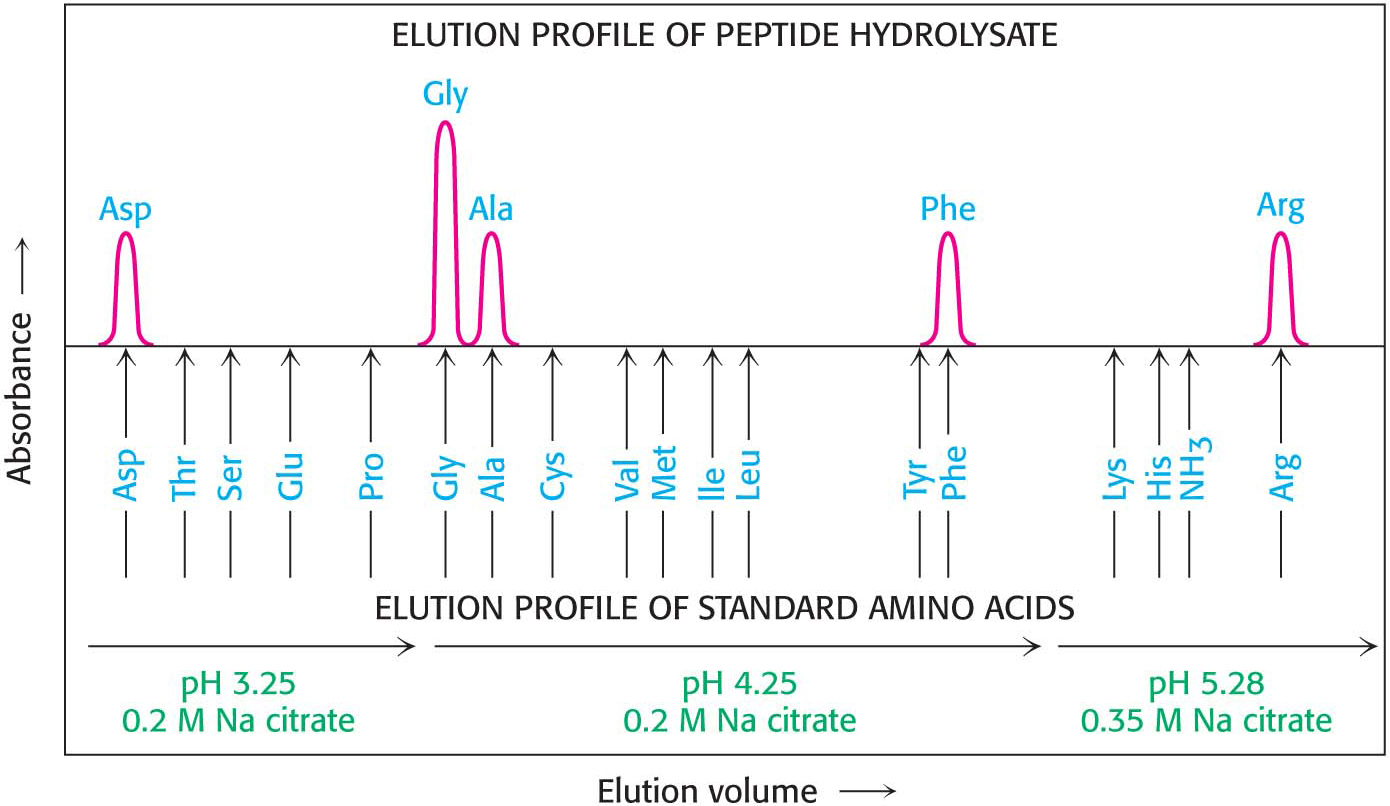
Figure 5.25 Determination of amino acid composition. Different amino acids in a peptide hydrolysate can be separated by ion-