PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS
Question 11.1
Word origin. Account for the origin of the term carbohydrate.
Question 11.2
Diversity. How many different oligosaccharides can be made by linking one glucose, one mannose, and one galactose? Assume that each sugar is in its pyranose form. Compare this number with the number of tripeptides that can be made from three different amino acids.
Question 11.3
They go together like a horse and carriage. Match each term with its description.
|
(a) Enantiomers ____ |
1. Has the molecular formula of (CH2O)n |
|
(b) Cellulose ____ |
2. Monosaccharides that differ at a single asymmetric carbon atom |
|
(c) Lectins ____ |
3. The storage form of glucose in animals |
|
(d) Glycosyltransferases ____ |
4. The storage form of glucose in plants |
|
(e) Epimers ____ |
5. Glycoprotein containing glycosaminoglycans |
|
(f) Starch ____ |
6. The most abundant organic molecule in the biosphere |
|
(g) Carbohydrates ____ |
7. N-Acetylgalactosamine is a key component of this glycoprotein |
|
(h) Proteoglycan ____ |
8. Carbohydrate- |
|
(i) Mucoprotein ____ |
9. Enzymes that synthesize oligosaccharides |
|
(j) Glycogen ____ |
10. Stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other |
Question 11.4
Couples. Indicate whether each of the following pairs of sugars consists of anomers, epimers, or an aldose–
D-
glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone D-
glucose and D- mannose D-
glucose and D- fructose α-d-glucose and β-d-glucose
D-
ribose and D- ribulose D-
galactose and D- glucose
Question 11.5
Carbons and carbonyls. To which classes of sugars do the monosaccharides shown here belong?
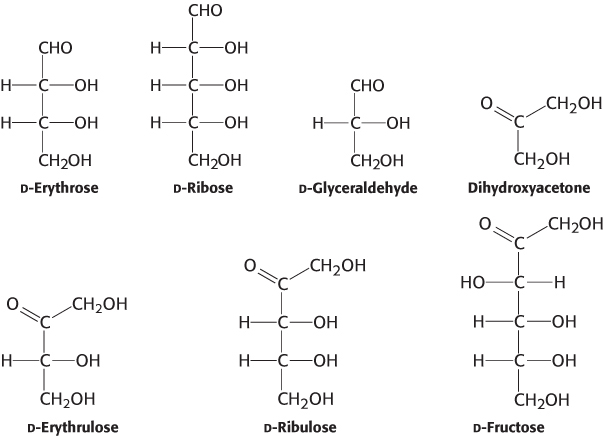
Question 11.6
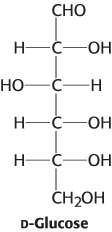
Chemical cousins. Although an aldose with 4 asymmetric carbon atoms is capable of forming 16 diastereoisomers, only 8 of the isomers are commonly observed, including glucose. They are listed below with their structural relation to glucose. Using the structure of glucose as a reference, draw the structures.
D-
Allose: Epimeric at C- 3 D-
Altrose: Isomeric at C- 2 and C- 3 D-
Mannose: Epimeric at C- 2 D-
Gulose: Isomeric at C- 3 and C- 4 D-
Idose: Isomeric at C- 2, C- 3 and C- 4 D-
Galactose: Epimeric at C- 4 D-
Talose: Isomeric at C- 2 and C- 4
Question 11.7
An art project. Draw the structure of the disaccharide α-glycosyl-
339
Question 11.8
Mutarotation. The specific rotations of the α and β anomers of D-
Question 11.9
Telltale marker. Glucose reacts slowly with hemoglobin and other proteins to form covalent compounds. Why is glucose reactive? What is the nature of the adduct formed?
Question 11.10
Periodate cleavage. Compounds containing hydroxyl groups on adjacent carbon atoms undergo carbon–
Question 11.11
Sugar lineup. Identify the following four sugars.
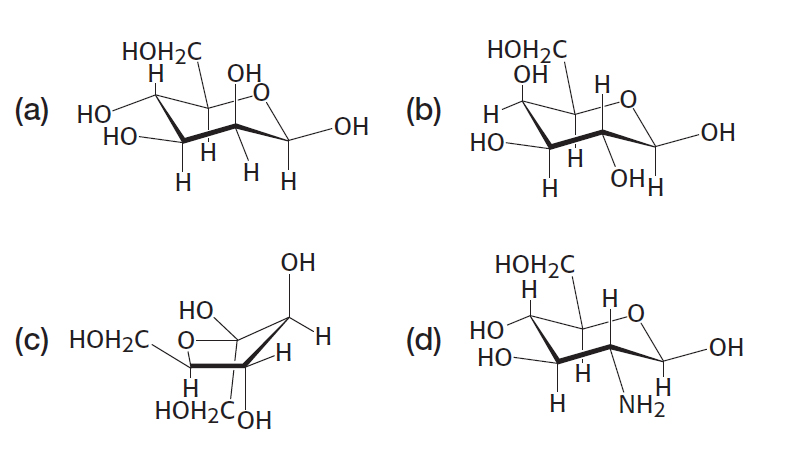
Question 11.12
Cellular glue. A trisaccharide unit of a cell-
Question 11.13
Mapping the molecule. Each of the hydroxyl groups of glucose can be methylated with reagents such as dimethyl sulfate under basic conditions. Explain how exhaustive methylation followed by the complete digestion of a known amount of glycogen would enable you to determine the number of branch points and reducing ends.
