8.1 Arc Length and Surface Area
We have seen that integrals are used to compute “total amounts” (such as distance traveled, total mass, total cost, etc.). Another such quantity is the length of a curve (also called arc length). We shall derive a formula for arc length using our standard procedure: approximation followed by passage to a limit.
Consider the graph of \(y=f(x)\) over an interval \([a,b]\). Choose a partition \(P\) of \([a,b]\) into \(N\) subintervals with endpoints \[ P: a = x_0 < x_1 < \cdots < x_N = b \]
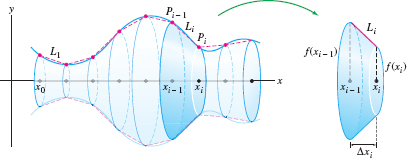
and let \(P_i = (x_i,f(x_i))\) be the point on the graph above \(x_i\). Now join these points by line segments \(L_i = \overline{P_{i-1}P_i}\). The resulting curve \(L\) is called a polygonal approximation (Figure 8.1). The length of \(L\), which we denote \(|L|\), is the sum of the lengths \(|L_i|\) of the segments: \[ |L| = |L_1| + |L_2| + \cdots + |L_N| = \sum_{i=1}^N\,|L_i| \]
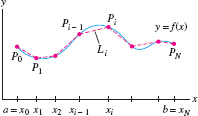
As may be expected, the polygonal approximations \(L\) approximate the curve more and more closely as the width of the partition decreases (Figure 8.2). Based on this idea, we define the arc length \(s\) of the graph to be the limit of the lengths \(|L|\) as the width \(\|P\|\) of the partition tends to zero: \[arc~length\,\, s = \lim_{\|P\|\to 0}\,\,\sum_{i=1}^N\,|L_i|\]
The letter \(s\) is commonly used to denote arc length.
468
To compute the arc length \(s\), we must express the limit of the polygonal approximations as an integral. Figure 8.3 shows that the segment \(L_i\) is the hypotenuse of a right triangle of base \(\Delta x_i = x_i-x_{i-1}\) and height \(|f(x_i)-f(x_{i-1})|\). By the Pythagorean Theorem, \[ |L_i| = \sqrt{\Delta x_i^2 + (f(x_i)-f(x_{i-1}))^2} \]
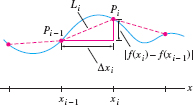
We shall assume that \(f'(x)\) exists and is continuous. Then, by the Mean Value Theorem, there is a value \(c_i\) in \([x_{i-1},x_i]\) such that \[ f(x_i)-f(x_{i-1}) = f'(c_i)(x_i - x_{i-1}) = f'(c_i)\Delta x_i \]
and therefore, \[ |L_i| = \sqrt{(\Delta x_i)^2 + (f'(c_i)\Delta x_i)^2} = \sqrt{(\Delta x_i)^2(1 + [f'(c_i)]^2)} = \sqrt{1 + [f'(c_i)]^2}\, \Delta x_i \]
We find that the length \(|L|\) is a Riemann sum for the function \(\sqrt{1 + [f'(x)]^2}\): \[ |L| = |L_1| + |L_2| + \cdots + |L_N| = \sum_{i=1}^N\,\,\sqrt{1 + [f'(c_i)]^2}\, \Delta x_i \]
Reminder
A Riemann sum for the integral \({\int_a^b g(x)\,dx}\) is a sum \[ \sum_{i=1}^Ng(c_i)\Delta x_i \] where \(x_0, x_1,\ldots,x_N\) is a partition of \([a,b]\), \(\Delta x_i = x_i-x_{i-1}\), and \(c_i\) is any number in \([x_{i-1},x_i]\).
This function is continuous, and hence integrable, so the Riemann sums approach \[{\int_a^b \sqrt{1+ [f'(x)]^2}\,dx}\]
as the norm (maximum of the widths \(\Delta x_i\)) of the partition tends to zero.
THEOREM 1 Formula for Arc Length
Assume that \(f'(x)\) exists and is continuous on \([a,b]\). Then the arc length \(s\) of \(y = f(x)\) over \([a,b]\) is equal to \[ \boxed{\bbox[#FAF8ED,5pt]{s = \int_a^b \sqrt{1 + [f'(x)]^2} \, dx}}\tag{1} \]
In Exercises 20-22, we verify that Eq. (1) correctly gives the lengths of line segments and circles.
EXAMPLE 1
Find the arc length \(s\) of the graph of \(f(x) = \tfrac1{12}x^3+x^{-1}\) over \([1,3]\) (Figure 8.4).
