7.8 Assess Your Understanding
530
Concepts and Vocabulary
Question
Multiple Choice If a function \(f\) is continuous on the interval \([a,\,\infty) \), then \( \int_{a}^{\infty }f(x)\,dx\) is called [(a) a definite,(b) an infinite, (c) an improper, (d) a proper ] integral.
Question
Multiple Choice If the \(\lim\limits_{b \rightarrow \infty }\int_{a}^{b} f(x)\,dx\) does not exist, the improper integral \(\int_{a}^{\infty }f(x)\,dx\) [ (a) converges, (b) diverges, (c) equals \(ab].\)
Question
True or False If a function \(f\) is continuous for all \(x\), then the improper integral \(\int_{-\infty }^{\,\infty }f(x)\,dx\) always converges.
Question
True or False If a function \(f\) is continuous and nonnegative on the interval \([a,\,\infty) \), and \( \int_{a}^{\infty } f( x) \,dx\) converges, then \( \int_{a}^{\infty }f(x)\,dx\) represents the area under the graph of \(y=f(x)\) for \(x \ge a.\)
Question
True or False If a function \(f\) is continuous for all \(x,\) then the improper integral \(\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }f(x)\,dx=\lim\limits_{a\,\rightarrow \,\infty }\int_{-a}^{a}f(x)\,dx\).
Question
To determine whether the improper integral \( \int_{a}^{b} f( x) \,dx\) converges or diverges, where \(f\) is continuous on \([a,\,b),\) but is not defined at \(b\), requires finding what limit?
Skill Building
In Problems 7–14, determine whether each integral is improper. For those that are improper, state the reason.
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }x^{2}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{5}x^{3}dx\)
Question
\(\int_{2}^{3}\dfrac{dx}{x-1}\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{2}\dfrac{dx}{x-1}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{1}\dfrac{1}{x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{-1}^{1}\dfrac{x\, dx}{x^{2}+1}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{1}\dfrac{x}{x^{2}-1}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }e^{-2x}\,dx\)
In Problems 15–24, determine whether each improper integral converges or diverges. If it converges, find its value.
Question
\(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{x^{3}}\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{-10}\dfrac{dx}{x^{2}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }e^{2x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }e^{-x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{-1}\dfrac{4}{x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{4}{x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{3}^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{(x-1)^{4}} \)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{0}\dfrac{dx}{(x-1) ^{4}}\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{x^{2}+4}\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{x^{2}+1}\)
In Problems 25–32, determine whether each improper integral converges or diverges. If it converges, find its value.
Question
\(\int_{0}^{1}\dfrac{dx}{x^{2}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{1}\dfrac{dx}{x^{3}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{1}\dfrac{dx}{x}\)
Question
\(\int_{4}^{6}\dfrac{dx}{x-4}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{4}\dfrac{dx}{\sqrt{4-x}}\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{5}\dfrac{x~dx}{\sqrt{5-x}}\)
Question
\(\int_{-1}^{1}\dfrac{dx}{\sqrt[3]{x}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{3}\dfrac{dx}{(x-2)^{2}}\)
In Problems 33–62, determine whether each improper integral converges or diverges. If it converges, find its value.
