REVIEW EXERCISES
Question
Opposite vertices of a rectangular box whose edges are parallel to the coordinate axes are (1, 0, 2) and (2, 3, 4). List the coordinates of the other six vertices of the box.
Question
Describe in words the set of all points \((x, y, z)\) that satisfy \(y=3\).
Question
The vector \(\mathbf{v}\) has initial point \(P_{1}=( 5, 0, -2)\) and terminal point \(P_{2}=( 7, 1, 3)\).
- Write the vector \(\mathbf{v}\) in terms of its components.
- Write the vector \(\mathbf{v}\) in terms of standard basis vectors.
Question
Find the magnitude of the vector \(\mathbf{v=}\) \(\mathbf{i}+2 \mathbf{j}+3\mathbf{k}\).
Question
Find the distance between the points \((1, 2, 3)\) and \((7, 5, 1)\).
Question
Write the equation of the sphere with center at the point \((1, 2, 3)\) and radius 4.
Question
Find the radius and center of the sphere: \(x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}-4x+8y=5\).
Question
If \(\mathbf{v}=\langle -2,-1,3\rangle \) and \(\mathbf{w} =\langle 5, 4, -2\rangle \), find \(3\mathbf{v}-2\mathbf{w}\).
Question
If \(\mathbf{v}=2\mathbf{i}+3\mathbf{j}-\mathbf{k}\) and \(\mathbf{w}=-\mathbf{i}-2\mathbf{j}+3\mathbf{k}\), find \(\Vert \mathbf{v}+\mathbf{w} \Vert \).
Question
Find a unit vector in the direction of \(\mathbf{v}=4\mathbf{i} +12\mathbf{j}-3\mathbf{k}\).
Question
Find a vector \(\mathbf{v}\) in the plane with magnitude \(25\) if the angle between \(\mathbf{v}\) and \(\mathbf{i}\) is \(120^\circ\).
Question
Find \(\mathbf{v}\) and \(\mathbf{w}\) if \[ \mathbf{w}-3\mathbf{v}=2\mathbf{i}+\mathbf{j}-\mathbf{k}\qquad\hbox{and}\qquad 2\mathbf{w}+\mathbf{v}=\mathbf{i}+\mathbf{j} \]
Question
- Find the magnitude and direction cosines of the vector \(\mathbf{v}=5\mathbf{i}+8\mathbf{j}-2\mathbf{k}\).
- Write \(\mathbf{v}\) in terms of its magnitude and direction cosines.
Question
Find the vector projection of \(\mathbf{v}=3\mathbf{i}+\mathbf{j} -2\mathbf{k}\) on \(\mathbf{w}=5\mathbf{i}-\mathbf{j}+\mathbf{k}\). Decompose \( \mathbf{v}\) into two vectors \(\mathbf{v}_{1}\) and \(\mathbf{v}_{2}\), where \( \mathbf{v}_{1}\) is parallel to \(\mathbf{w}\) and \(\mathbf{v}_{2}\) is orthogonal to \(\mathbf{w}\).
Question
Find the work done in moving an object along a vector \(\mathbf{u }=3\,\mathbf{i}+2\,\mathbf{j}-5\mathbf{k}\) if the applied force is \(\mathbf{F }=2\mathbf{i}-\,\mathbf{j}-\mathbf{k}\) . Use meters for distance and newtons for force.
Question
Three forces are applied to an object in mutually orthogonal directions: \(12\) units along the \(x\)-axis, \(16\) units along the \(y\)-axis, and \(15\) units along the \(z\)-axis. What is the resultant force?
Question
Find the angle between the vectors \(\mathbf{u}=\mathbf{i}+2 \mathbf{j}+3\mathbf{k}\) and \(\mathbf{v}=2\mathbf{i}-3\mathbf{j}-\mathbf{k}\).
Question
Find the angle at the vertex \(A\) of the triangle \(ABC\) with vertices \(A=(1, 0, 1)\), \(B=(2, -1, 1)\), and \(C=(-2, 1, 0)\).
