PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS
Question 18.1
Breathe or ferment? Compare fermentation and respiration with respect to electron donors and electron acceptors.
Question 18.2
Reference states. The standard oxidation–
Question 18.3
Less energetic electrons. Why are electrons carried by FADH2 not as energy rich as those carried by NADH? What is the consequence of this difference?
Question 18.4
Now prove it. Calculate the energy released by the reduction of O2 with FADH2.
Question 18.5
Thermodynamic constraint. Compare the ΔG°′ values for the oxidation of succinate by NAD+ and by FAD. Use the data given in Table 18.1 to find the 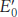 of the NAD+ – NADH and fumarate-
of the NAD+ – NADH and fumarate-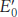 for the FAD – FADH2 redox couple is nearly 0.05 V. Why is FAD rather than NAD+ the electron acceptor in the reaction catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase?
for the FAD – FADH2 redox couple is nearly 0.05 V. Why is FAD rather than NAD+ the electron acceptor in the reaction catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase?
Question 18.6
Give and accept. Distinguish between an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent.
Question 18.7
The benefactor and beneficiary. Identify the oxidant and the reductant in the following reaction.
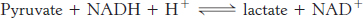
Question 18.8
Six of one, half dozen of the other. How is the redox potential (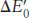 ) related to the free-
) related to the free-
Question 18.9
Location, location, location. Iron is a component of many of the electron carriers of the electron-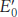 value is +0.77 V, as seen in Table 18.1?
value is +0.77 V, as seen in Table 18.1?
Question 18.10
Line up. Place the following components of the electron-
cytochrome c
Q-
cytochrome c oxidoreductase NADH-
Q reductase cytochrome c oxidase
ubiquinone
Question 18.11
Like mac and cheese. Match each term with its description.
|
(a) Respiration _______ (b) Redox potential _______ (c) Electron- (d) Flavin mononucleotide (FMN) _______ (e) Iron– (f) Coenzyme Q _______ (g) Cytochrome c _______ (h) Q cycle _______ (i) Superoxide dismutase _______ (j) Catalase _______ |
1. Converts reactive oxygen species into hydrogen peroxide 2. Electron flow from NADH and FADH2 to O2 3. Facilitates electron flow from FMN to coenzyme Q in Complex I 4. An ATP- 5. Measure of the tendency to accept or donate electrons 6. Converts hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water 7. Funnels electrons from a two- 8. Lipid- 9. Donates electrons to Complex IV 10. Accepts electrons from NADH in Complex I |
561
Question 18.12
Match ’em.
|
(a) Complex I _______ |
1. Q- |
|
(b) Complex II _______ |
2. Coenzyme Q |
|
(c) Complex III _______ |
3. Succinate- |
|
(d) Complex IV _______ |
4. NADH- |
|
(e) Ubiquinone _______ |
5. Cytochrome c oxidase |
Question 18.13
Structural considerations. Explain why coenzyme Q is an effective mobile electron carrier in the electron-
Question 18.14
Inhibitors. Rotenone inhibits electron flow through NADH-
NAD+
NADH-
Q oxidoreductase coenzyme Q
cytochrome c1
cytochrome c
cytochrome a
Question 18.15
Rumored to be a favorite of Elvis. Amytal is a barbiturate sedative that inhibits electron flow through Complex I. How would the addition of amytal to actively respiring mitochondria affect the relative oxidation–
Question 18.16
Efficiency. What is the advantage of having Complexes I, III, and IV associated with one another in the form of a respirasome?
Question 18.17
Linked In. What citric acid cycle enzyme is also a component of the electron-
Question 18.18
ROS, not ROUS. What are the reactive oxygen species and why are they especially dangerous to cells?
Question 18.19
Reclaim resources. Humans have only about 250 g of ATP, but even a couch potato needs about 83 kg of ATP to open the bag of chips and use the remote. How is this discrepancy between requirements and resources reconciled?
Question 18.20
Energy harvest. What is the yield of ATP when each of the following substrates is completely oxidized to CO2 by a mammalian cell homogenate? Assume that glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation are fully active.
