PROBLEMS
Question 13.1
What are the four possible fates of a replication fork that encounters a template strand with a break or some other type of unrepaired DNA lesion?
Question 13.2
A branched, circular DNA substrate is constructed to mimic one possible structure of a stalled replication fork, as shown below. An enzyme is added that promotes regression of the fork structure.
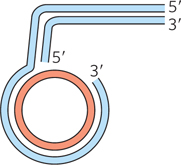
Draw the structure of the product obtained if regression proceeds halfway around the circle.
Draw the structure of the product if regression proceeds all the way around the circle. Assume the arm is the same length as the circle and has the same sequence.
Question 13.3
Draw a Holliday intermediate and label the ends of each DNA strand so that the strand polarity is evident.
Question 13.4
The RecBCD enzyme acts as a nuclease and a helicase in preparing DNA ends for RecA binding and strand invasion. RecBCD has several functions built into its three subunits. Indicate the subunit (RecB, RecC, or RecD) responsible for each of the following functions.
3′→5′ helicase motor
Nuclease
5′→3′ helicase
Having a “pin” structure that helps separate DNA strands
Binding to chi sites
Question 13.5
Describe the three steps that initiate almost all processes related to homologous genetic recombination (the recombinational DNA repair of double-
Question 13.6
Replication forks of a bacterial species are found to stall at double-
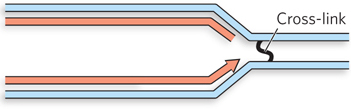
Question 13.7
In E. coli cells with mutations that eliminate the RecBCD enzyme, about 20% of the cells have linearized chromosomes when grown under normal aerobic conditions. Under similar growth conditions, fewer than 3% of the chromosomes are linearized in wild-
Question 13.8
Eukaryotes have two RecA-
Question 13.9
During meiosis in yeast, if the diploid cell has alleles a and A of a particular gene, it normally forms two spores with A and two spores with a. Rarely, meiosis yields one spore with A and three with a, or three with A and one with a. How could this happen?
Question 13.10
Unlike recombination, the repair of double-
Question 13.11
At the yeast mating-
Question 13.12
In the study by Keeney, Giroux, and Kleckner (see this chapter’s How We Know section), Spo11 was identified as the protein that introduces double-
482
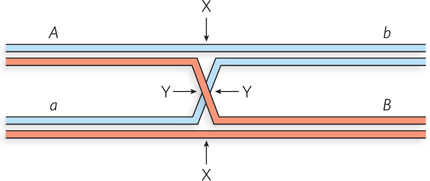
Question 13.13
A Holliday intermediate is formed between two chromosomes at a point between two genes, A and B, as shown below. The two chromosomes have different alleles of the two genes (A and a; B and b). Where would the Holliday intermediate have to be cleaved (points X and/or Y) to generate a chromosome with (a) an Ab genotype or (b) an ab genotype?
Question 13.14
Ionizing radiation causes double-