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }\cos x\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }\sin (\pi x) \,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{0}e^{x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{0}e^{-x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\pi /2}\dfrac{x\,dx}{\sin x^{2}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{1}\dfrac{\ln x\,dx}{x}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{1}\dfrac{dx}{1-x^{2}}\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{2}\dfrac{dx}{\sqrt{x^{2}-1}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{1}\dfrac{x\,dx}{(1-x^{2})^{2}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{2}\dfrac{dx}{(x-1)^{2}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\pi /4}\tan (2x) \,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\pi /2}\csc x\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }\dfrac{x\,dx}{\sqrt{x+1}}\)
Question
\(\int_{2}^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{x\sqrt{x^{2}-1}}\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{x^{2}+4x+5}\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{2}\dfrac{dx}{\sqrt{4-x}}\)
Question
\(\int_{-\infty }^{1}\dfrac{x\,dx}{\sqrt{2-x}}\)
Question
\(\int_{2}^{4}\dfrac{2x\,dx}{\sqrt[3]{x^{2}-4}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\pi }\dfrac{1}{1-\cos x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{-1}^{1}\dfrac{1}{x^{3}}\,dx \)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{2}\dfrac{dx}{x-1}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{2}\dfrac{dx}{(x-1)^{1/3}}\)
Question
\(\int_{-1}^{1}\dfrac{dx}{x^{5/3}}\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{2}\dfrac{dx}{(2-x)^{3/4}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{4}\dfrac{dx}{\sqrt{8x-x^{2}}}\)
Question
\(\int_{a}^{3a}\dfrac{2x\,dx}{(x^{2}-a^{2})^{3/2}}\), \(a \gt 0\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{3}\dfrac{x\,dx}{(9-x^{2})^{3/2}}\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }xe^{-x^{2}}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }e^{-x}\sin x\,dx\)
In Problems 63–70:
- Use the Comparison Test for Improper Integrals to determine whether each improper integral converges or diverges. (Hint: Use the fact that \(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{x^{p}}\) converges if \(p \gt1\) and diverges if \(p \le 1.)\)
 If the integral converges, use a CAS to find its value.
If the integral converges, use a CAS to find its value.
Question
\(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x^{2}-1}}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{2}^{\infty }\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x^{2}-4}}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{1+e^{-x}}{x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{3e^{-x}}{x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{\sin ^{2}x}{x^{2}}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{\cos ^{2}x}{x^{2}}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{(x+1) \sqrt{x}}\)
Question
\(\int_{1}^{\infty }\dfrac{dx}{x\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}\)
531
Applications and Extensions
Question
Area Between Graphs Find the area, if it is defined, of the region enclosed by the graphs of \(y=\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) and \(y=\dfrac{1}{x+2}\) on the interval \([0,\infty )\). See the figure.
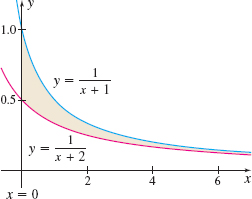
Question
Area Between Graphs Find the area, if it is defined, under the graph of \(y=\dfrac{1}{1+x^{2}}\) to the right of \(x=0\). See the figure below.
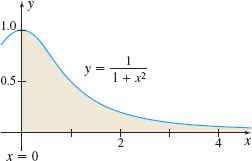
Question
Volume of a Solid of Revolution Find the volume, if it is defined, of the solid of revolution generated by revolving the region bounded by the graph of \(y=e^{-x}\) and the \(x\)-axis to the right of \(x=0\) about the \(x\)-axis. See the figure below.
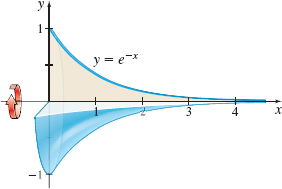
Question
Volume of a Solid of Revolution Find the volume, if it is defined, of the solid of revolution generated by revolving the region bounded by the graph of \(y=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\) and the \(x\)-axis to the right of \(x=1\) about the \(x\)-axis. See the figure below.
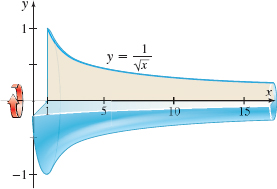
Question
Area Between Graphs Find the area, if it is defined, between the graph of \(y=\dfrac{8a^{3}}{x^{2}+4a^{2}}\), \(a>0\), and its horizontal asymptote.
Question
Drug Reaction The rate of reaction \(r\) to a given dose of a drug at time \(t\) hours after administration is given by \(r(t)=t\,e^{-t^{2}}\) (measured in appropriate units).
- Why is it reasonable to define the total reaction as the area under the graph of \(y=r(t)\) on \([0,\infty) \)?
- Find the total reaction to the given dose of the drug.
