15.6 Assess Your Understanding
1025
Concepts and Vocabulary
Question
Multiple Choice A smooth surface has a [(a) normal plane, (b) tangent plane, (c) coordinate plane] at each point.
Question
Multiple Choice Suppose \(x=x(u,v) ,\) \(y=y(u,v) ,\) \(z=z(u,v) \) are functions defined on a region \(R\) in the \(uv\)-plane. The set of points defined by \(( x,y,z) =( x(u,v) ,y(u,v) ,z(u,v) ) \) is called a(n) [(a) real surface, (b) uniform surface, (c) parametric surface.
Question
Multiple Choice The parametric equations \(x=5\cos (u)\sin (v),\) \(y=5\sin (u)\sin (v),\) \(z=5\cos (v)\) define a [(a) plane, (b) circle, (c) sphere, (d) cylinder, (e) paraboloid].
Question
Multiple Choice The parametrization \(\mathbf{r}(u,v)=( 1-u+2v) \mathbf{i}+5u\,\mathbf{j}+\left( 2u+3v-7\right) \mathbf{k}\) parametrizes a [(a) plane, (b) sphere, (c)line, (d) cylinder, (e) hyperboloid].
Skill Building
In Problems 5–8:
- Identify the coordinate curves for \(u=0\) and \(v=0\) of each parametrization \({\bf r} (u,v) = x(u,v) {\bf i} +y(u,v){\bf j}+z(u,v){\bf k}\) .
- Find a rectangular equation for each parametric surface.
Question
\(x(u,v) =u-5v, y(u,v) =2u, z(u,v) =-u+v+1\)
Question
\(x(u,v) =u, y(u,v) =v\mathbf{,} z(u,v) =9-u^{2}-v^{2}\)
Question
\(x(u,v) =u\cos v, y(u,v) =u\sin v, z(u,v) =u; 0\leq u\leq 2,\) \(0\leq v\leq \pi \)
Question
\(x(u,v) =\cos u\sin v\,\mathbf{,} y(u,v) =\sin u\sin v, z(u,v) =\cos v; \\ 0\leq u\leq 2\pi , 0\leq v\leq \dfrac{\pi }{2}\)
In Problems 9–12, find a parametrization for each surface.
Question
The part of the plane \(z=4-x-2y\) that lies in the first octant
Question
The part of the surface \(z=e^{-x^{2}+y^{2}}\) that lies inside the cylinder \(x^{2}+y^{2}=4\)
Question
The part of the surface \(z=\sin (x^{2}y)\) that lies above the region bounded by the graphs of \(y=x+2\) and \(y=x^{2}\)
Question
The part of the surface \(y+e^{xz}=5\) that lies inside the cylinder \(x^{2}+z^{2}=1\)
In Problems 13–16:
- Find an equation of the tangent plane to each surface at the given point.
- Find an equation of the normal line to the tangent plane at the point.
Question
\(\mathbf{r}(u,v) = ( 3u+2v)\mathbf{i}+5u^{3}\mathbf{j}+v^{2}\mathbf{k}\) at \((7,5,4)\)
Question
\(\mathbf{r}(u,v) = ( 3u-v) \mathbf{i} + ( 2-u-v) \mathbf{j}+ ( 1+3v) \mathbf{k}\) at \((11,1,-5) \)
Question
\(\mathbf{r}(u,v) =u\,\mathbf{i}+u\cos v\,\mathbf{j}+u\sin v\,\mathbf{k}\) at \( \left( 5,\dfrac{5\sqrt{2}}{2},\dfrac{5\sqrt{2}}{2 }\right) \)
Question
\(\mathbf{r}(u,v) = ( 3\cos u\sin v+1) \, \mathbf{i}+ ( 2\sin u\sin v-1) \,\mathbf{j}+\cos v\,\mathbf{k}\) at \(\left( 1,0,\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right) \)
In Problems 17–22, find the surface area of each surface \(S\).
Question
\(S\) is parameterized by \(\mathbf{r}(u,v)=u\cos v \mathbf{i}+u^{3}\mathbf{j}+u\sin v\,\mathbf{k}\), \(0\leq u\leq 1,\) \(-\pi \leq v\leq \pi \).
Question
\(S\) is parameterized by \(\mathbf{r}(u,v)=(3u^{2}+v)\mathbf{i}+u^{2}\mathbf{j}+(v-u^{2})\mathbf{k,} 0\leq u\leq 2, -1\leq v\leq 1\).
Question
\(S\) is the part of the plane \(2x-y+4z=3\) that lies inside the cylinder \((x-2)^{2}+y^{2}=4\).
Question
\(S\) is the part of the paraboloid \(z=4-x^{2}-y^{2}\) that lies above the \(xy\)-plane.
