PROBLEMS
- Figure 9-1 shows the Home no-trade equilibrium under perfect competition (with the price PC) and under monopoly (with the price PM). In this problem, we compare the welfare of Home consumers in these two situations.
Question
Under perfect competition, with the price PC, label the triangle of consumer surplus and the triangle of producer surplus. Outline the area of total Home surplus (the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus).
Prob 9 1a. Under perfect competition, with the price PC, label the triangle of consumer surplus and the triangle of producer surplus. Outline the area of total Home surplus (the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus).Question
Under monopoly, with the price PM, label the consumer surplus triangle.
Prob 9 1b. Under monopoly, with the price PM, label the consumer surplus triangle.Question
Producer surplus is the same as the profits earned by the monopolist. To measure this, label the point in Figure 9-1 where the MR curve intersects MC at point B′. For selling the units between zero and QM, marginal costs rise along the MC curve, up to B′. The monopolist earns the difference between the price PM and MC for each unit sold. Label the difference between the price and the MC curve as producer surplus, or profits.
Prob 9 1c. Producer surplus is the same as the profits earned by the monopolist. To measure this, label the point in Figure 9-1 where the MR curve intersects MC at point B′. For selling the units between zero and QM, marginal costs rise along the MC curve, up to B′. The monopolist earns the difference between the price PM and MC for each unit sold. Label the difference between the price and the MC curve as producer surplus, or profits.Question
Outline the area of total Home surplus with a Home monopoly.
Prob 9 1d. Outline the area of total Home surplus with a Home monopoly.Question
Compare your answers to parts (a) and (d), and outline what the difference between these two areas is. What is this difference called and why?
Prob 9 1e. Compare your answers to parts (a) and (d), and outline what the difference between these two areas is. What is this difference called and why?
- Figure 9-2 shows the free-trade equilibrium under perfect competition and under monopoly (both with the price PW). In this problem, we compare the welfare of Home consumers in the no-trade situation and under free trade.
Question
Under perfect competition, with the price PW, label the triangle of consumer surplus and the triangle of producer surplus. Outline the area of total Home surplus (the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus).
Prob 9 2a. Under perfect competition, with the price PW, label the triangle of consumer surplus and the triangle of producer surplus. Outline the area of total Home surplus (the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus).Question
Based on your answers to part (a) in this problem and part (a) of the last problem, outline the area of gains from free trade under perfect competition.
Prob 9 2b. Based on your answers to part (a) in this problem and part (a) of the last problem, outline the area of gains from free trade under perfect competition.Question
Under monopoly, still with the price PW, again label the triangle of consumer surplus and the triangle of producer surplus.
Prob 9 2c. Under monopoly, still with the price PW, again label the triangle of consumer surplus and the triangle of producer surplus.Question
Based on your answers to part (c) in this problem and part (d) in the last problem, outline the area of gains from free trade under Home monopoly.
Prob 9 2d. Based on your answers to part (c) in this problem and part (d) in the last problem, outline the area of gains from free trade under Home monopoly.Question
Compare your answers to parts (b) and (d). That is, which area of gains from trade is higher and why?
Prob 9 2e. Compare your answers to parts (b) and (d). That is, which area of gains from trade is higher and why?
- Rank the following in ascending order of Home welfare and justify your answers. If two items are equivalent, indicate this accordingly.
Question
Tariff t in a small country with perfect competition
Prob 9 3a. Tariff t in a small country with perfect competitionQuestion
Tariff t in a small country with a Home monopoly
Prob 9 3b. Tariff t in a small country with a Home monopolyQuestion
Quota with the same imports M in a small country, with a Home monopoly
Prob 9 3c. Quota with the same imports M in a small country, with a Home monopolyQuestion
Tariff t in a country facing a Foreign monopoly
Prob 9 3d. Tariff t in a country facing a Foreign monopoly
- Refer to the prices of Japanese auto imports under the VER (Figure 9-5) and answer the following:
Question
What component of the price of imported automobiles from Japan rose the most over the period 1980 to 1985?