Question
Present Value of Money The present value \(PV\) of a capital asset that provides a perpetual stream of revenue that flows continuously at a rate of \(R(t)\) dollars per year is given by \[ PV= \int_{0}^{\infty }R(t)e^{-rt}\,dt \]
where \(r,\) expressed as a decimal, is the annual rate of interest compounded continuously.
- Find the present value of an asset if it provides a constant return of \(\$100\) per year and \(r=8\%\).
- Find the present value of an asset if it provides a return of \(R(t)=1000+80t\) dollars per year and \(r=7\%\).
Question
Electrical Engineering In a problem in electrical theory, the integral \(\int_{0}^{\infty }Ri^{2}\,dt\) occurs, where the current \( i=Ie^{-Rt/L}\), \(t\) is time, and \(R\), \(I\), and \(L\) are positive constants. Find the integral.
Question
Magnetic Potential The magnetic potential \(u\) at a point on the axis of a circular coil is given by \[ u=\dfrac{2\pi NIr}{10}\! \int_{x}^{\infty }\dfrac{dy}{(r^{2}+y^{2})^{3/2}} \]
where \(N\), \(I\), \(r\), and \(x\) are constants. Find the integral.
Question
Electrical Engineering The field intensity \(F\) around a long (“infinite”) straight wire carrying electric current is given by the integral \[ F=\dfrac{rIm}{10}\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }\dfrac{dy}{(r^{2}+y^{2})^{3/2}} \]
where \(r,\) \(I\), and \(m\) are constants. Find the integral.
Question
Work The force \(F\) of gravitational attraction between two point masses \(m\) and \(M\) that are \(r\) units apart is \(F=\dfrac{GmM}{r^{2}}\) , where \(G\) is the universal gravitational constant. Find the work done in moving the mass \(m\) along a straight-line path from \(r=1\) unit to \(r=\infty \).
Question
For what numbers \(a\) does \(\int_{0}^{1}x^{a}\,dx\) converge?
In Problems 83–86, use integration by parts and perhaps L'Hôpital's Rule to find each improper integral.
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }xe^{-x}\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{1}x\ln x\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty}e^{-x}\cos x\,dx\)
Question
\(\int_{0}^{\infty }\tan^{-1}x\,dx \)
Question
Show that \(\int_{0}^{\infty }\sin x\,dx\) and \(\int_{-\infty }^{0}\sin x\,dx\) each diverge, yet \(\lim\limits_{t\,\rightarrow \,\infty }\int_{-t}^{t}\sin x\, dx=0\).
532
Question
Find a function \(f\) for which \(\int_{0}^{\infty }f(x)\,dx\) and \(\int_{-\infty }^{0}f(x)\,dx\) each diverge, yet \(\lim\limits_{t\,\rightarrow \,\infty }\int_{-t}^{t}f(x)\,dx=1\).
Question
Use the Comparison Test for Improper Integrals to show that \(\int_{0}^{\infty }\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2+\sin x}}\,dx\) diverges.
Question
Use the Comparison Test for Improper Integrals to show that \( \int_{2}^{\infty }\dfrac{\ln x}{\sqrt{x^{2}-1}}\,dx\) diverges.
Question
If \(n\) is a positive integer, show that:
- \(\int_{0}^{\infty }x^{n}\,e^{-x}\,dx=n\int_{0}^{\infty }x^{n-1}\,e^{-x}\,dx\)
- \(\int_{0}^{\infty }x^{n}\,e^{-x}\,dx=n!\)
Question
Show that \(\int_{e}^{\infty }\dfrac{\,dx}{x ( \ln x) ^{p}}\) converges if \(p \gt 1\) and diverges if \(p \le 1\).
Question
Show that \(\int_{a}^{b}\dfrac{dx}{(x-a) ^{p}}\) converges if \(0 \lt p \lt 1\) and diverges if \(p \ge 1.\)
Question
Show that \(\int_{a}^{b}\dfrac{dx}{(b-x)^{p}}\) converges if \(0 \lt p \lt 1\) and diverges if \(p \ge 1.\)
Question
Refer to Problems 93 and 94. Discuss the convergence or divergence of the integrals if \(p \le 0.\) Support your explanation with an example.