Question 11.14
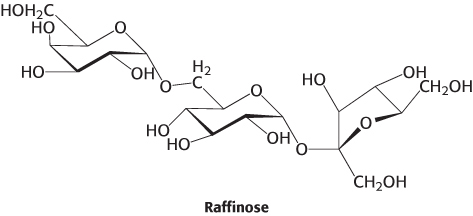
Component parts. Raffinose is a trisaccharide and a minor constituent in sugar beets.
Is raffinose a reducing sugar? Explain.
What are the monosaccharides that compose raffinose?
β-Galactosidase is an enzyme that will remove galactose residues from an oligosaccharide. What are the products of β-galactosidase treatment of raffinose?
Question 11.15
Anomeric differences. α-d-Mannose is a sweet-
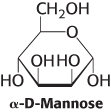
Question 11.16
A taste of honey. Fructose in its β-d-pyranose form accounts for the powerful sweetness of honey. The β-d-furanose form, although sweet, is not as sweet as the pyranose form. The furanose form is the more stable form. Draw the two forms and explain why it may not always be wise to cook with honey.
Question 11.17
Making ends meet.
(a) Compare the number of reducing ends to nonreducing ends in a molecule of glycogen.
(b) As we will see in Chapter 21, glycogen is an important fuel-
storage form that is rapidly mobilized. At which end— the reducing or nonreducing —would you expect most metabolism to take place?
Question 11.18
A lost property. Glucose and fructose are reducing sugars. Sucrose, or table sugar, is a disaccharide consisting of both fructose and glucose. Is sucrose a reducing sugar? Explain.
Question 11.19
Meat and potatoes. Compare the structures of glycogen and starch.
Question 11.20
Straight or with a twist? Account for the different structures of glycogen and cellulose.
Question 11.21
Sweet proteins. List the key classes of glycoproteins, their defining characteristics, and their biological functions.
Question 11.22
Life extender. What is the function of the carbohydrate moiety that is attached to EPO?
Question 11.23
Cushioning. What is the role of the glycosaminoglycan in the cushioning provided by cartilage?
Question 11.24
Undelivered mail. Not returned to sender. I-
340
Question 11.25
Appropriate peg. Which amino acids are used for the attachment of carbohydrates to proteins?
Question 11.26
From one, many. What is meant by a glycoform?
Question 11.27
Ome. What is meant by the glycome?
Question 11.28
Exponential expansion? Compare the amount of information inherent in the genome, the proteome, and the glycome.
Question 11.29
Attachments. Suppose, one Sunday afternoon, you are relaxing by reading amino acid sequences of various proteins. Being a bit hungry, you are also thinking of sweet snacks. Combining your interests, you wonder whether you can detect N-glycosylation sites by simply looking at amino acid sequence. Your roomate, who is taking a biochemistry course, says “You sure can, to some degree at least, and here’s how.” What did your roomate say to explain?
Question 11.30
Locks and keys. What does the fact that all organisms contain lectins suggest about the role of carbohydrates?
Question 11.31
Carbohydrates—
Question 11.32
Carbohydrates and proteomics. Suppose that a protein contains six potential N-linked glycosylation sites. How many possible proteins can be generated, depending on which of these sites is actually glycosylated? Do not include the effects of diversity within the carbohydrate added.
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 11.33
Like a jigsaw puzzle. Why is it more difficult to determine the structure of the oligosaccharides compared to amino acid sequences or nucleotide sequences?
Question 11.34
Stereospecificity. Sucrose, a major product of photosynthesis in green leaves, is synthesized by a battery of enzymes. The substrates for sucrose synthesis, D-
Question 11.35
Specific recognition. How might the technique of affinity chromatography be used to purify lectins ?
Data Interpretation Problem
Question 11.36
Sore joints. A contributing factor to the development of arthritis is the inappropriate proteolytic destruction of the aggrecan component of cartilage by the proteolytic enzyme aggrecanase. The immune-
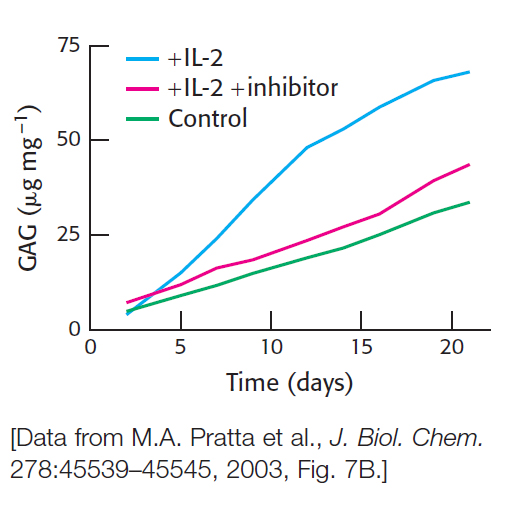
Aggrecan degradation was measured by the release of glycosaminoglycan. What is the rationale for this assay?
Why might glycosaminoglycan release not indicate aggrecan degradation?
What is the purpose of the control—
cartilage incubated with no additions? What is the effect of adding IL-
2 to the system? What is the response when an aggrecanase inhibitor is added in addition to IL-
2? Why is there some aggrecan destruction in the control with the passage of time?