Question
Find the distance between the parallel planes \[ \begin{array}{l@{\quad}rcl} p_{1} :& x+y-z&=&1 \\ p_{2} :& -2x-2y+2z&=&2 \end{array} \]
Question
A rigid body rotates with constant angular speed of \(\omega\) radians per second about a line through the origin and parallel to \(2\mathbf{ i}+3\mathbf{j}+6\mathbf{k}\). Find the speed of an object on this body at the instant it passes through the point \((1, 2, 3)\). Assume the distance is in meters.
Question
Find the line perpendicular to the lines \[ \begin{array}{lrcl@{\qquad}rcl@{\qquad}rcl} l: & \quad x&=&1-t, \quad & y&=&t, \quad & z&=&2t-1 \\ m: & \quad x&=&t+1, & y&=&-t, & z&=&t-1 \end{array} \]
Question
Find the line containing the point \((1, 2, 3)\) in the direction of \(\mathbf{v}=2\mathbf{i}-\mathbf{j}-4\mathbf{k}\).
Question
Find the scalar \(a\) so that \(\mathbf{v}=2\mathbf{i}-\mathbf{j} -4\mathbf{k}\) and \(\mathbf{w}=a\mathbf{i}+a\mathbf{j}+3\mathbf{k}\) are orthogonal.
Question
Find an equation of the sphere with \((2, 2, -3)\) and \((-2, 6, 5)\) as endpoints of a diameter. Graph the sphere.
Question
Find the line of intersection of the two planes \(p_{1}\): \( x-y+z=3\) and \(p_{2}\): \(2x+2y-z=1.\)
Question
Find an equation of the plane with nonzero intercepts \((a, 0, 0)\) , \((0, b, 0)\), \((0, 0, c)\).
Question
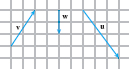
Use the vectors in the figure to graph each of the following vectors:
- \(( 2+3) \mathbf{v}\)
- \(2( \mathbf{u-w})\)
- \(( \mathbf{u+v}) +\mathbf{w}\)
- \(\mathbf{v}+( -\mathbf{v})\)
- \(\mathbf{u}-3\mathbf{v}\)
Question
Determine whether the lines \(l_{1}\) and \(l_{2}\) intersect, are parallel, or are skew. \[ \begin{array}[t]{ll} l_{1}\hbox{:}~ & ~\dfrac{x+5}{6}=\dfrac{y-2}{3}=\dfrac{z+4}{7} \\ l_{2}\hbox{:}~ & ~\dfrac{x+5}{6}=\dfrac{y+1}{3}=\dfrac{z-2}{7} \end{array} \]
Question
Find the general equation of the plane containing the point \( ( 2, -1, 4)\) and normal to the line \(\dfrac{x+3}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{3} =z\).
Question
Determine whether the lines \(l_{1}\) and \(l_{2}\) intersect, are parallel, or are skew. \[ \begin{equation*} \begin{array}{ll} l_{1}\hbox{:}&x=t+1,\qquad y=3t,\qquad z=t-1 \\ l_{2}\hbox{:}&\dfrac{x+3}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{3}=z \end{array} \end{equation*}\]
Question
Find a line normal to the plane containing the lines \[ \begin{equation*} x-2=\frac{y+1}{2}=\frac{z-1}{2}\qquad \hbox{and }\qquad x+1=\frac{y+8}{3}= \frac{z}{-3} \end{equation*}\]
at their point of intersection.
Question
Find the line containing the points \(P_{1}=( 4,0,7) \) and \(P_{2}=( 5,3,6)\).
In Problems 33–37:
- Identify each quadric surface.
- List its intercepts and traces.
 Graph the quadric surface.
Graph the quadric surface.
Question
\(\dfrac{x^{2}}{4}-\dfrac{y^{2}}{9}=1\)
Question
\(x^{2}+y^{2}-\dfrac{z^{2}}{4}=-1\)
Question
\(z=\dfrac{x^{2}}{4}-\dfrac{y^{2}}{9}\)
Question
\(z^{2}=\dfrac{x^{2}}{4}+\dfrac{y^{2}}{9}\)
Question
\(\dfrac{x^{2}}{4}+\dfrac{y^{2}}{9}+z^{2}=1\)