DATA ANALYSIS PROBLEM
Livet, J., T.A. Weissman, H.N. Kang, R.W. Draft, J. Lu, R.A. Bennis, J.R. Sanes, and J.W. Lichtman. 2007. Transgenic strategies for combinatorial expression of fluorescent proteins in the nervous system. Nature 450:56–
Question 14.15
Site-
The Cre recombinase was inserted into the genome of a different group of mice, the cloned enzyme structured so that it was expressed uniquely in brain tissue, for a brief time, during neuron development. When mice containing the cassettes were mated to mice containing the cloned Cre recombinase, Cre-
Suggest why the Flp recombination system rather than Cre-
lox was used to insert the cassettes into the mouse genome. 517
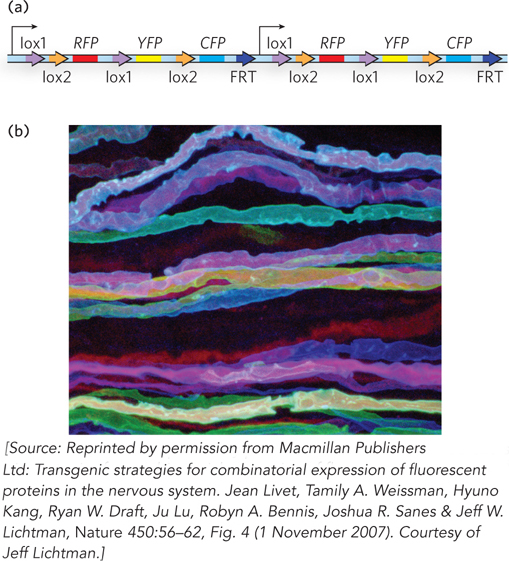 FIGURE 1
FIGURE 1If one GFP cassette was already present in the mouse genome, how could more cassettes be added?
In the cassette shown in Figure 1a, two different lox sites are used. What sequences in the lox sites must be different to prevent the two sites from recombining with each other?
When two or more different GFP variants are expressed in a neuron, the final color is a blend that reflects the amount of each GFP present. In mice with three cassettes, one GFP variant is expressed from each cassette (assuming that the lox sites preclude recombination between cassettes). Ten different colors are possible. Describe the combinations leading to the different colors.