The Election of 1856
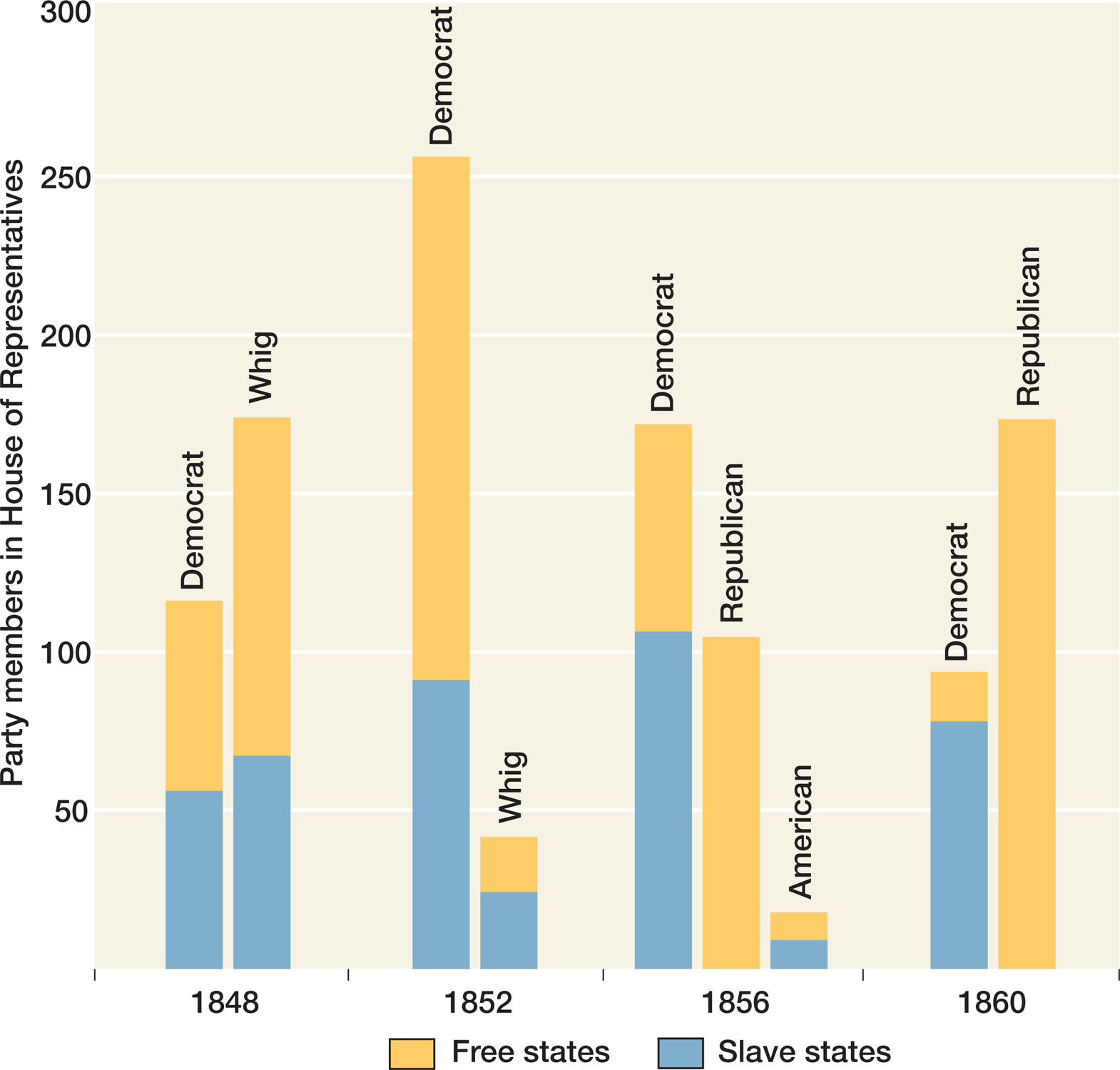
The election of 1856 revealed that the Republicans had become the Democrats’ main challenger, and slavery in the territories, not immigration, was the election’s principal issue. When the Know-
The Republican platform focused mostly on “making every territory free.” When they labeled slavery a “relic of barbarism,” they signaled that they had written off the South. For president, they nominated the soldier and California adventurer John C. Frémont. Frémont lacked political credentials, but his wife, Jessie Frémont, the daughter of Senator Thomas Hart Benton of Missouri, knew the political map well. Though careful to maintain a proper public image, the vivacious young mother and antislavery zealot helped attract voters and draw women into politics.

The Democrats, successful in 1852 in bridging sectional differences by nominating a northern man with southern principles, chose another “doughface,” James Buchanan of Pennsylvania. They portrayed the Republicans as extremists (“Black Republican Abolitionists”) whose support for the Wilmot Proviso risked pushing the South out of the Union.
The Democratic strategy carried the day for Buchanan, who won 174 electoral votes against Frémont’s 114 and Fillmore’s 8 (see Map 14.4). But the big news was that the Republicans, campaigning under the banner “Free soil, Free men, Fremont,” carried all but five of the states north of the Mason-
REVIEW Why did the Whig Party disintegrate in the 1850s?