STEP-BY-STEP TECHNOLOGY GUIDE: Z test for μ
We will use the birth weight data from Example 14 (page 512).
TI-83/84
If you have the data values:
- Step 1 Enter the data into list L1.
- Step 2 Press STAT, highlight TESTS.
- Step 3 Press 1 (for Z-Test; see Figure 17a).
- Step 4 For input (Inpt), highlight Data, and press ENTER (Figure 17b).
- For μ0, enter the value of μ0, 3200.
- For σ, enter the value of σ, 528.
- For List, press 2nd, then L1.
- For Freq, enter 1.
- For μ, select the form of Ha. Here, we have a two-tailed test, so highlight ≠ μ0 and press ENTER.
- Highlight Calculate and press ENTER. The results are shown in Figure 9 in Example 14.
If you have the summary statistics:
- Step 1 Press STAT, highlight TESTS.
- Step 2 Press 1 (for Z-Test; see Figure 17a).
- Step 3 For input (Inpt), highlight Stats and press ENTER (Figure 17c).
- For μ0, enter the value of μ0, 3200.
- For σ, enter the value of σ, 528.
- For x̄, enter the sample mean 3276.
- For n, enter the sample size 44.
- For μ, select the form of Ha. Here, we have a two-tailed test, so highlight ≠ μ0 and press ENTER.
- Highlight Calculate and press ENTER. The results are shown in Figure 9 in Example 14.
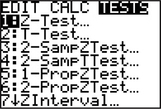 FIGURE 17a
FIGURE 17a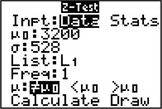 FIGURE 17b
FIGURE 17b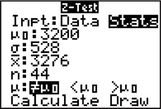 FIGURE 17c
FIGURE 17c
Page 520
EXCEL
JMP add-in for Excel.
There is a JMP add-in for Excel, which is activated when JMP is installed. This allows you to easily call upon JMP from within Excel, in order to conduct analyses that Excel itself does not provide. After installation of the JMP add-in for Excel, when you select JMP > Data Table, a new JMP workspace is created using the data from your Excel spreadsheet. Use the JMP add-in for Excel.
MINITAB
If you have the data values:
- Step 1 Enter the data into column C1.
- Step 2 Click Stat > Basic Statistics > 1-Sample Z….
- Step 3 Select One or more samples, each in a column from the drop-down menu. Click inside the box below the drop-down menu and select C1.
- Step 4 Enter 528 as Standard Deviation.
- Step 5 Select Perform hypothesis test. For Hypothesized Mean, enter 3200.
- Step 6 Click Options…
- Choose your Confidence Level as 100(1 − α). Our level of significance α here is 0.10, so the confidence level is 90.0.
- For Alternative hypothesis, select Mean ≠ hypothesized mean to symbolize the two-tailed test.
- Step 7 Click OK and click OK again. The results are shown in Figure 10 in Example 14.
If you have the summary statistics:
- Step 1 Click Stat > Basic Statistics > 1-Sample Z....
- Step 2 From the drop-down menu, select Summarized Data.
- Step 3 Enter the Sample Size 44, Sample Mean 3276, and Known standard deviation 528.
- Step 4 Select Perform hypothesis test, and enter the Hypothesized mean 3200.
- Step 5 Click Options...
- Choose your Confidence Level as 100(1 − α). Our level of significance α here is 0.10, so the confidence level is 90.0.
- For Alternative hypothesis, select Mean ≠ hypothesized mean to symbolize the two-tailed test.
- Step 6 Click OK and click OK again. The results are shown in Figure 10 in Example 14.
JMP
If you have the data values:
- Step 1 Click File > New > Data Table. Enter the data into Column 1.
- Step 2 Click Analyze > Distribution. Click Column 1 and then Y, Columns. Click OK.
- Step 3 Click the red triangle beside Column 1, and select Test Mean. For Specify Hypothesized Mean, enter 3200. For Enter True Standard Deviation to do z test rather than t test, enter 528. Click OK. The results are shown in Figure 11 in Example 14.
CRUNCHIT!
If you have the data values:
- Step 1 Click File, highlight Load from Larose, Discostat3e > Chapter 9, and click on Example 03_14.
- Step 2 Click Statistics, highlight z, and select 1-sample.
- Step 3 With the Columns tab chosen, for Sample select Birth weight (in grams). For Standard Deviation, enter 528.
- Step 4 Select the Hypothesis Test tab. For Mean under null hypothesis, enter 3200. For Alternative select Two-sided. Then click Calculate.
If you have the summary statistics:
- Step 1 Click Statistics, highlight z, and select 1-sample.
- Step 2 Choose the Summarized tab. For n, enter the sample size 44. For Sample Mean, enter 3276. For Standard Deviation, enter 528.
- Step 3 Select the Hypothesis Test tab. For Mean under null hypothesis, enter 3200. For Alternative, select Two-sided. Then click Calculate.
[Leave] [Close]