Why did Archaic Native Americans shift to foraging and hunting smaller animals?
> CHRONOLOGY
ca. 10,000–3000 BP
|
ca. 5000 BP
|
ca. 4000 BP
|
ca. 3500 BP
|
ca. 2500 BP
|
ca. 2500–2100 BP
|
ca. 2100 BP–AD 400
|
ca. AD 200–900
|
ca. AD 500
|
Archaeologists use the term Archaic to describe the many different hunting and gathering cultures that descended from Paleo-Indians and the long period of time when those cultures dominated the history of ancient America—roughly from 10,000 BP to somewhere between 4000 BP and 3000 BP. The term describes the era in the history of ancient America that followed the Paleo-Indian big-game hunters and preceded the development of agriculture. It denotes a hunter-gatherer way of life that persisted in North America long after European colonization.
Like their Paleo-Indian ancestors, Archaic Indians hunted with spears, but they also took smaller game with traps, nets, and hooks. Unlike their Paleo-Indian predecessors, many Archaic peoples became excellent basket makers in order to collect and store seeds, roots, nuts, and berries they gathered from wild plants. They prepared food from these plants by using a variety of stone tools. A characteristic Archaic artifact is a grinding stone used to pulverize seeds into edible form. Most Archaic Indians migrated from place to place to harvest plants and hunt animals. They usually did not establish permanent villages, although they often returned to the same river valley or fertile meadow year after year. In regions with especially rich resources—such as present-day California and the Pacific Northwest—they developed permanent settlements. Archaic peoples followed these practices in distinctive ways in the different environmental regions of North America (Map 1.2). [[LP Map: M01.02 Native North American Cultures- MAP ACTIVITY /
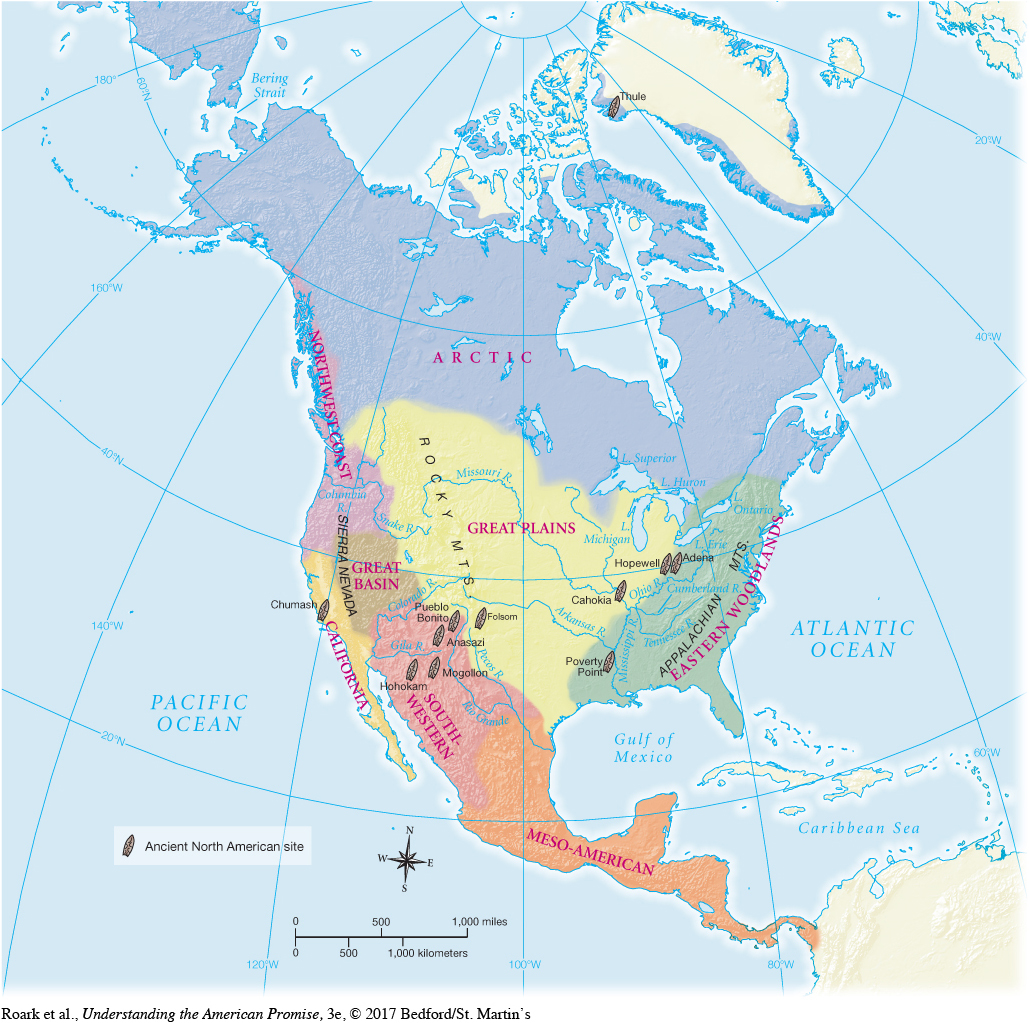
Understanding the American Promise 3ePrinted Page 9