Prob 9 4a. What component of the price of imported automobiles from Japan rose the most over the period 1980 to 1985?Question
Sketch how Figures 9-5 and 9-6 might have looked if the United States had applied a tariff to Japanese auto imports instead of the VER (with the same level of imports). In words, discuss how the import prices and U.S. prices might have compared under a tariff and the VER.
Prob 9 4b. Sketch how Figures 9-5 and 9-6 might have looked if the United States had applied a tariff to Japanese auto imports instead of the VER (with the same level of imports). In words, discuss how the import prices and U.S. prices might have compared under a tariff and the VER.Question
Which policy—a tariff or the VER—would have been least costly to U.S. consumers?
Prob 9 4c. Which policy—a tariff or the VER—would have been least costly to U.S. consumers?
- In this problem, we analyze the effects of an import quota applied by a country facing a Foreign monopolist. In Figure 9-7, suppose that the Home country applies an import quota of X2, meaning that the Foreign firm cannot sell any more than that amount.
Question
To achieve export sales of X2, what is the highest price that the Foreign firm can charge?
Prob 9 5a. To achieve export sales of X2, what is the highest price that the Foreign firm can charge?Question
At the price you have identified in part (a), what is the Home consumer surplus?
Prob 9 5b. At the price you have identified in part (a), what is the Home consumer surplus?Question
Compare the consumer surplus you identify in part (b) with the consumer surplus under free trade. Therefore, outline in Figure 9-7 the Home losses due to the quota. Hint: Remember that there is no Home firm, so you do not need to take into account Home producer surplus or tariff revenue. Assume that quota rents go to Foreign firms.
Prob 9 5b. Compare the consumer surplus you identify in part (b) with the consumer surplus under free trade. Therefore, outline in Figure 9-7 the Home losses due to the quota. Hint: Remember that there is no Home firm, so you do not need to take into account Home producer surplus or tariff revenue. Assume that quota rents go to Foreign firms.Question
Based on your answer to (c), which has the greater loss to the Home country—a tariff or a quota, leading to the same level of sales X2 by the Foreign firm?
Prob 9 5c. Based on your answer to (c), which has the greater loss to the Home country—a tariff or a quota, leading to the same level of sales X2 by the Foreign firm?
- Suppose that the demand curve for a good is represented by the straight line
P = 10 − Q
Fill in the missing information in the following chart: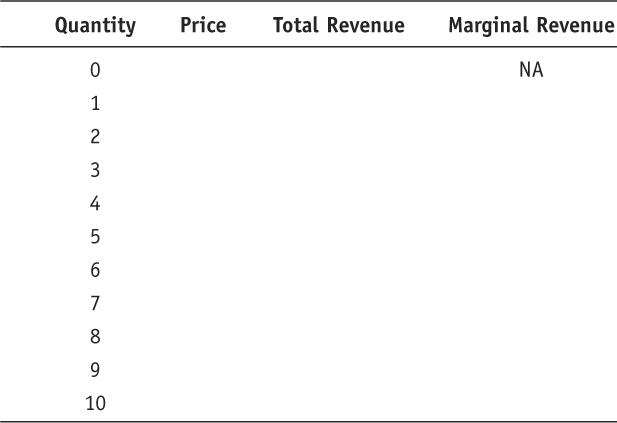
Question
Draw a graph containing both the demand curve and marginal revenue curve.
Prob 9 6a. Draw a graph containing both the demand curve and marginal revenue curve.Question
Is the marginal revenue curve a straight line as well? What is the slope of the marginal revenue curve? How does that slope compare with that of the demand curve?
Prob 9 6b. Is the marginal revenue curve a straight line as well? What is the slope of the marginal revenue curve? How does that slope compare with that of the demand curve?Question
Does the marginal revenue curve contain negative values over the specified range of quantities? Explain why or why not.
