18.5Many Shuttles Allow Movement Across Mitochondrial Membranes
Many Shuttles Allow Movement Across Mitochondrial Membranes
The inner mitochondrial membrane must be impermeable to most molecules, yet much exchange has to take place between the cytoplasm and the mitochondria. This exchange is mediated by an array of membrane-
Electrons from cytoplasmic NADH enter mitochondria by shuttles
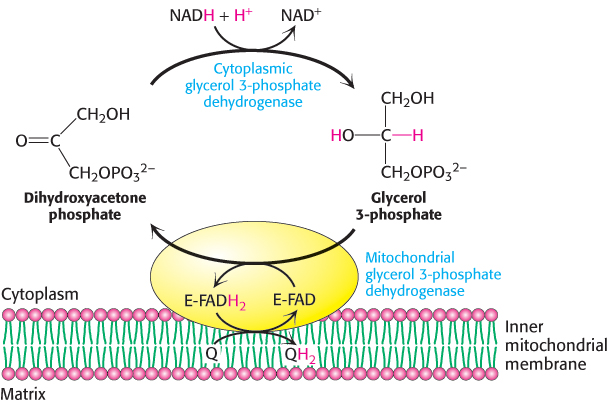
One function of the respiratory chain is to regenerate NAD+ for use in glycolysis. NADH generated by the citric acid cycle and fatty acid oxidation is already in the mitochondrial matrix, but how is cytoplasmic NADH reoxidized to NAD+ under aerobic conditions? NADH cannot simply pass into mitochondria for oxidation by the respiratory chain, because the inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to NADH and NAD+. The solution is that electrons from NADH, rather than NADH itself, are carried across the mitochondrial membrane. One of several means of introducing electrons from NADH into the electron-
550
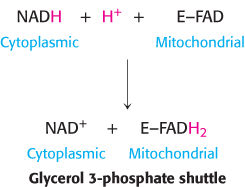
The reduced flavin transfers its electrons to the electron carrier Q, which then enters the respiratory chain as QH2. When cytoplasmic NADH transported by the glycerol 3-
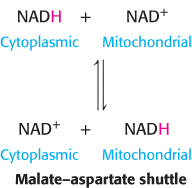
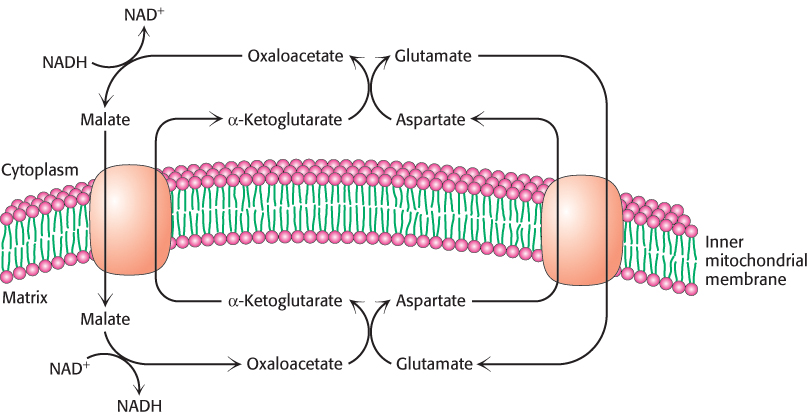
In the heart and liver, electrons from cytoplasmic NADH are brought into mitochondria by the malate–
The entry of ADP into mitochondria is coupled to the exit of ATP by ATP-ADP translocase
The major function of oxidative phosphorylation is to generate ATP from ADP. ATP and ADP do not diffuse freely across the inner mitochondrial membrane. How are these highly charged molecules moved across the inner membrane into the cytoplasm? A specific transport protein, ATP-
551
Most important, the flows of ATP and ADP are coupled. ADP enters the mitochondrial matrix only if ATP exits, and vice versa.This process is carried out by the translocase, an antiporter:
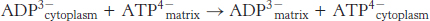
ATP-
The 30-
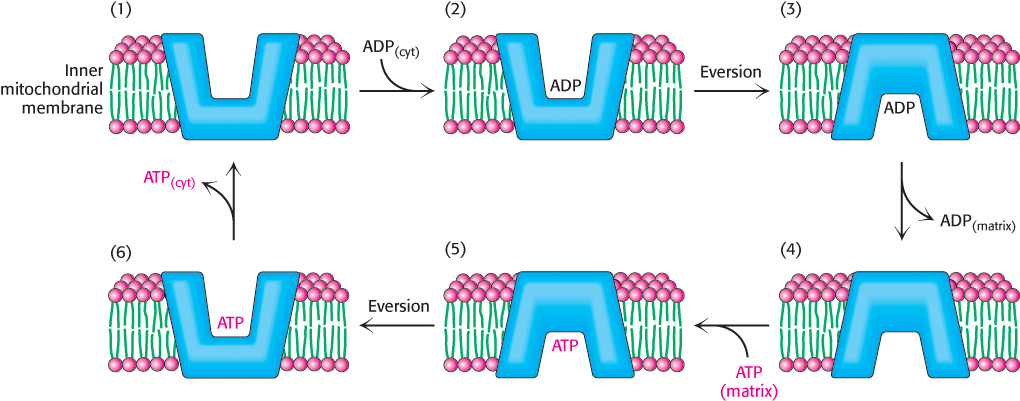
Mitochondrial transporters for metabolites have a common tripartite structure
Examination of the amino acid sequence of the ATP-
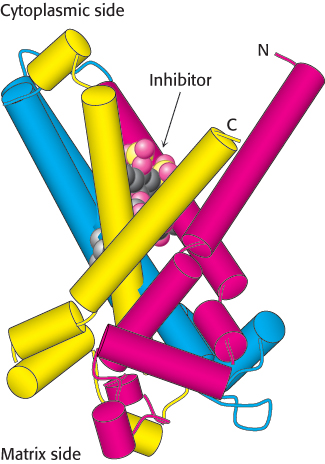
 FIGURE 18.38 Structure of mitochondrial transporters. The structure of the ATP-
FIGURE 18.38 Structure of mitochondrial transporters. The structure of the ATP-552
ATP-
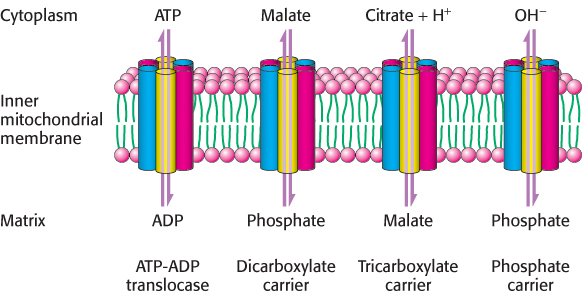
Other homologous carriers also are present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The dicarboxylate carrier enables malate, succinate, and fumarate to be exported from the mitochondrial matrix in exchange for Pi. The tricarboxylate carrier exchanges citrate and H+ for malate. In all, more than 40 such carriers are encoded in the human genome. A different type of carrier is responsible for pyruvate transport into the mitochondria. Pyruvate in the cytoplasm enters the mitochondrial membrane by way of a heterodimer composed of two small transmembrane proteins.