Chapter 29
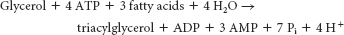
Glycerol 3-
phosphate is formed primarily by the reduction of dihydroxyacetone phosphate, a glycolytic intermediate, and to a lesser extent by the phosphorylation of glycerol. Three. One molecule of ATP to form phosphorylethanolamine and two molecules of ATP to regenerate CTP from CMP.
All are synthesized from ceramide. In sphingomyelin, the terminal hydroxyl group of ceramide is modified with phosphorylcholine. In a cerebroside, the hydroxyl group has a glucose or galactose attached. In a ganglioside, oligosaccharide chains are attached to the hydroxyl group.
Complete the interactive matching exercise to see answers.
(a) CDP-
diacylglycerol; (b) CDP- ethanolamine; (c) acyl CoA; (d) CDP- choline; (e) UDP- glucose or UDP- galactose; (f) geranyl pyrophosphate No need to make a new plan, Stan. Just listen to me.
(1) Activate the diacylglycerol as CDP-
DAG. (2) Activate the alcohol as CDP- alcohol. Phosphatidic acid phosphatase (PAP). PAP controls the extent to which triacylglycerols are synthesized relative to phospholipids and regulates the type of phospholipid synthesized.
Such mutations are seen in mice. The amount of adipose tissue would decrease severely because diacylglycerol could not be formed. Normally, diacylglycerol is acylated to form triacylglycerols. If there were deficient phosphatidic acid phosphatase activity, no triacylglycerols would form.
Excess PAP activity would increase the amount of diacylglycerol. After the phospholipid needs requiring diacylglycerol had been met, the excess diacylglycerol would be converted into triacylglycerol and obesity would result.
C31
The three stages are (1) the synthesis of activated isoprene units (isopentyl pyrophosphate), (2) the condensation of six of the activated isoprene units to form squalene, and (3) cyclization of the squalene to form cholesterol.
(a and b) None, because the label is lost as CO2
The hallmark of this genetic disease is elevated cholesterol levels in the blood of even young children. The excess cholesterol is taken up by macrophages, which eventually results in the formation of plaques and heart disease. There are many mutations that cause the disease, but all result in malfunctioning of the LDL receptor.
The amount of reductase and its activity control the regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis. Transcriptional control is mediated by SREBP. Translation of the reductase mRNA also is controlled. The reductase itself may undergo regulated proteolysis. Finally, the activity of the reductase is inhibited by phosphorylation by AMP-
dependent kinase when ATP levels are low. Statins are competitive inhibitors of HMG-
CoA reductase. They are used as drugs to inhibit cholesterol synthesis in patients who have high levels of cholesterol. No. Cholesterol is essential for membrane function and as a precursor for bile salts and steroid hormones. A complete lack of cholesterol would be lethal.
Progestagens, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens
Recall that dihydrotestosterone is crucial for the development of male characteristics in the embryo. If a pregnant woman were to be exposed to Propecia, the 5α-reductase of the male embryo would be inhibited, which could result in severe developmental abnormalities.
“None of your business” and “I don’t talk biochemistry until after breakfast” are appropriate but rude and uninformative answers. A better answer might be: “Although it is true that cholesterol is a precursor to steroid hormones, the rest of the statement is oversimplified. Cholesterol is a component of membranes, and membranes literally define cells, and cells make up tissues. But to say that cholesterol ‘makes’ cells and tissues is wrong.”
The core structure of a steroid is four fused rings: three cyclohexane rings and one cyclopentane ring. In vitamin D, the second cyclohexane ring from the left, called the B ring, is split by ultraviolet light.
The LDL contains apolipoprotein B-
100, which binds to an LDL receptor on the cell surface in a region known as a coated pit. On binding, the complex is internalized by endocytosis to form an internal vesicle. The vesicle is separated into two components. One, with the receptor, is transported back to the cell surface and fuses with the membrane, allowing continued use of the receptor. The other vesicle fuses with lysosomes inside the cell. The cholesteryl esters are hydrolyzed, and free cholesterol is made available for cellular use. The LDL protein is hydrolyzed to free amino acids. This knowledge would enable clinicians to characterize the likelihood of a patient having an adverse drug reaction or being susceptible to chemical-
induced illnesses. It would also permit a personalized and especially effective drug- treatment regime for diseases such as cancer. The honeybees may be especially sensitive to environmental toxins, including pesticides, because these chemicals are not readily detoxified, owing to the minimal P450 system.
The attachment of isoprenoid side chains confers hydrophobic character. Proteins having such a modification are targeted to membranes.
Note that a cytidine nucleotide plays the same role in the synthesis of these phosphoglycerides as a uridine nucleotide does in the formation of glycogen. In all of these biosyntheses, an activated intermediate (UDP-
glucose, CDP- diacylglycerol, or CDP- alcohol) is formed from a phosphorylated substrate (glucose 1- phosphate, phosphatidate, or a phosphorylalcohol) and a nucleoside triphosphate (UTP or CTP). The activated intermediate then reacts with a hydroxyl group (the terminus of glycogen, the side chain of serine, or a diacylglycerol). Citrate is transported out of mitochondria in times of plenty. ATP-
citrate lyase yields acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate. The acetyl CoA can then be used to synthesize cholesterol. 3-
Hydroxy- 3- methylglutaryl CoA is also a precursor for ketone- body synthesis. If fuel is needed elsewhere in the body, as might be the case during a fast, 3- hydroxy- 3- methylglutaryl CoA is converted into the ketone acetoacetate. If energy needs are met, the liver will synthesize cholesterol. Mutations could occur in the gene encoding sodium channel that would prevent the action of DDT. Alternatively, P450 enzyme synthesis could be increased to accelerate metabolism of the insecticide to inactive metabolites. In fact, both types of responses to insecticides have been observed.
There is no effect.
Because actin is not controlled by cholesterol, the amount isolated should be the same in both experimental groups. A difference would suggest a problem in the RNA isolation.
The presence of cholesterol in the diet dramatically reduces the amount of HMG-
CoA reductase protein. A common means of regulating the amount of a protein present is to regulate transcription, which is clearly not the case here.
Translation of mRNA could be inhibited. The protein could be rapidly degraded.
The categories of mutations are (1) no receptor is synthesized; (2) receptors are synthesized but do not reach the plasma membrane, because they lack the signals for intracellular transport or do not fold properly; (3) receptors reach the cell surface, but they fail to bind LDL normally because of a defect in the LDL-
binding domain; (4) receptors reach the cell surface and bind LDL, but they fail to cluster in coated pits because of a defect in their carboxyl- terminal regions. Benign prostatic hypertrophy can be treated by inhibiting 5α-reductase. Finasteride, a steroid analog of dihydrotestosterone, competitively inhibits the reductase but does not act on androgen receptors. Patients taking finasteride have a markedly lower plasma level of dihydrotestosterone and a nearly normal level of testosterone. The prostate gland becomes smaller, but testosterone-
dependent processes such as fertility, libido, and muscle strength appear to be unaffected. In cartoons, plants can run from their predators. In real life, it is not the case, and the predators might eat the plants. Consequently, as a means of self-
defense, it behooves plants to produce a wide array of toxins so that they can ward off those who might eat them. Many hydrophobic odorants are deactivated by hydroxylation. Molecular oxygen is activated by a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase. NADPH serves as the reductant. One oxygen atom of O2 goes into the odorant substrate, whereas the other is reduced to water.