Pyruvate
Lactate
Fructose 1,6-
bisphosphate Phosphoenolpyruvate
Galactose
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Question 18.21
Potent poisons. What is the effect of each of the following inhibitors on electron transport and ATP formation by the respiratory chain?
Azide
Atractyloside
Rotenone
DNP
Carbon monoxide
Antimycin A
Question 18.22
A question of coupling. What is the mechanistic basis for the observation that the inhibitors of ATP synthase also lead to an inhibition of the electron-
Question 18.23
A Brownian ratchet wrench. What causes the c subunits of ATP synthase to rotate? What determines the direction of rotation?
Question 18.24
An essential residue. The conduction of protons by the F0 unit of ATP synthase is blocked by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, which reacts readily with carboxyl groups. What are the most likely targets of action of this reagent? How might you use site-
Question 18.25
Alternative routes. The most common metabolic sign of mitochondrial disorders is lactic acidosis. Why?
Question 18.26
Connections. How does the inhibition of ATP-
Question 18.27
O2 consumption. Oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria is often monitored by measuring oxygen consumption. When oxidative phosphorylation is proceeding rapidly, the mitochondria will rapidly consume oxygen. If there is little oxidative phosphorylation, only small amounts of oxygen will be used. You are given a suspension of isolated mitochondria and directed to add the following compounds in the order from a to h. With the addition of each compound, all of the previously added compounds remain present. Predict the effect of each addition on oxygen consumption by the isolated mitochondria.
Glucose
ADP + Pi
Citrate
Oligomycin
Succinate
Dinitrophenol
Rotenone
Cyanide
Question 18.28
P : O ratios. The number of molecules of inorganic phosphate incorporated into organic form per atom of oxygen consumed, termed the P : O ratio, was frequently used as an index of oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the relation of the P : O ratio to the ratio of the number of protons translocated per electron pair (H+/2 e−) and the ratio of the number of protons needed to synthesize ATP and transport it to the cytoplasm (P/H+)?
What are the P : O ratios for electrons donated by matrix NADH and by succinate?
562
Question 18.29
Cyanide antidote. The immediate administration of nitrite is a highly effective treatment for cyanide poisoning. What is the basis for the action of this antidote? (Hint: Nitrite oxidizes ferrohemoglobin to ferrihemoglobin.)
Question 18.30
Runaway mitochondria 1. Suppose that the mitochondria of a patient oxidize NADH irrespective of whether ADP is present. The P : O ratio for oxidative phosphorylation by these mitochondria is less than normal. Predict the likely symptoms of this disorder.
Question 18.31
Recycling device. The cytochrome b component of Q-
Question 18.32
Crossover point. The precise site of action of a respiratory-
Question 18.33
Runaway mitochondria 2. Years ago, uncouplers were suggested to make wonderful diet drugs. Explain why this idea was proposed and why it was rejected. Why might the producers of antiperspirants be supportive of the idea?
Question 18.34
Everything is connected. If actively respiring mitochondria are exposed to an inhibitor of ATP-
Question 18.35
Identifying the inhibition. You are asked to determine whether a chemical is an electron-
Question 18.36
To each according to its needs. It has been noted that the mitochondria of muscle cells often have more cristae than the mitochondria of liver cells. Provide an explanation for this observation.
Question 18.37
Opposites attract. An arginine residue (Arg 210) in the a subunit of the E. coli ATP synthase is near the aspartate residue (Asp 61) in the matrix-
Question 18.38
Variable c subunits. Recall that the number of c subunits in the c ring appears to range between 8 and 14. This number is significant because it determines the number of protons that must be transported to generate a molecule of ATP. Each 360-
Question 18.39
Counterintuitive. Under some conditions, mitochondrial ATP synthase has been observed to actually run in reverse. How would that situation affect the proton-
Question 18.40
Etiology? What does that mean? What does the fact that rotenone appears to increase the susceptibility to Parkinson disease indicate about the etiology of Parkinson disease?
