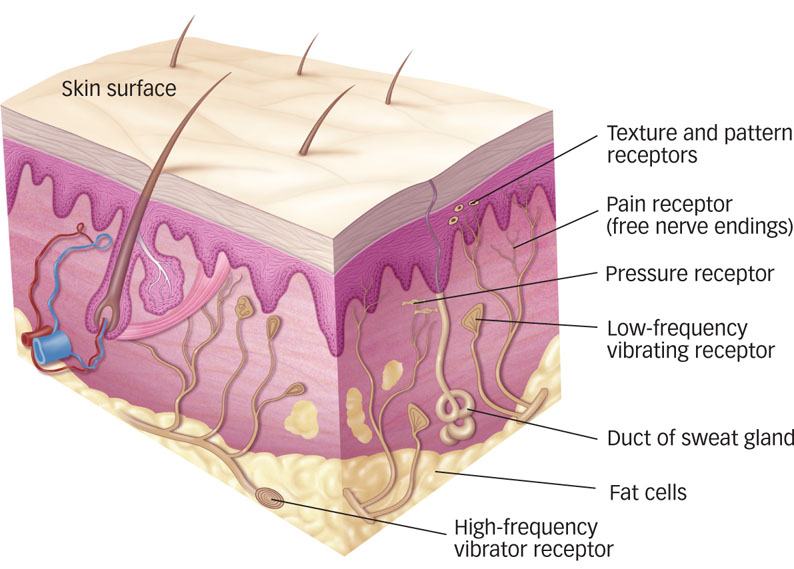
Touch Receptors Specialized sensory neurons form distinct groups of haptic receptors that detect pressure, temperature, and vibrations against the skin. Touch receptors respond to stimulation within their receptive fields, and their long axons enter the brain via the spinal or cranial nerves. Pain receptors populate all body tissues that feel pain; they are distributed around bones and within muscles and internal organs as well as under the skin surface. Both types of pain receptors (the fibers that transmit immediate, sharp pain sensations quickly and those that signal slow, dull pain that lasts and lasts) are free nerve endings.