Chapter 16
Section 16.1
1. 2; 1
2. True
3. True
4. False
5. This is a first-order differential equation of degree 1. The differential equation is linear.
7. This is a fourth-order differential equation of degree 1. The differential equation is linear.
9. This is a second-order differential equation of degree 1. The differential equation is nonlinear.
11. This is a second-order differential equation of degree 3. The differential equation is nonlinear.
13. This is a second-order differential equation of degree 1. The differential equation is linear.
15. See Student Solutions Manual.
17. See Student Solutions Manual.
19. See Student Solutions Manual.
21. See Student Solutions Manual.
23. See Student Solutions Manual.
25. See Student Solutions Manual.
27. See Student Solutions Manual.
29. See Student Solutions Manual.
31. See Student Solutions Manual.
33. See Student Solutions Manual.
35. See Student Solutions Manual.
37. See Student Solutions Manual.
39. n = −3, 2
41. The Schrödinger equation is a second-order differential equation of degree 1.
Section 16.2
1. 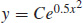
2. True
3. Trajectories
4. y = xυ(x); υ = υ(x)
5. 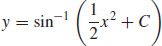
7. y = −ln(e−x + C)
9. 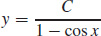
11. 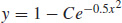
13. 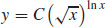 where C ≠ 0 is a constant.
where C ≠ 0 is a constant.
15. 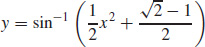
17. y = x
19. 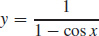
21. Function f is a homogeneous function of degree 2.
23. Function f is not a homogeneous function.
25. Function f is a homogeneous function of degree 1.
27. Function f is a homogeneous function of degree 0.
29. Function f is a homogeneous function of degree 0.
31. y = Cx − x ln |x|
33. 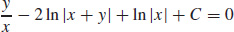
35. 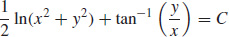
37. y = x(C + ln |x|)
39. 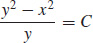
41. 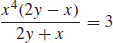
43. The orthogonal trajectories for the family xy = C is the family y2 = x2 + K. The graph of xy = 2 and y2 = x2 − 3 is shown.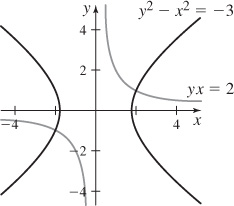
45. The orthogonal trajectories for the family y = Cx2 is the family x2 + 2y2 = K. The graph of 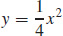 and x2 + 2y2 = 6 is shown.
and x2 + 2y2 = 6 is shown.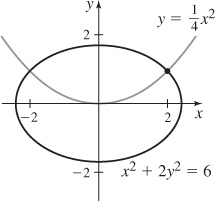
47. 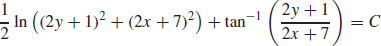
49. 2x2 + y2 = K
51. (a) u = T − C ·e−kt
(b) u = T − (T − u0)e−kt
(c) After 1 minute, the temperature of the bar is 86.533°C.
(d) The graph of the particular solution to the differential equation is shown.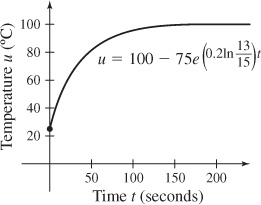
(e) The temperature of the bar will be within 0.5°C of the temperature of the boiling water after approximately 175.1 seconds, or about 3 minutes.
53. (a) y(t) = 20(1 − e(0.5 ln 0.85)t)
(b) During the eighth year of operation, the sales will be approximately 9.56 million dollars.
(c) Sales will reach $12 million dollars in approximately 11.28 years.
(d) The graph of the annual sales of the company for its first 20 years of operation is shown.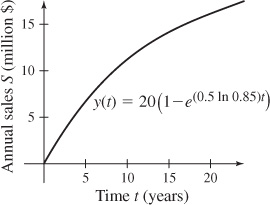
55. (a) After 25 hours of practice, the person can text approximately 64.1 words per minute.
(b) The person will need approximately 49.2 hours of practice in order to text 100 words per minute.
(c) The graph of texting speed as a function of hours of practice is shown.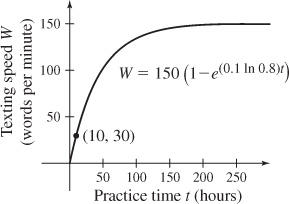
57. (a) 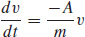
(b) 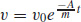
(c) A = 15 kg/s
(d) The sled will slow down to 10% of its initial speed in approximately 3.84 seconds.