Prob 9 6c. Does the marginal revenue curve contain negative values over the specified range of quantities? Explain why or why not.
- Consider the case of a Foreign monopoly with no Home production, shown in Figure 9-7. Starting from free trade at point A, consider a $10 tariff applied by the Home government.
Question
If the demand curve is linear, as in Problem 6, what is the shape of the marginal revenue curve?
Prob 9 7a. If the demand curve is linear, as in Problem 6, what is the shape of the marginal revenue curve?Question
How much does the tariff-inclusive Home price increase because of the tariff, and how much does the net-of-tariff price received by the Foreign firm fall?
Prob 9 7b. How much does the tariff-inclusive Home price increase because of the tariff, and how much does the net-of-tariff price received by the Foreign firm fall?Question
Discuss the welfare effects of implementing the tariff. Use a graph to illustrate under what conditions, if any, there is an increase in Home welfare.
Prob 9 7c. Discuss the welfare effects of implementing the tariff. Use a graph to illustrate under what conditions, if any, there is an increase in Home welfare.
- Suppose the Home firm is considering whether to enter the Foreign market. Assume that the Home firm has the following costs and demand:
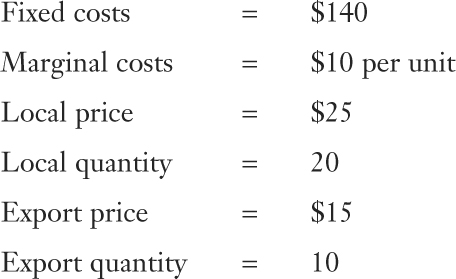
Question
Calculate the firm’s total costs from selling only in the local market.
Prob 9 8a. Calculate the firm’s total costs from selling only in the local market.Question
What is the firm’s average cost from selling only in the local market?
Prob 9 8b. What is the firm’s average cost from selling only in the local market?Question
Calculate the firm’s profit from selling only in the local market.
Prob 9 8c. Calculate the firm’s profit from selling only in the local market.Question
Should the Home firm enter the Foreign market? Briefly explain why.
Prob 9 8d. Should the Home firm enter the Foreign market? Briefly explain why.Question
Calculate the firm’s profit from selling to both markets.
Prob 9 8e. Calculate the firm’s profit from selling to both markets.Question
Is the Home firm dumping? Briefly explain.
Prob 9 8f. Is the Home firm dumping? Briefly explain.
- Suppose that in response to a threatened antidumping duty of t, the Foreign monopoly raises its price by the amount t.
Question
Illustrate the losses for the Home country.
Prob 9 9a. Illustrate the losses for the Home country.Question
How do these losses compare with the losses from a safeguard tariff of the amount t, applied by the Home country against the Foreign monopolist?
Prob 9 9b. How do these losses compare with the losses from a safeguard tariff of the amount t, applied by the Home country against the Foreign monopolist?Question
In view of your answers to (a) and (b), why are antidumping cases filed so often?
Prob 9 9c. In view of your answers to (a) and (b), why are antidumping cases filed so often?
Question
Why is it necessary to use a market failure to justify the use of infant industry protection?
Prob 9 10. Why is it necessary to use a market failure to justify the use of infant industry protection?Question
What is a positive externality? Explain the argument of knowledge spillovers as a potential reason for infant industry protection.
Prob 9 11. What is a positive externality? Explain the argument of knowledge spillovers as a potential reason for infant industry protection.Question
If infant industry protection is justified, is it better for the Home country to use a tariff or a quota, and why?
