DATA ANALYSIS PROBLEM
Grossman, A.D., J.W. Erickson, and C.A. Gross. 1984. The htpR gene product of Escherichia coli is a sigma factor for heat shock promoters. Cell 38:383–
Question 15.15
In E. coli, σ70 is the major but not the only sigma factor. Several other sigma factors direct RNA polymerase to bind to different sets of promoters. The second sigma factor to be discovered was σ32, which participates in the expression of genes involved in the heat shock response. When the environmental temperature suddenly rises, cellular production of about 20 proteins increases. These proteins help protect the cell from any ill effects of the higher temperature. Some of the proteins are chaperones that facilitate protein folding (see Chapter 4). In the 1970s, a gene required for normal heat shock response was discovered and named htpR. Carol Gross and her colleagues later identified its protein product, HtpR, as the first alternative sigma factor in E. coli (several had previously been discovered in B. subtilis); they renamed the gene rpoH (rpo genes encode RNA polymerase subunits) and named the protein σ32. Was this renaming justified?
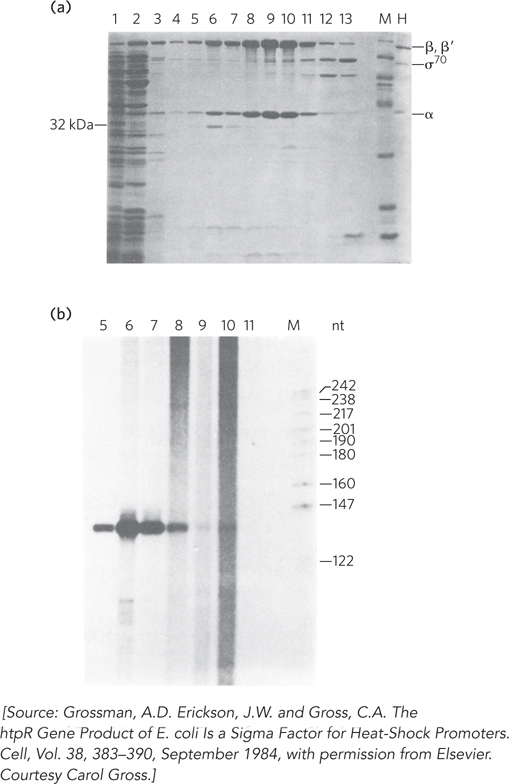
Gross and coworkers purified the 32 kDa HtpR protein. At a late stage in the purification, they ran the protein preparation over a cation-
Which fractions contain visible amounts of σ70?
Which fractions contain visible amounts of the 32 kDa protein (the putative σ32)?
Which fractions contain other RNA polymerase subunits?
Which fractions produced the most transcription from the PHS promoter?
What conclusion can you draw from this experiment?
The investigators then reconstituted the RNA polymerase, using purified RNA polymerase subunits but replacing σ70 with the 32 kDa protein that was now fairly pure. They used σ70-containing RNA polymerase as a control. To find out whether the 32 kDa protein could direct RNA synthesis from more than one heat shock promoter, they constructed a plasmid with two such promoters (P1 and P2), then cut it with restriction enzymes. Transcription from the promoters would generate RNA transcripts with lengths of 215 and 140 nucleotides, respectively. The results are shown in Figure 2. Lanes 1 and 3 show RNA synthesis by the polymerase with the 32 kDa protein; lanes 2 and 4 show synthesis by the polymerase with σ70.
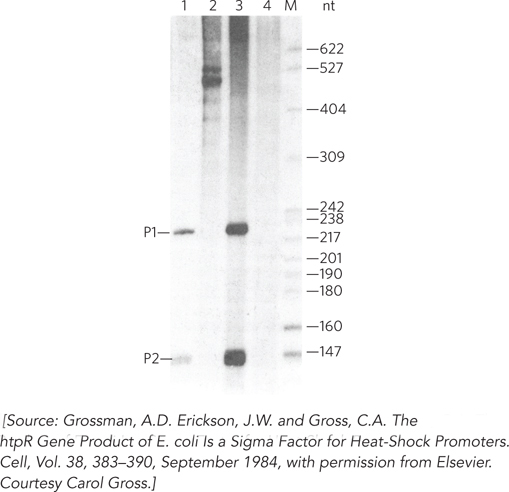
551
What conclusion can you draw from these data?
What is the advantage to the cell of having specialized sigma factors that recognize unique promoter sequences?