6 Verb Forms
6
Verb Forms
Except for be, all English verbs have five forms.
Base Form |
Past Tense |
Past Participle |
Present Participle |
-s Form |
| move | moved | moved | moving | moves |

6a Use -s or -es endings for present tense verbs that have third-person singular subjects
The -s form is made up of the verb’s base form plus -s or -es.

A third-person singular subject can consist of a singular noun, a singular pronoun (he, she, and it), or a singular indefinite pronoun (such as everyone).
SINGULAR NOUN |
The flower opens. |
SINGULAR PRONOUN |
He opens the door. |
SINGULAR INDEFINITE PRONOUN |
Everybody knows the truth. |

6b Do not omit -ed endings on verbs
For regular verbs, both the past tense and the past participle are formed by adding -ed or -d to the base form of the verb. (For more on verb tense, see 1c and 27a.)
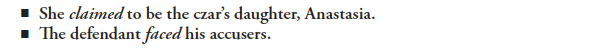
Some speakers do not fully pronounce the -ed endings of verbs (asked, fixed, supposed to, used to). As a result, they may unintentionally omit these endings in their writing.

6c Use the correct form of irregular verbs such as lay and lie
The verb pairs lay and lie and sit and set have similar forms and are often confused. Each verb has its own meaning: lie means to recline or rest on a surface, and lay means to put or place something; sit means to be seated, as in a chair, and set means to place something on a surface.

For more on irregular verbs, see 1c.
6d Use the active and passive voice appropriately
When a verb is in the active voice, the subject performs the action.
ACTIVE VOICE |
The Mississippi River flows into the Gulf of Mexico. |
When a verb is in the passive voice, the subject receives the action.
PASSIVE VOICE |
The computer file was deleted. |
|
Notice that the sentence in the passive voice does not tell who deleted the file. |
The active voice expresses ideas more vividly and emphatically than does the passive voice. Whenever possible, use the active voice in your sentences.
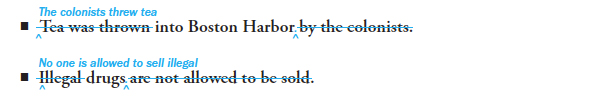
Sentences in the passive voice may seem indirect, as if the writer is purposely withholding information. In general, use the passive voice sparingly. There are two situations in which it is the better choice, however.
 macmillanhighered.com/successfulwriting LearningCurve > Active and Passive Voice
macmillanhighered.com/successfulwriting LearningCurve > Active and Passive Voice
- When you do not know or do not want to reveal who performed the action of the verb:
PASSIVE
Several historic buildings had been torn down. - When you want to emphasize the object of the action rather than the person who causes the action:
PASSIVE
The poem “My Last Duchess” by Robert Browning was discussed in class.
In this sentence, the title of the poem is more important than the people who discussed it.
6e Use the present tense when writing about literary works, even though they were written in the past

6f Be sure to distinguish between the immediate past and the less immediate past
Use the past perfect form of the verb, formed by adding had to the past participle, to indicate an action that was completed before another action or a specified time.
UNCLEAR |
Roberto finished three research papers when the semester ended. |
| Roberto did not finish all three right at the end of the semester. | |
REVISED |
Roberto had finished three research papers when the semester ended. |
For more on verb tense, see see 1c and see 27a.