Question 18.41
Exaggerating the difference. Why must ATP-
Question 18.42
Respiratory control. The rate of oxygen consumption by mitochondria increases markedly when ADP is added and then returns to its initial value when the added ADP has been converted into ATP (Figure 18.39). Why does the rate decrease?
Question 18.43
Same, but different. Why is the electroneutral exchange of H2PO4− for OH− indistinguishable from the electroneutral symport of H2PO4− and H+?
Question 18.44
Multiple uses. Give an example of the use of the proton-
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 18.45
Just obeying the laws. Why do isolated F1 subunits of ATP synthase catalyze ATP hydrolysis?
Question 18.46
The right location. Some cytoplasmic kinases, enzymes that phosphorylate substrates at the expense of ATP, bind to voltage-
Question 18.47
No exchange. Mice that completely lack ATP-
563
Question 18.48
Maybe you shouldn’t take your vitamins. Exercise is known to increase insulin sensitivity and to ameliorate type 2 diabetes (Chapter 27). Recent research suggests that taking antioxidant vitamins might mitigate the beneficial effects of exercise with respect to ROS protection.
What are the antioxidant vitamins?
How does exercise protect against ROS?
Explain why vitamins might counteract the effects of exercise.
Chapter Integration and Data Interpretation Problem
Question 18.49
Monitoring energy sources. XF technology (Seahorse Bioscience) now allows the measurement of the rate of aerobic respiration and lactic acid fermentation simultaneously in real time in cultured cells. The extent of aerobic respiration is determined by measuring the oxygen consumption rate (OCR, measured in picomoles of oxygen consumed per minute) while the rate of glycolysis correlates with the extracellular acidification rate [ECAR-
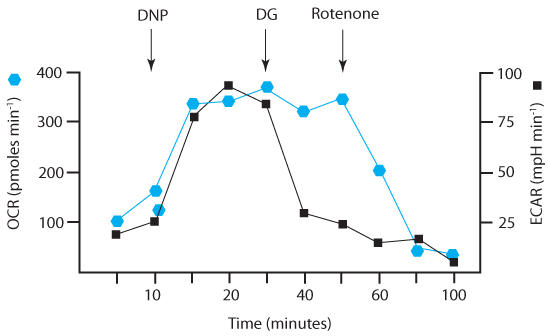
Dinitrophenol (DNP), the glycolysis inhibitor 2-
What is the effect on OCR and ECAR of adding DNP to the cell culture? Explain these results.
Explain the effect of the addition of 2-
deoxyglucose. Explain how 2-
deoxyglucose acts as an inhibitor of glycolysis? Explain the effect of the addition of rotenone.
Data Interpretation Problem
Question 18.50
Mitochondrial disease. A mutation in a mitochondrial gene encoding a component of ATP synthase has been identified. People who have this mutation suffer from muscle weakness, ataxia, and retinitis pigmentosa. A tissue biopsy was performed on each of three patients having this mutation, and submitochondrial particles were isolated that were capable of succinate-
|
ATP synthase activity (nmol of ATP formed min−1 mg−1) |
|
|---|---|
|
Controls |
3.0 |
|
Patient 1 |
0.25 |
|
Patient 2 |
0.11 |
|
Patient 3 |
0.17 |
What was the purpose of the addition of succinate?
What is the effect of the mutation on succinate-
coupled ATP synthesis? Next, the ATPase activity of the enzyme was measured by incubating the submitochondrial particles with ATP in the absence of succinate.
ATP hydrolysis
(nmol of ATP hydrolyzed min−1 mg−1)
Controls
33
Patient 1
30
Patient 2
25
Patient 3
31
Why was succinate omitted from the reaction?
What is the effect of the mutation on ATP hydrolysis?
What do these results, in conjunction with those obtained in the first experiment, tell you about the nature of the mutation?
Mechanism Problem
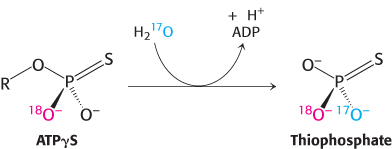
Question 18.51
Chiral clue. ATPγS, a slowly hydrolyzed analog of ATP, can be used to probe the mechanism of phosphoryl-
564