Why did the relationship between urban and rural America deteriorate in the 1920s?
> CHRONOLOGY
1921
|
1924
|
1925
|
1927
|
1928
|
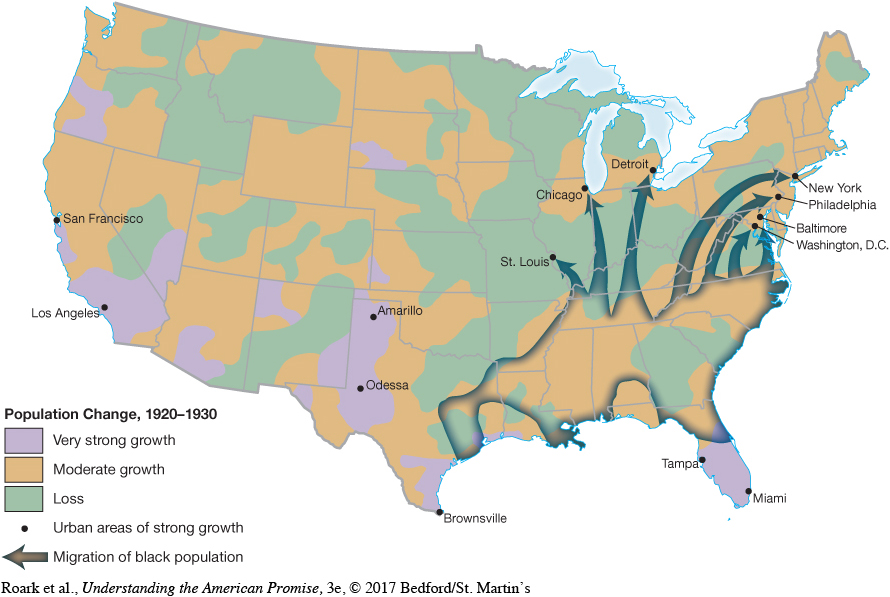
Large areas of the country did not share in the wealth of the 1920s. By the end of the decade, 40 percent of the nation’s farmers were landless, and 90 percent of rural homes lacked indoor plumbing, gas, or electricity. Rural America’s traditional distrust of urban America turned to despair in the 1920s when the census reported that the majority of the population had shifted to the city (Map 23.2). Once the “backbone of the republic,” rural Americans had become poor country cousins. Urban domination over the nation’s political and cultural life and sharply rising economic disparity drove rural Americans in often ugly, reactionary directions.[[LP Map: M23.02 The Shift from Rural to Urban Population, 1920–1930 – MAP ACTIVITY/
Cities seemed to stand for everything rural areas stood against. Rural America imagined itself as solidly Anglo-Saxon (despite the presence of millions of African Americans in the South and Mexican Americans, Native Americans, and Asian Americans in the West), and the cities seemed to be filled with undesirable immigrants. Rural America was the home of old-time Protestant religion, and the cities teemed with Catholics, Jews, liberal Protestants, and atheists. Rural America championed old-fashioned moral standards—abstinence and self-denial—while the cities spawned every imaginable vice. In the 1920s, frustrated rural people sought to recapture their country by helping to push through prohibition, dam the flow of immigrants, revive the Ku Klux Klan, defend the Bible as literal truth, and defeat an urban Roman Catholic for president.
Understanding the American Promise 3ePrinted Page 661