Solution First, let's calculate \(1+f'(x)^2\). Since \(f'(x) = \frac14\, x^2-x^{-2}\), \[ \begin{align*} 1+f'(x)^2 & = 1+\left(\frac14\, x^2-x^{-2}\right)^2=1+\left(\frac1{16}\, x^4-\frac12+x^{-4}\right) \\ & =\frac1{16}\, x^4+\frac12+x^{-4} = \left(\frac14\, x^2+x^{-2}\right)^2 \end{align*} \]
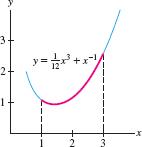
Fortunately, \( 1+f'(x)^2\) is a square, so we can easily compute the arc length: \[ \begin{align*} s = \int_1^3\sqrt{1+f'(x)^2}\,dx &= \int_1^3 \left(\frac14\, x^2+x^{-2}\right) dx= \left(\frac1{12}x^3-x^{-1}\right)\bigg|_1^3\\ &= \left(\frac94-\frac13\right)-\left(\frac1{12}-1\right) = \frac{17}6 \end{align*} \]
469
EXAMPLE 2 Arc Length as a Function of the Upper Limit
Find the arc length \(s(a)\) of \(y = \cosh x\) over \([0,a]\) (Figure 8.5). Then find the arc length over \([0,2]\).
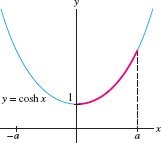
Solution Recall that \(y'=(\cosh x)' = \sinh x\). By Eq. (2) in the margin, \[1+(y')^2 = 1+\sinh^2x =\cosh^2x\]
Because \(\cosh x > 0\), we have \(\sqrt{1 + (y')^2} =\cosh x\) and \[s(a) = \int_0^a \sqrt{1 + (y')^2}\,dx = \int_0^a \cosh x\, dx = \sinh x\bigg|_0^a = \sinh a\]
The arc length over \([0,2]\) is \(s(2) = \sinh 2 \approx 3.63\).
Reminder
\[\cosh x = \frac{1}{2}(e^x + e^{-x})\] \[\sinh x = \frac{1}{2}(e^x - e^{-x})\] \[\cosh^2x - \sinh^2x=1\tag{2}\]
In Examples 1 and 2, the quantity \(1+f'(x)^2\) turned out to be a perfect square, and we were able to compute \(s\) exactly. Usually, \(\sqrt{1+f'(x)^2}\) does not have an elementary antiderivative and there is no explicit formula for the arc length. However, we can always approximate arc length using numerical integration.
EXAMPLE 3 No Exact Formula for Arc Length
![]() Approximate the length \(s\) of \(y = \sin x\) over \([0,\pi]\)
using Simpson's Rule \(S_N\) with \(N=6\).
Approximate the length \(s\) of \(y = \sin x\) over \([0,\pi]\)
using Simpson's Rule \(S_N\) with \(N=6\).
Solution We have \(y'=\cos x\) and \(\sqrt{1 + (y^\prime)^2} = \sqrt{1 + \cos^2x}\). The arc length is \[ s = \int_0^{\pi} \sqrt{1 + \cos^2x}\, dx \]
This integral cannot be evaluated explicitly, so we approximate it by applying Simpson's Rule (Section 7.8) to the integrand \(g(x)=\sqrt{1 + \cos^2x}\). Divide \([0,\pi]\) into \(N=6\) subintervals of width \(\Delta x = \pi/6\). Then \[ \begin {eqnarray} S_6 &=&\frac{\Delta x}{3}\left(g(0)+4g\left(\frac{\vphantom{1}\pi}6\right) + 2g\left(\frac{2\pi}6\right) + 4g\left(\frac{3\pi}6\right) + 2g\left(\frac{4\pi}6\right) + 4g\left(\frac{5\pi}6\right) + g(\pi)\right)\notag\\ &\approx & \frac{\pi}{18}(1.4142 + 5.2915 + 2.2361 + 4 + 2.2361 + 5.2915 + 1.4142) \approx 3.82 \notag \end {eqnarray} \]
Thus \(s\approx 3.82\) (Figure 8.6). A computer algebra system yields the more accurate approximation \(s\approx 3.820198\).
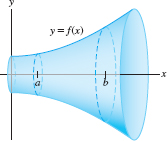
The surface area \(S\) of a surface of revolution (Figure 8.7) can be computed by an integral that is similar to the arc length integral. Suppose that \(f(x)\ge 0\), so that the graph lies above the \(x\)-axis. We can approximate the surface by rotating a polygonal approximation to \(y = f(x)\) about the \(x\)-axis. The result is a surface built out of truncated cones (Figure 8.8).