(e) While slowing down to 1.0 m/s, the sled will travel 15 meters.
59. (a) 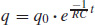
(b) The discharging capacitor will lose 99% of its initial charge in approximately 0.00345 seconds.
61. 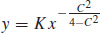
63. (a) See Student Solutions Manual.
(b) 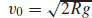
65. See Student Solutions Manual.
Section 16.3
1. True
2. False
3. False
4. Integrating factor
5. (a) 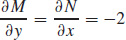
(b) 2x2 − 2xy + y2 + 5x + C = 0
7. (a) 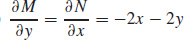
(b) 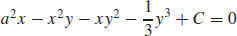
9. (a) 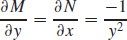
(b) 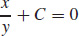
11. (a) 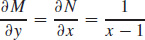
(b) y ln(x − 1) + y ln(2) + ln |y| + C = 0
13. (a) 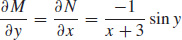
(b) 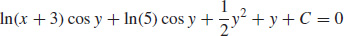
15. (a) 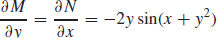
(b) sin(x + y2) + C = 0
17. (a) 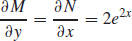
(b) 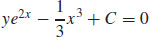
19. (a) 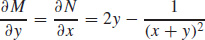
(b) ln |x + y| + xy2 + C = 0
21. (a) 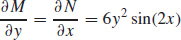
(b) −y3 cos(2x) + C = 0
23. 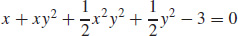
25. x2 y + cos x − y2 = 0
27. See Student Solutions Manual.
29. (a) 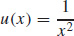
(b) 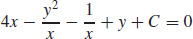
(c) See Student Solutions Manual.
31. (a) 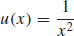
(b) 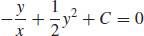
(c) See Student Solutions Manual.
33. (a) 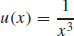
(b) 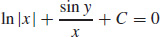
(c) See Student Solutions Manual.
Section 16.4
1. True
2. True
3. False
4. False
5. 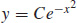
7. 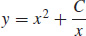
9. 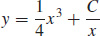
11. 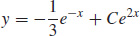
13. 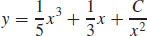
15. 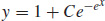
17. y = x cos x + C cos x
19. 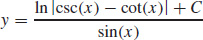
21. 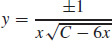
23. 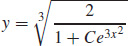
25. 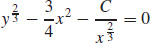
27. y = x(ex + C)
29. 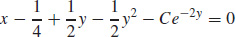
31. 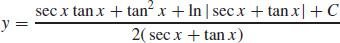
33. 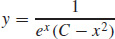
35. 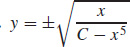
37. x6 + 3x4 y2 + C = 0
39. 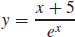
41. 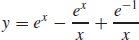
43. (a) 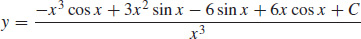
(b) 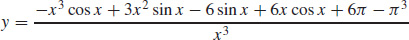
(c) The graph of the particular solution over the interval [0, 10] is shown below.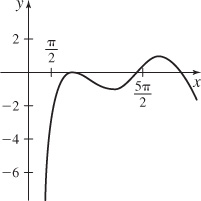
45. 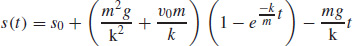
47. (a) The skydiver will be falling at a velocity of −44.89 ft/s.
(b) The skydiver will land on the ground in approximately 241.250 seconds.
(c) The skydiver will land with a velocity of −40 ft/s.
49. After 5 minutes, there are approximately 98.9 kg of salt in the tank. After a long time, there will be 300 kg of salt in the tank.
51. (a) The solution of the differential equation is 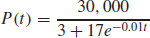
(b) The limiting size of the population is 10,000.
(c) The population will be equal to 5000 (i.e. one-half of the limiting value) in 173.46 months.
(d) The graph of the predicted population for 0 ≤ t ≤ 600 months is shown.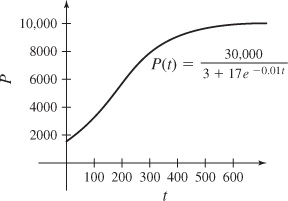
53. 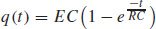
55. (a) N(t) = Nmax exp(−e−p(t+C))
(b) N(t) = 400 exp(−e−0.0526(t−20.847))
(c) After 43 years, there will be approximately 293 fish.
