PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS
Question 2.1
Identify. Examine the following four amino acids (A–
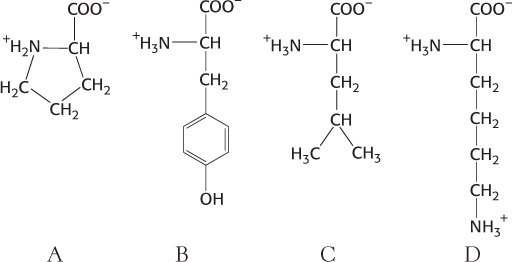
What are their names, three-
Question 2.2
Properties. In reference to the amino acids shown in Problem 1, which are associated with the following characteristics?
Hydrophobic side chain ______________
Basic side chain ______________
Three ionizable groups ______________
pKa of approximately 10 in proteins ______________
Modified form of phenylalanine ______________
Question 2.3
Match ’em. Match each amino acid in the left-
|
(a) Leu |
(1) hydroxyl- |
|
(b) Glu |
(2) acidic |
|
(c) Lys |
(3) basic |
|
(d) Ser |
(4) sulfur- |
|
(e) Cys |
(5) nonpolar aromatic |
|
(f) Trp |
(6) nonpolar aliphatic |
Question 2.4
Solubility. In each of the following pairs of amino acids, identify which amino acid would be more soluble in water: (a) Ala, Leu; (b) Tyr, Phe; (c) Ser, Ala; (d) Trp, His.
Question 2.5
Bonding is good. Which of the following amino acids have R groups that have hydrogen-
Question 2.6
Name those components. Examine the segment of a protein shown here.
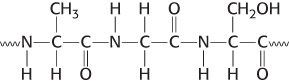
What three amino acids are present?
Of the three, which is the N-
terminal amino acid? Identify the peptide bonds.
Identify the α-carbon atoms.
Question 2.7
Who’s charged? Draw the structure of the dipeptide Gly-
Question 2.8
Alphabet soup. How many different polypeptides of 50 amino acids in length can be made from the 20 common amino acids?
Question 2.9
Sweet tooth, but calorie conscious. Aspartame (NutraSweet), an artificial sweetener, is a dipeptide composed of Asp-
Question 2.10
Vertebrate proteins? What is meant by the term polypeptide backbone?
Question 2.11
Not a sidecar. Define the term side chain in the context of amino acid or protein structure.
Question 2.12
One from many. Differentiate between amino acid composition and amino acid sequence.
Question 2.13
Shape and dimension. (a) Tropomyosin, a 70-
Question 2.14
Contrasting isomers. Poly-
Question 2.15
Exceptions to the rule. Ramachandran plots for two amino acids differ significantly from that shown in Figure 2.23. Which two, and why?
Question 2.16
Active again. A mutation that changes an alanine residue in the interior of a protein to valine is found to lead to a loss of activity. However, activity is regained when a second mutation at a different position changes an isoleucine residue to glycine. How might this second mutation lead to a restoration of activity?
64
Question 2.17
Exposure issues. Many of the loops on proteins are composed of hydrophilic amino acids. Why might this be the case?
Question 2.18
Shuffle test. An enzyme that catalyzes disulfide–
Question 2.19
Stretching a target. A protease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the peptide bonds of target proteins. How might a protease bind a target protein so that its main chain becomes fully extended in the vicinity of the vulnerable peptide bond?
Question 2.20
Often irreplaceable. Glycine is a highly conserved amino acid residue in the evolution of proteins. Why?
Question 2.21
Potential partners. Identify the groups in a protein that can form hydrogen bonds or electrostatic bonds with an arginine side chain at pH 7.
Question 2.22
Permanent waves. The shape of hair is determined in part by the pattern of disulfide bonds in keratin, its major protein. How can curls be induced?
Question 2.23
Location is everything 1. Most proteins have hydrophilic exteriors and hydrophobic interiors. Would you expect this structure to apply to proteins embedded in the hydrophobic interior of a membrane? Explain.
Question 2.24
Location is everything 2. Proteins that span biological membranes often contain α helices. Given that the insides of membranes are highly hydrophobic (Section 12.2), predict what type of amino acids would be in such an α helix. Why is an α helix particularly suited to existence in the hydrophobic environment of the interior of a membrane?
Question 2.25
Neighborhood peer pressure? Table 2.1 shows the typical pKa values for ionizable groups in proteins. However, more than 500 pKa values have been determined for individual groups in folded proteins. Account for this discrepancy.
Question 2.26
Greasy patches. The α and β subunits of hemoglobin bear a remarkable structural similarity to myoglobin. However, in the subunits of hemoglobin, certain residues that are hydrophilic in myoglobin are hydrophobic. Why might this be the case?
Question 2.27
Maybe size does matter. Osteogenesis imperfecta displays a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe. On the basis of your knowledge of amino acid and collagen structure, propose a biochemical basis for the variety of symptoms.
Question 2.28
Issues of stability. Proteins are quite stable. The lifetime of a peptide bond in aqueous solution is nearly 1000 years. However, the free energy of hydrolysis of proteins is negative and quite large. How can you account for the stability of the peptide bond in light of the fact that hydrolysis releases much energy?
Question 2.29
Minor species. For an amino acid such as alanine, the major species in solution at pH 7 is the zwitterionic form. Assume a pKa value of 8 for the amino group and a pKa value of 3 for the carboxylic acid. Estimate the ratio of the concentration of the neutral amino acid species (with the carboxylic acid protonated and the amino group neutral) to that of the zwitterionic species at pH 7 (Section 1.3).
Question 2.30
A matter of convention. All l amino acids have an S absolute configuration except l-cysteine, which has the R configuration. Explain why l-cysteine is designated as having the R absolute configuration.
Question 2.31
Hidden message. Translate the following amino acid sequence into one-
Question 2.32
Who goes first? Would you expect Pro—
Question 2.33
Matching. For each of the amino acid derivatives shown here (A–
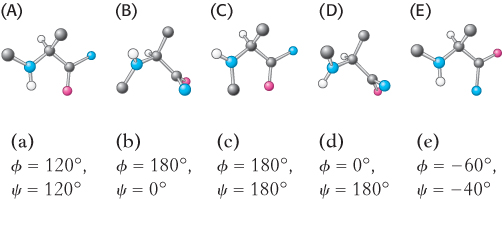
Question 2.34
Scrambled ribonuclease. When performing his experiments on protein refolding, Christian Anfinsen obtained a quite different result when reduced ribonuclease was reoxidized while it was still in 8 M urea and the preparation was then dialyzed to remove the urea. Ribonuclease reoxidized in this way had only 1% of the enzymatic activity of the native protein. Why were the outcomes so different when reduced ribonuclease was reoxidized in the presence and absence of urea?