Prob 9 12. If infant industry protection is justified, is it better for the Home country to use a tariff or a quota, and why?- Figures A, B, and C are taken from a paper by Chad Bown: “The Pattern of Antidumping and Other Types of Contingent Protection” (World Bank, PREM Notes No. 144, October 21, 2009), and updated from Chad Bown, 2012, “Global Antidumping Database,” available at http://econ.worldbank.org/ttbd/
Question
Figure A shows the number of newly initiated trade remedy investigations, including safeguard (SF), China safeguard (CSF), antidumping (AD), and countervailing duty (CVD) (a countervailing duty is used when foreign firms receive a subsidy from their government, and then the CVD prevents them from charging lower prices in the importing country). Each bar shows the number of new cases in each quarter of the year (Q1, Q2, etc.) for 2007 through Q1 of 2012. The number of cases is graphed separately for developing countries and developed countries. What does this graph tell us about what has happened to the number of such cases since 2007? What might have caused this pattern?
 Prob 9 13a. Figure A shows the number of newly initiated trade remedy investigations, including safeguard (SF), China safeguard (CSF), antidumping (AD), and countervailing duty (CVD) (a countervailing duty is used when foreign firms receive a subsidy from their government, and then the CVD prevents them from charging lower prices in the importing country). Each bar shows the number of new cases in each quarter of the year (Q1, Q2, etc.) for 2007 through Q1 of 2012. The number of cases is graphed separately for developing countries and developed countries. What does this graph tell us about what has happened to the number of such cases since 2007? What might have caused this pattern?
Prob 9 13a. Figure A shows the number of newly initiated trade remedy investigations, including safeguard (SF), China safeguard (CSF), antidumping (AD), and countervailing duty (CVD) (a countervailing duty is used when foreign firms receive a subsidy from their government, and then the CVD prevents them from charging lower prices in the importing country). Each bar shows the number of new cases in each quarter of the year (Q1, Q2, etc.) for 2007 through Q1 of 2012. The number of cases is graphed separately for developing countries and developed countries. What does this graph tell us about what has happened to the number of such cases since 2007? What might have caused this pattern?Question
Figure B shows the number of safeguard (SF) tariff initiations by WTO members. Since 1995 what three years saw the largest numbers of safeguards? What might explain these increases? (Hint: Consider the U.S. business cycle over these years.)
 Prob 9 13b. Figure B shows the number of safeguard (SF) tariff initiations by WTO members. Since 1995 what three years saw the largest numbers of safeguards? What might explain these increases? (Hint: Consider the U.S. business cycle over these years.)
Prob 9 13b. Figure B shows the number of safeguard (SF) tariff initiations by WTO members. Since 1995 what three years saw the largest numbers of safeguards? What might explain these increases? (Hint: Consider the U.S. business cycle over these years.)Question
According to Figure B, year 2002 had the most safeguard actions by WTO members. How many action were started that year, and what U.S. safeguard case that year was discussed in this chapter?
Prob 9 13c. According to Figure B, year 2002 had the most safeguard actions by WTO members. How many action were started that year, and what U.S. safeguard case that year was discussed in this chapter?Question
Figure C shows the number of newly initiated antidumping (AD) investigations, for quarters of the year from 2007 through Q1 of 2012. Compare the number of cases in this graph with Figure A, which included safeguard (SF), China safeguard (CSF), antidumping (AD), and countervailing duty (CVD). What can you conclude about the total number of SF, CSF, and CVD cases as compared with the number of AD cases?
 Prob 9 13d. Figure C shows the number of newly initiated antidumping (AD) investigations, for quarters of the year from 2007 through Q1 of 2012. Compare the number of cases in this graph with Figure A, which included safeguard (SF), China safeguard (CSF), antidumping (AD), and countervailing duty (CVD). What can you conclude about the total number of SF, CSF, and CVD cases as compared with the number of AD cases?
Prob 9 13d. Figure C shows the number of newly initiated antidumping (AD) investigations, for quarters of the year from 2007 through Q1 of 2012. Compare the number of cases in this graph with Figure A, which included safeguard (SF), China safeguard (CSF), antidumping (AD), and countervailing duty (CVD). What can you conclude about the total number of SF, CSF, and CVD cases as compared with the number of AD cases?