Question
\(S\) is the part of the sphere \(x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}=16\) that lies above the plane \(z=2.\)
Question
\(S\) is the frustum of the cone \(z=3\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}\) that lies between \(z=3\) and \(z=6\).
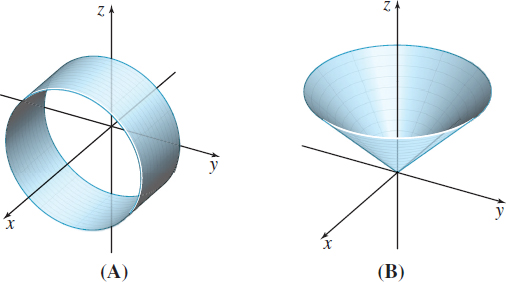
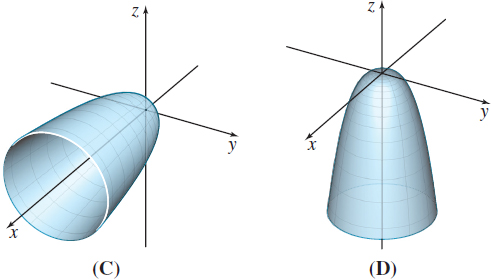
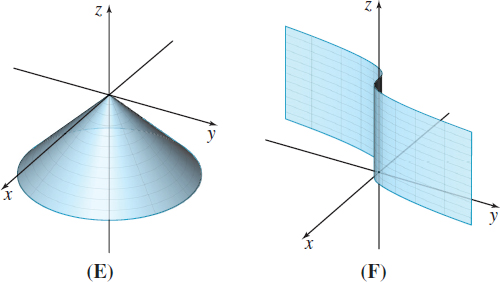
In Problems 23–28, match each parametrization with its parametric surface.
Question
\(\mathbf{r}\ (u,v) =u\cos v\,\mathbf{i}+u\sin v\, \mathbf{j} -u\,\mathbf{k,} 0\leq u\leq 4, 0\leq v \leq 2\pi \)
Question
\(\mathbf{r}\ (u,v) =u^{3}\,\mathbf{i}+u\sin v\, \mathbf{j}+u\cos v\,\mathbf{k,} 0\leq u\leq 4, 0\leq v \leq 2\pi \)
Question
\(\mathbf{r}\ (u,v) =u\sin v\,\mathbf{i}+u\cos v\, \mathbf{j}+u\,\mathbf{k,} 0\leq u\leq 4, 0\leq v \leq 2\pi \)
Question
\(\mathbf{r}\ (u,v) =u\,\mathbf{i}+4\sin v\, \mathbf{j}+4\cos v\,\mathbf{k,} 0\leq u\leq 4, 0\leq v \leq 2\pi \)
Question
\(\mathbf{r}\ (u,v) =u\cos v\,\mathbf{i}+u\sin v\, \mathbf{j}-u^{3}\,\mathbf{k,} 0\leq u\leq 4, 0\leq v \leq 2\pi \)
Question
\(\mathbf{r}\ (u,v) =v\,\mathbf{i}+v^{3}\,\mathbf{j}+u\,\mathbf{k,} 0\leq u\leq 4, -4\leq v \leq 4\)
1026
Applications and Extensions
Question
Parametrize the part of the cylinder \(x^{2}+y^{2}=16\) that lies above the \(xy\)-plane and below \(z=3\).
Question
Parametrize the sphere \(x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}=25\).
Question
Part of the paraboloid \(z=9-x^{2}-y^{2}\) lies inside the cylinder \((x-1)^{2}+y^{2}=1\).
- Parametrize the surface using rectangular coordinates.
- Parametrize the surface using cylindrical coordinates.
Question
Parametrize the lumpy sphere \(x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}=3 \sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}}+z\).
(Hint: Use spherical coordinates.)
In Problems 33 and 34, parametrize each surface:
- Using rectangular coordinates.
- Using cylindrical coordinates.
- Using spherical coordinates.
Give bounds for the parameters, if necessary.
Question
The part of the sphere \(x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}=4\) lying in the first octant
Question
The plane \(x-\sqrt{3}y=0,\) where \(x\geq 0\), \(y\geq 0\)
Question
Tangent Plane to a Torus
- Find the tangent plane to the torus parametrized by \(\mathbf{r}(u,v) =\cos u( 3+\cos v) \,\mathbf{i}+\sin u( 3+\cos v) \,\mathbf{j}+\sin v\, \mathbf{k}\) at the point \(\left(\dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}, \dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}, 1 \right) \)
- Find an equation of the normal line to the tangent plane at the same point.
Question
Surface Area Find the surface area \(S\) of the torus parametrized by \(\mathbf{r}(u,v)=(2+\cos v)\cos u\mathbf{i}+(2+\cos v)\sin u \mathbf{j}+\sin v\mathbf{k}\), \(0\leq u\leq 2\pi ,\) \(\ 0\leq v\leq 2\pi \).