(d) See Student Solutions Manual.
(e) The graph of N = N(t) is shown.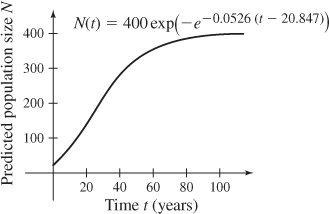
57. See Student Solutions Manual.
59. After 1 hour, the percentage of carbon dioxide is approximately 0.0752%. After 2 hours, the percentage of carbon dioxide is approximately 0.0448%.
61. 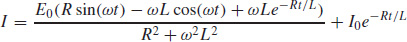
Section 16.5
1. 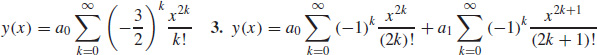
5. 
7. 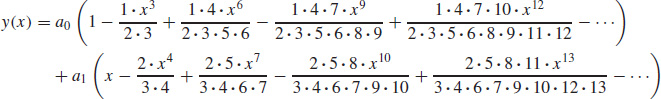
9. 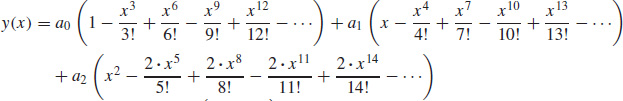
11. 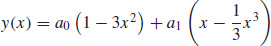
13. (a) 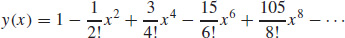
(b) 
15. (a) 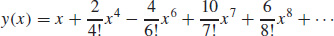
(b) 
17. (a) 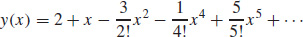
(b) 
19. (a) 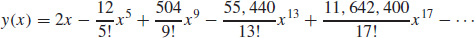
(b) 
21. (a) 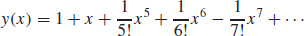
(b) 
23. (a) 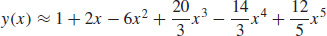
(b) y(x) = e−2x(1 + 4x)
(d) See Student Solutions Manual.
(e) 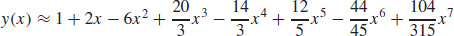 (c and f) The graphs are shown. See Student Solutions Manual for explanation.
(c and f) The graphs are shown. See Student Solutions Manual for explanation.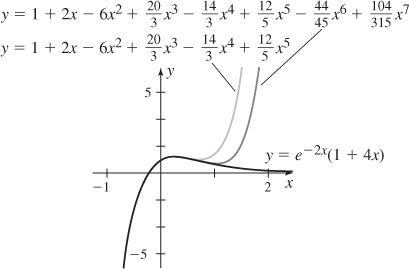
25. (a) See Student Solutions Manual.
(b) See Student Solutions Manual.
(c) The lower bound is 3.506 × 108 years.
Review Exercises
1. This is a first-order differential equation of degree 1. The differential equation is linear.
3. This is a third-order differential equation of degree 1. The differential equation is linear.
5. See Student Solutions Manual.
7. See Student Solutions Manual.
9. Function f is a homogeneous function of degree 3.
11. Function f is a homogeneous function of degree 1.
13. (a) The differential equation is separable.
(b) 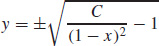
15. (a) The differential equation is first-order linear and exact.
(b) 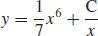
17. (a) The differential equation is exact.
(b) x2 y3 + y2 sin x − x2 + C = 0
19. (a) The differential equation is separable and exact.
(b) 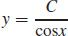
21. (a) The differential equation is homogeneous of degree 1.
(b) y = x cos−1(Cx)
23. (a) The differential equation is Bernoulli.
(b) 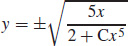
25. 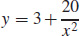
27. 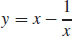
29. 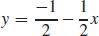
31. 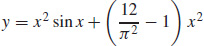
33. 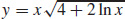
35. 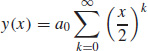
37. (a) 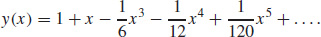
(b) 
39. y = M − Ce−kt
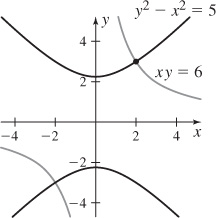
41. The orthogonal trajectories for the family xy = c is the family y2 − x2 = K. The graph of xy = 6 and y2 – x2 = 5 is shown.