The Election of 1848
Printed Page 395
Section Chronology

When President James Polk chose not to seek reelection, the Democratic convention nominated Lewis Cass of Michigan, the man most closely associated with popular sovereignty. The Whigs nominated a Mexican-American War hero, General Zachary Taylor. The Whigs declined to adopt a party platform, betting that the combination of a military hero and total silence on the slavery issue would unite their divided party. Taylor, who owned more than one hundred slaves on plantations in Mississippi and Louisiana, was hailed by Georgia politician Robert Toombs as a “Southern man, a slaveholder, a cotton planter.”
Antislavery Whigs balked. Senator Charles Sumner called for a major political realignment, “one grand Northern party of Freedom.” In the summer of 1848, antislavery Whigs and antislavery Democrats founded the Free-Soil Party, nominating a Democrat, Martin Van Buren, for president and a Whig, Charles Francis Adams, for vice president. The platform boldly proclaimed, “Free soil, free speech, free labor, and free men.”
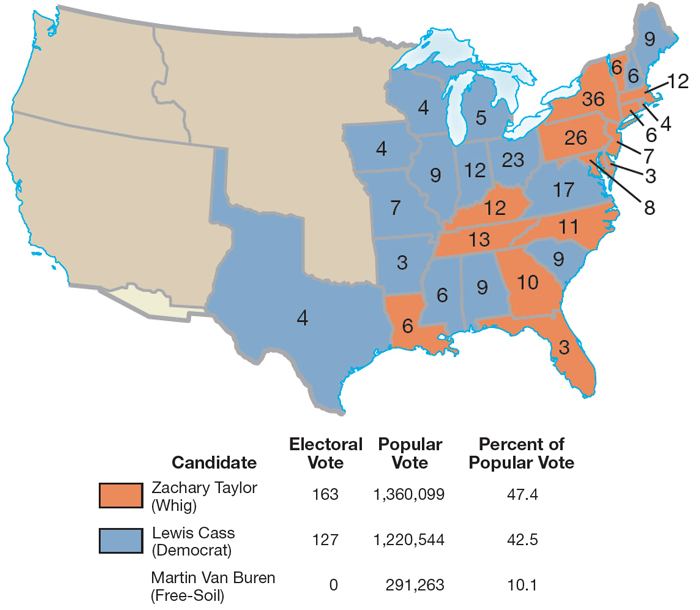
The November election dashed the hopes of the Free-Soilers. They did not carry a single state. Taylor won the all-important electoral vote 163 to 127, carrying eight of the fifteen slave states and seven of the fifteen free states (Map 14.1). (Wisconsin had entered the Union earlier in 1848 as the fifteenth free state.) Northern voters were not yet ready for Sumner’s “one grand Northern party of Freedom,” but the struggle over slavery in the territories had shaken the major parties badly.