Question
Comparison Test for Improper Integrals Show that if two functions \(f\) and \(g\) are nonnegative and continuous on the interval \([ a,\infty ) \), and if \(f( x) \geq g( x) \) for all numbers \(x > c,\) where \(c \geq a,\) then
- If \(\int_{a}^{\infty }f( x)\, dx\) converges, then \(\int_{a}^{\infty }g( x)\,dx\) also converges.
- If \(\int_{a}^{\infty }g( x)\, dx\) diverges, then \(\int_{a}^{\infty }f( x)\, dx\) also diverges.
Laplace transforms are useful in solving a special class of differential equations. The Laplace transform L {f( x)} of a function \(f\) is defined as \[ L \{f( x)\} =\int_{0}^{\infty }e^{-sx} f(x) \,dx, x \ge 0, s \hbox{ a complex number } \]
In Problems 97–102, find the Laplace transform of each function.
Question
\(f(x) =x\)
Question
\(f(x) =\cos x\)
Question
\(f(x) =\sin x\)
Question
\(f(x) =e^{x} \)
Question
\(f(x) =e^{ax}\)
Question
\(f(x) =1\)
Challenge Problems
Question
Find the arc length of \(y=\sqrt{x-x^{2}}-\sin ^{-1}\sqrt{x}\).
Question
Find \(\int_{-\infty }^{a}e^{(x-e^{x})}\,dx.\)
Question
Find \(\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }e^{(x-e^{x})}\,dx.\)
Question
- Show that the area of the region in the first quadrant bounded by the graph of \(y=e^{-x}\) and the \(x\)-axis is divided into two equal parts by the line \(x=\ln 2\).
- If the two regions with equal areas described in (a) are rotated about the \(x\)-axis, are the resulting volumes equal? If they are unequal, which one is larger and by how much?
In Problems 107 and 108, use the following definition: A probability density function is a function \(f,\) whose domain is the set of all real numbers, with the following properties:
- \(f(x) \ge 0\) for all \(x\)
- \(\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }f(x)\,dx=1\)
Question
Uniform Density Function Show that the function \(f\) below is a probability density function. \[ f(x)=\left\{ \begin{array}{c@{\qquad}l@{\quad}rl} 0 & \hbox{if} & x& \lt a \\ \dfrac{1}{b-a} & \hbox{if} & a & \le x \le b, a \lt b \\ 0 & \hbox{if} & x& \gt b \end{array} \right. \]
Question
Exponential Density Function Show that the function \(f\) is a probability density function for \(a>0\). \[ f(x)=\left\{ \begin{array}{l@{\qquad}l@{\quad}ll} \dfrac{1}{a}e^{-x/a} & \hbox{if}&x & \ge 0 \\ 0&\hbox{if}&x & \lt 0 \end{array} \right. \]
In Problems 109 and 110, use the following definition: The expected value or mean \(\mu\) associated with a probability density function \(f\) is defined by \[ \mu =\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }x f(x)\,dx \]
The expected value can be thought of as a weighted average of its various probabilities.
Question
Find the expected value \(\mu \) of the uniform density function \(f\) given in Problem 107.
Question
Find the expected value \(\mu \) of the exponential probability density function \(f\) defined in Problem 108.
In Problems 111 and 112, use the following definitions: The variance \(\sigma ^{2}\) of a probability density function \(f\) is defined as \[ \sigma ^{2}=\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }(x-\mu )^{2} f(x)\,dx \] The variance is the average of the squared deviation from the mean. The standard deviation \(\sigma \) of a probability density function \(f\) is the square root of its variance \(\sigma ^{2}\).
Question
Find the variance \(\sigma ^{2}\) and standard deviation \( \sigma \) of the uniform density function defined in Problem 107.
Question
Find the variance \(\sigma ^{2}\) and standard deviation \( \sigma \) of the exponential density function defined in Problem 108.
