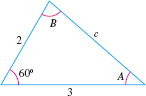
Using the Law of Cosines to Solve a Triangle
Solve the triangle: \(a=2\), \(b=3\), \(\ C=60^\circ\) shown in Figure 64.
Side \(c\) is of length \(\displaystyle\sqrt{7}\). To find either the angle \(A\) or \(B\), use the Law of Cosines. For \(A\), \begin{eqnarray*} a^{2} &=&b^{2}+c^{2}-2bc\cos A \\[3pt] 2bc\cos A &=&b^{2}+c^{2}-a^{2} \\[6pt] \cos A &=&\dfrac{b^{2}+c^{2}-a^{2}}{2bc}=\dfrac{9+7-4}{2\cdot 3\displaystyle\sqrt{7}}=\dfrac{12}{6\displaystyle\sqrt{7}}=\dfrac{2\displaystyle\sqrt{7}}{7} \\[6pt] A &\approx& 40.9^\circ \end{eqnarray*}
Then to find the third angle, use the fact that the sum of the angles of a triangle, when measured in degrees, equals \(180 {{}^\circ}.\) That is, \begin{eqnarray*} 40.9^\circ+B+60^\circ&=&180^\circ\nonumber \\[0pt] B &=&79.1^\circ \end{eqnarray*}