Question
Surface Area Find the surface area \(S\) of the helicoid parametrized by \(\mathbf{r}(u,v)=u\cos (2v)\mathbf{i}+u\sin (2v)\mathbf{j}+v \mathbf{k}\), \(0\leq u\leq 1,\) \(0\leq v\leq 2\pi \).
Question
![]() Surface Area Find the surface area \(S\) of the Möbius strip parametrized by \(\mathbf{r}(u,v)=\left( 2\cos {u}+ v\cos\dfrac{u}{2}\right) \mathbf{i}+\left( 2\sin u+v \cos \dfrac{u}{2}\right) \mathbf{j} -v\sin \dfrac{u}{2}\,\mathbf{k}\), \(0\leq u\leq 2\pi ,\) \(-0.5 \leq v\leq 0.5\).
Surface Area Find the surface area \(S\) of the Möbius strip parametrized by \(\mathbf{r}(u,v)=\left( 2\cos {u}+ v\cos\dfrac{u}{2}\right) \mathbf{i}+\left( 2\sin u+v \cos \dfrac{u}{2}\right) \mathbf{j} -v\sin \dfrac{u}{2}\,\mathbf{k}\), \(0\leq u\leq 2\pi ,\) \(-0.5 \leq v\leq 0.5\).
Question
Ellipsoid
- Find a parametrization of the ellipsoid \(x^{2}+ \dfrac{y^{2}}{9}+\dfrac{z^{2}}{4}=1.\) (Hint: Use modified spherical coordinates.)
 Graph the parametrized surface.
Graph the parametrized surface.- Set up, but do not find, the double integral for the surface area of the parametrized ellipsoid.
Question
![]() Helicoid
Helicoid
- Graph the helicoid defined by the parametric equations \(x=u\cos (2v),\) \(y=u\sin (2v),\) \(z=v\), \(0\leq u\leq 3\) and \(0\leq v\leq 2\pi \).
- Parametrize the helicoid
- Find an equation of the tangent plane to the helicoid at the point \(\left( \dfrac{1}{3},\pi \right) \).
- Find an equation of the normal line to the tangent plane at the point \(\left( \dfrac{1}{3},\pi \right) \).
Question
![]() Dini's Surface
Dini's Surface
- Graph Dini's surface defined by the parametric equations \[ \begin{eqnarray*} &&x=6\cos u\sin v\qquad y=6\sin u\sin v,\\ && z=6\left[ \cos v+\ln \left( \tan \dfrac{v}{2}\right) \right] +u \end{eqnarray*} \] \(0.01\leq v\leq 1\) and \(0\leq u\leq 6\pi \).
- Find an equation of the tangent plane to Dini's surface at the point \(\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{\pi }{4}\right) .\)
- Find an equation of the normal line to the tangent plane at the point \(\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{\pi }{4}\right) \).
Challenge Problems
Question
Suppose \(\Delta ABC\) is a triangle with vertices \( A=(a_{1},a_{2},a_{3})\), \(B=(b_{1},b_{2},b_{3})\), and \(C=(c_{1},c_{2},c_{3})\) . Parametrize \(\Delta ABC\).
Question
Torus A torus is formed by rotating a circle about another circle.
- Parametrize the torus obtained by rotating a circle of radius \(a>0\) about a circle of radius \(b>0\).
- Find an implicit rectangular equation for the torus.
Question
Surface Area Find the surface area of \(S\), where \(S\) is the part of the cylinder \((x-1)^{2} + y^{2} = 1\) outside the sphere \(x^{2}+y^{2} + z^{2} = 4\), above the \(xy\)-plane, and below \(z=1\).
Question
An Archimedean Ratio Suppose \(C\) is a right circular cone, \(S\) is an upper hemisphere, and \(L\) is a right circular cylinder. Suppose that all three surfaces have radii \(r\) and the heights \(h\) of the cone and the cylinder are \(r\). Archimedes was able to show that the ratio of the surface areas among these surfaces is \(\sqrt{2}:2:2\). Show this by parametrizing each of these surfaces and deriving the formulas for their surface areas.
Question
Hyperboloid of One Sheet
- Use hyperbolic functions to parametrize the hyperboloid of one sheet: \(x^{2}+y^{2}-z^{2}=c,\) \(c>0\).
 Graph the parametric surface for \(c=1.\)
Graph the parametric surface for \(c=1.\)
Question
Hyperboloid of Two Sheets
- Use hyperbolic functions to parametrize the sheet where \(x>0\) in the hyperboloid of two sheets: \(\dfrac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\dfrac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}-\dfrac{z^{2}}{c^{2}}=1\).
 Graph the parametric surface for \(a=1,\) \(b=2,\) \(c=3.\)
Graph the parametric surface for \(a=1,\) \(b=2,\) \(c=3.\)