The surface area of a truncated cone is equal to \(\pi\) times the sum of the left- and right-hand radii times the length of the slanted side. Using the notation from the derivation of the arc length formula above, we find that the surface area of the truncated cone along the subinterval \([x_{i-1},x_i]\) is \[ \pi\,\underbrace{\big(f(x_{i-1})+f(x_i)\big)}_{\textrm{Sum of radii}} \underbrace{|\overline{P_{i-1}P_i}|}_{\textrm{Slant length}} = 2\pi\,\left(\frac{f(x_{i-1})+f(x_i)}{2}\right)\sqrt{1+f'(c_i)^2}\Delta x_i \]
470
The surface area \(S\) is equal to the limit of the sums of the surface areas of the truncated cones as \(N\to\infty\). We can show that the limit is not affected if we replace \(x_{i-1}\) and \(x_i\) by \(c_i\). Therefore \[ S = 2\pi \lim_{N\to\infty}\sum_{i=1}^N f(c_i)\sqrt{1+f'(c_i)^2}\Delta x_i \]
This is a limit of Riemann sums that converges to the integral in Eq.(3) below.
Area of a Surface of Revolution
Assume that \(f(x)\ge 0\) and that \(f'(x)\) exists and is continuous on \([a,b]\). The surface area \(S\) of the surface obtained by rotating the graph of \(f(x)\) about the \(x\)-axis for \(a\le x \le b\) is equal to \[ \boxed{\bbox[#FAF8ED,5pt]{S = 2\pi \int_a^b f(x)\sqrt{1 + f'(x)^2} \, dx}}\tag{3} \]
EXAMPLE 4
Calculate the surface area of a sphere of radius \(R\).
Solution The graph of \(f(x) =\sqrt{R^2-x^2}\) is a semicircle of radius \(R\) (Figure 8.9). We obtain a sphere by rotating it about the \(x\)-axis. We have \[ \begin{align*} f'(x) = -\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{R^2 - x^2}},\qquad 1 + f'(x)^2 = 1 + \frac{x^2}{R^2 - x^2} = \frac{R^2}{R^2 - x^2} \end{align*} \]
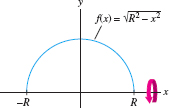
The surface area integral gives us the usual formula for the surface area of a sphere: \[ \begin {eqnarray} S & = & 2\pi \int_{-R}^R f(x)\sqrt{1 + f'(x)^2} \, dx = 2 \pi \int_{-R}^R \sqrt{R^2 - x^2} \, \frac{R}{\sqrt{R^2 - x^2}} \, dx \notag\\ & = & 2 \pi R \int_{-R}^R \, dx = 2 \pi R (2R) = 4 \pi R^2.\notag\end {eqnarray} \]
EXAMPLE 5
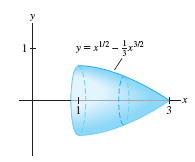
Find the surface area \(S\) of the surface obtained by rotating the graph of \(y=x^{1/2}-\frac13x^{3/2}\) about the \(x\)-axis for \(1\le x \le 3\).
Solution Let \(f(x)=x^{1/2}-\frac13x^{3/2}\). Then \(f'(x)=\frac12(x^{-1/2}-x^{1/2})\) and \[ \begin{align*} 1+f'(x)^2 & = 1+\left(\frac{x^{-1/2}-x^{1/2}}2 \right)^2 = 1 + \frac{x^{-1}-2+x}4 \\ & = \frac{x^{-1}+2+x}4 = \left(\frac{x^{1/2}+x^{-1/2}}2 \right)^2 \end{align*} \]
471
The surface area (Figure 8.10) is equal to \[ \begin {eqnarray} S &=& 2\pi \int_1^3 f(x)\sqrt{1 + f'(x)^2} \, dx = 2\pi\int_1^3 \left(x^{1/2}-\frac13x^{3/2}\right) \left(\frac{x^{1/2}+x^{-1/2}}2\right) dx \notag\\ &=& \pi\int_1^3 \left(1+\frac23x-\frac13x^2\right) dx =\pi\left(x+\frac13x^{2}-\frac19x^{3} \right)\bigg|_1^3 =\frac{16\pi}9 \notag \end {eqnarray} \]
8.1.1 Summary
- The arc length of \(y = f(x)\) over \([a,b]\) is \[{s = \int_a^b \sqrt{1 + f'(x)^2} \, dx}\]
- Use numerical integration to approximate arc length when the arc length integral cannot be evaluated explicitly.
- Assume that \(f(x)\geq 0\). The surface area of the surface obtained by rotating the graph of \(f(x)\) about the \(x\)-axis for \(a\le x \le b\) is \[ \textrm{Surface area} = 2\pi \int_a^b f(x)\sqrt{1 + f'(x)^2} \, dx \]